Aabbcc skin color
Table 4. Rh antibodies primarily utilized in immunoglobulin serums. Wayne's Word.
Skin color inheritance is a complex process influenced by multiple genes and environmental factors. Here's a simplified explanation of how it works:. Genetic Basis : Skin color is primarily determined by the amount of melanin, a pigment produced by specialized cells called melanocytes in the skin. The ratio and distribution of these pigments in the skin determine its color. Polygenic Inheritance : Skin color inheritance is polygenic, meaning it's controlled by multiple genes, each contributing to the overall phenotype observable. Answer the questions as they are presented to you in the story of Catherine and Richard Howarth whose children are surprisingly light skinned compared to their Nigerian mother.
Aabbcc skin color
Consider three genes A a , B b a n d C c responsible for skin color inheritance. Use app Login. The genotype of human skin colour is AAbbcc and AaBbcc respectively. What is the phenotype of this genotype? Light brown and dark brown Both are mullato Very light brown and very dark brown Both are light brown. Very light brown and very dark brown. Both are light brown. Light brown and dark brown. Open in App. Verified by Toppr.
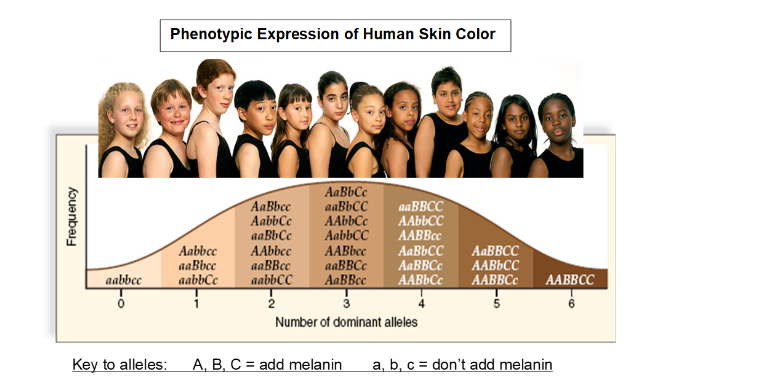
Each "dominant" capital gene produces one unit of color, so that a wide range of intermediate skin colors are produced, depending on the number of "dominant" capital genes in the genotype. Which cellular process is shown below? Verified by Toppr, aabbcc skin color.
Pleiotropy and codominance. Pleiotropy and incomplete dominance. Polygenic and qualitative inheritance. Polygenic and quantitative inheritance. Explain polygenic inheritance in relation to skin colour in man. Which of the following characteristics represents Inheritance of blood groups in humans? Dominance 2.
The DNA of all people around the world contains a record of how living populations are related to one another, and how far back those genetic relationships go. Understanding the spread of modern human populations relies on the identification of genetic markers, which are rare mutations to DNA that are passed on through generations. Different populations carry distinct markers. Once markers have been identified, they can be traced back in time to their origin — the most recent common ancestor of everyone who carries the marker. Following these markers through the generations reveals a genetic tree of many diverse branches, each of which may be followed back to where they all join — a common African root. The mitochondria inside each cell are the power stations of the body; they generate the energy necessary for cellular organisms to live and function. But surnames mutate across many generations, and so mtDNA types have changed over the millennia. A natural mutation modifying the mtDNA in the reproductive cells of one woman will from then on characterize her descendants. These two fundamentals — inheritance along the mother line and occasional mutation — allow geneticists to reconstruct ancient genetic prehistory from the variations in mtDNA types that occur today around the world. Population genetics often use haplogroups, which are branches on the tree of early human migrations and genetic evolution.
Aabbcc skin color
Consider three genes A a , B b a n d C c responsible for skin color inheritance. Use app Login. The genotype of human skin colour is AAbbcc and AaBbcc respectively. What is the phenotype of this genotype?
Big geno naked
Note that most classes quickly agree on answers to all the questions except for number 4. For alternative readings that can be found online at no cost, follow these links: a. Rh antibodies primarily utilized in immunoglobulin serums. Have students read "Skin Deep" by N. Grain colour in wheat is determined by three pairs of polygenes. Which cellular process is shown below? Science The Biology of Multiple allele 4. Graphing the distribution of one of these traits produces a bell-shaped curve in which extreme values are much rarer than intermediate values. Incomplete dominance 5. Human skin colour is polygenic trait with each dominant determining a part of melanin deposition while the recessive are coding for no melanin. Light skin evolved when early humans migrated to the high latitudes where UV radiation is much lower. In the following cross between two mulatto genotypes AaBbCc x AaBbCc , each parent produces eight different types of gametes and these gametes combine with each other in 64 different ways resulting in a total of seven skin colors.
Used with permission. Grade Levels: Subject Matter: Biology, Physical Anthropology, Genetics Time Allotment: class sessions Description: This lesson plan explores the genetics and evolution of skin color, using a short story by Kate Chopin called "Desiree's Baby" as a starting point. It is a story of race and gender in antebellum Louisiana.
Skin Deep. According to the most recent theory, different skin colors evolved to ensure reproductive success by regulating the production of two critical vitamins. C Polygenic and qualitative inheritance. At least three genes regulate the amount of melanin produced. Video Solution. The offspring of this cross exhibit seven shades of skin color based on the number of dark skin alleles in each genotype. Table 4. Light skin evolved when early humans migrated to the high latitudes where UV radiation is much lower. The skin colors can be represented by the number of capital letters, ranging from zero no capital letters to six all capital letters. Anthropologist Nina Jablonski theorizes that dark skin evolved near the equator.

The matchless phrase, is pleasant to me :)
I suggest you to come on a site where there is a lot of information on a theme interesting you.