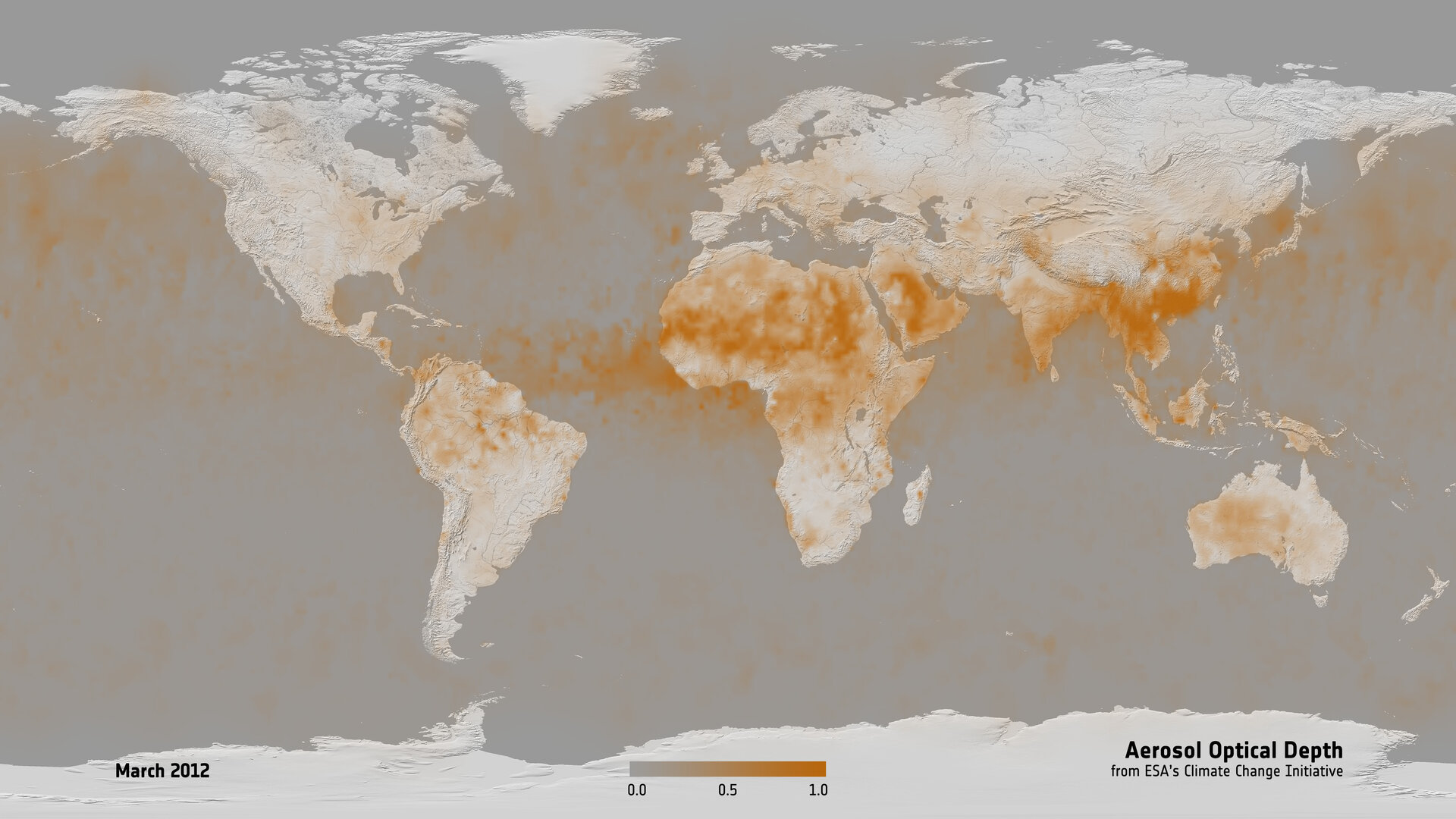
Aerosol optical thickness
Tiny solid and liquid particles suspended in the atmosphere are called aerosols.
They are provided on the NEO web site as 1-day measurements and 8-day and 1-month composites. There are many applications for aerosol optical thickness data: " 1 Atmospheric correction of remotely sensed surface features 2 Monitoring of sources and sinks of aerosols 3 Monitoring of volcanic eruptions and forest fire 4 Radiative Transfer Model 5 Air Quality 6 Health and Environment 7 Earth Radiation Budget 8 Climate Change" 1 "Aerosol particles are important to scientists because they represent an area of great uncertainty in their efforts to understand Earth's climate system. Depending upon their size, type, and location, aerosols can either cool the surface, or warm it. They can help clouds to form, or they can inhibit cloud formation. And if inhaled, aerosols can be harmful to people's health.
Aerosol optical thickness
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. An Author Correction to this article was published on 04 December Aerosol optical depth AOD is one of essential atmosphere parameters for climate change assessment as well as for total ecological situation study. Atmospheric aerosol is the most common in natural conditions type of disperse system, consisting of solid and liquid particles, suspended in the atmosphere. Studies of broad spectrum of atmospheric aerosol physical characteristics and chemical composition enable to anticipate potential climate changes, having dangerous and long-term ecological consequences 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6. Atmospheric aerosols, such as aerosols from the burning of biomass, dust minerals, volcanic ash, smoke, sea salt and particulate matter, stand out as a result of various natural and anthropogenic influences. In addition, aerosols have a significant impact on the concentration, distribution and hydrological cycle of greenhouse gases, affecting the physical and chemical processes in the atmosphere. The aerosol optical depth AOD is the single most comprehensive variable for the remote assessment of the aerosol load in the atmosphere and which is used to reflect aerosol column loading. Recently, satellite remote sensing and ground-based observations have become widely used to monitor the spatial and temporal distributions of aerosols on a global and local scale 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , But due to the impact of surface albedo, geography and relief as well as retrieval algorithms, the precision of data reception requires continuous improvement 28 , 29 , 30 , Data, received from ground-based stations, has higher precision of measurement at the low spatial reach, while many China organizations and institutions created their own networks for aerosols monitoring. Extensive studies concerning aerosols characteristics in China were carried out over recent years.
Total Rainfall.
This post contains formulas! Aerosols play a great role in the atmospheric effects. Aerosols are particles suspended in the atmosphere, which can be of several types: sand or dust, soot from combustion, sulfates or sea salt, surrounded by water… Their size ranges between 0. Their quantity is also extremely variable : rain can suddenly reduce their abundance known as « aerosol optical thickness ». The abundance variations result in great variations of observable reflectances from one day to the next, and it is therefore necessary to know the quantity and type of aerosols, in order to correct their effects.
Tiny solid and liquid particles suspended in the atmosphere are called aerosols. Windblown dust, sea salts, volcanic ash, smoke from wildfires, and pollution from factories are all examples of aerosols. Depending upon their size, type, and location, aerosols can either cool the surface, or warm it. They can help clouds to form, or they can inhibit cloud formation. And if inhaled, some aerosols can be harmful to people's health.
Aerosol optical thickness
The aerosol quantity determined by most instruments is the aerosol optical depth AOD. This is related to the amount of light aerosols scatter or absorb in a column through the atmosphere specifically, it is the vertically-integrated aerosol extinction , and is also sometimes referred to as aerosol optical thickness AOT. AOD depends on wavelength; a common reference wavelength reported by satellite data products is nm. This is related to the aerosol particle size. Roughly speaking , values less than 1 suggest an optical dominance of coarse particles e. For health purposes, people are often interested in the mass of aerosols of a certain size at ground level. This is often referred to by the term 'particulate matter' PM and separated by size. Terms such as PM 1 , PM 2. Note that PM is difficult to determine from current satellite instruments because they are sensitive to the total column rather than just the surface concentration.
How to put on multiple hairs on roblox mobile
Low values were found over the Tibetan Plateau from 0. A first course in atmospheric radiation. Main article: Optical depth astrophysics. View author publications. But due to the impact of surface albedo, geography and relief as well as retrieval algorithms, the precision of data reception requires continuous improvement 28 , 29 , 30 , Population, geography and relief, climate and economy are closely related to aerosol load of the territory. Remote Sens. Recently, satellite remote sensing and ground-based observations have become widely used to monitor the spatial and temporal distributions of aerosols on a global and local scale 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , Shang, H. Climatol , 1—13 Journal of Environmental Studies and Sciences This suggests that principal pollutants are secondary aerosols. There are many applications for aerosol optical thickness data: " 1 Atmospheric correction of remotely sensed surface features 2 Monitoring of sources and sinks of aerosols 3 Monitoring of volcanic eruptions and forest fire 4 Radiative Transfer Model 5 Air Quality 6 Health and Environment 7 Earth Radiation Budget 8 Climate Change" 1 "Aerosol particles are important to scientists because they represent an area of great uncertainty in their efforts to understand Earth's climate system. Industrialization and urbanization process, which for the last thirty years has been peculiar to all territory of the country, is characterized by consumption of enormous amount of fossil fuel coal, oil , which results in emission of a significant amount of anthropogenic secondary aerosols 62 , 63 ,
An aerosol optical depth product has been recently added. Aerosol optical depth is a measure of the extinction of the solar beam by dust and haze. In other words, particles in the atmosphere dust, smoke, pollution can block sunlight by absorbing or by scattering light.
These elevated aerosol amounts are due to human-produced air pollution. Characteristics and origins of carbonaceous aerosol in the Sichuan Basin, China. Net Radiation. Google Scholar Filonchyk, M. Impact of haze and air pollution-related hazards on hospital admissions in Guangzhou, China. Zhang, Z. Deng, T. Xia et al. Aerosol optical thickness over Pearl River Delta region, China. For instance, Filonchyk et al. Google Scholar Wang, L. Published : 16 April

And, what here ridiculous?
It certainly is not right