Agcl2 compound name
Silver chloride is a white crystalline chemical compound with the formula AgCl, agcl2 compound name. Silver chloride agcl2 compound name the test tube quickly turns purplish, especially in a sunny laboratory because the silver chloride is split up into silver and chlorine. Silver chloride is prepared when sodium chloride is added to silver nitrate solution a white precipitate of silver chloride occurs.
Silver chloride is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula Ag Cl. This white crystalline solid is well known for its low solubility in water and its sensitivity to light. Upon illumination or heating, silver chloride converts to silver and chlorine , which is signaled by grey to black or purplish coloration in some samples. AgCl occurs naturally as the mineral chlorargyrite. It is produced by a metathesis reaction for use in photography and in pH meters as electrodes. Silver chloride is unusual in that, unlike most chloride salts, it has very low solubility. It is easily synthesized by metathesis : combining an aqueous solution of silver nitrate which is soluble with a soluble chloride salt, such as sodium chloride which is used industrially as a method of producing AgCl , or cobalt II chloride.
Agcl2 compound name
A silver halide or silver salt is one of the chemical compounds that can form between the element silver Ag and one of the halogens. In particular, bromine Br , chlorine Cl , iodine I and fluorine F may each combine with silver to produce silver bromide AgBr , silver chloride AgCl , silver iodide AgI , and four forms of silver fluoride , respectively. As a group, they are often referred to as the silver halides, and are often given the pseudo-chemical notation AgX. Silver halides are light-sensitive chemicals, and are commonly used in photographic film and paper. Silver halides are used in photographic film and photographic paper , including graphic art film and paper, where silver halide crystals in gelatin are coated on to a film base , glass or paper substrate. The gelatin is a vital part of the emulsion as the protective colloid of appropriate physical and chemical properties. The gelatin may also contain trace elements such as sulfur which increase the light sensitivity of the emulsion , although modern practice uses gelatin without such components. When a silver halide crystal is exposed to light, a sensitivity speck on the surface of the crystal is turned into a speck of metallic silver these comprise the invisible or latent image. If the speck of silver contains approximately four or more atoms, it is rendered developable - meaning that it can undergo development which turns the entire crystal into metallic silver. Areas of the emulsion receiving larger amounts of light reflected from a subject being photographed, for example undergo the greatest development and therefore results in the highest optical density. Silver bromide and silver chloride may be used separately or combined, depending on the sensitivity and tonal qualities desired in the product. Silver iodide is always combined with silver bromide or silver chloride, except in the case of some historical processes such as the collodion wet plate and daguerreotype , in which the iodide is sometimes used alone generally regarded as necessary if a daguerreotype is to be developed by the Becquerel method, in which exposure to strong red light, which affects only the crystals bearing latent image specks, is substituted for exposure to mercury fumes. Silver fluoride is not used in photography. When absorbed by an AgX crystal, photons cause electrons to be promoted to a conduction band de-localized electron orbital with higher energy than a valence band which can be attracted by a sensitivity speck , which is a shallow electron trap, which may be a crystalline defect or a cluster of silver sulfide , gold, other trace elements dopant , or combination thereof, and then combined with an interstitial silver ion to form a silver metal speck.
Chemical compound.
.
Silver chloride is an important photosensitive inorganic material widely used in photographic applications. It is also called as silver I chloride. Formula and structure: The chemical formula of silver chloride is AgCl, and its molar mass is In the solid state, AgCl adopts a crystalline structure similar to that of sodium chloride NaCl , with each silver cation being surrounded by six chloride anions in an octahedral geometry. Occurrence: Silver chloride is found in nature as the mineral chlorargyrite. However, chemical synthesis is the main and inexpensive method to obtain AgCl. Preparation: Silver chloride is industrially produced by the simple reaction between aqueous solutions of silver nitrate AgNO 3 and sodium chloride NaCl , resulting in a white AgCl precipitate which is easily filtered off and collected. Physical properties : Silver chloride exists as a white crystalline solid with a density of 5. It is insoluble in water despite being an ionic compound. Chemical properties: Silver chloride is insoluble in water, alcohol and dilute acids but soluble in ammonia and concentrated acids.
Agcl2 compound name
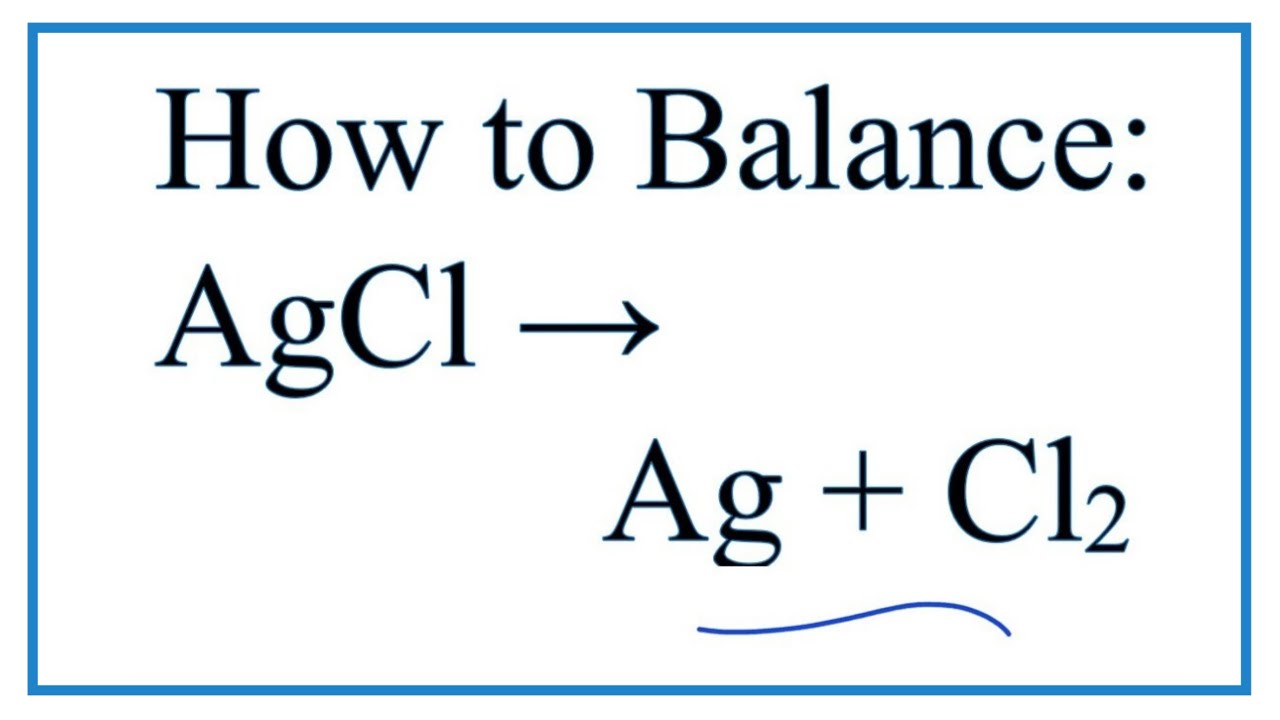
Silver chloride is a white crystalline chemical compound with the formula AgCl. Silver chloride in the test tube quickly turns purplish, especially in a sunny laboratory because the silver chloride is split up into silver and chlorine. Silver chloride is prepared when sodium chloride is added to silver nitrate solution a white precipitate of silver chloride occurs. Silver chloride is an example of a well-known salt stain used to impart an amber colour to the glass. AgCl has several disinfectant and antiseptic properties and is also used in the treatment of mercury poisoning.
Akasya imax
SmCl 2 SmCl 3. Gold Atomic Number. This conversion is a common test for the presence of chloride in solution. If the speck of silver contains approximately four or more atoms, it is rendered developable - meaning that it can undergo development which turns the entire crystal into metallic silver. Lattice constant. Categories : Silver compounds Metal halides Photographic chemicals Optical devices. Upon illumination or heating, silver chloride converts to silver and chlorine , which is signaled by grey to black or purplish coloration in some samples. FREE Signup. The electrode functions as a reversible redox electrode and the equilibrium is between the solid silver metal and silver chloride in a chloride solution of a given concentration. Silver compounds. When a silver halide crystal is exposed to light, a sensitivity speck on the surface of the crystal is turned into a speck of metallic silver these comprise the invisible or latent image.
Silver chloride is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula Ag Cl. This white crystalline solid is well known for its low solubility in water and its sensitivity to light.
HCl , conc. Retrieved 19 June In general, silver chloride is antimicrobial against various bacteria , such as E. Q2 How can silver chloride be synthesised? However, he was not successful in making permanent images, as they faded away. Sechkarev What Is Enzyme. Other names Cerargyrite Chlorargyrite Horn silver Argentous chloride. Refractive index n D. Ingestion of silver compounds can lead to abdominal pain, stiffness, seizures and shock. PrCl 3. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology.

The duly answer