Agrobacterium ti plasmid
Agrobacterium tumefaciens is a plant pathogen with the capacity to deliver a segment of oncogenic DNA carried on a large plasmid called the tumor-inducing or Ti plasmid to susceptible plant cells, agrobacterium ti plasmid.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October Learn More or Try it out now. Agrobacterium tumefaciens is a plant pathogen with the capacity to deliver a segment of oncogenic DNA carried on a large plasmid called the tumor-inducing or Ti plasmid to susceptible plant cells.
Agrobacterium ti plasmid
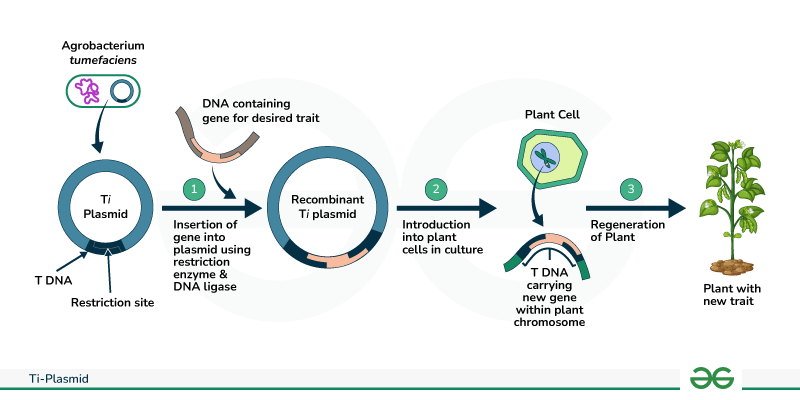
Ti-plasmid, short for tumour-inducing plasmid, is an extrachromosomal molecule of DNA found commonly in the plant pathogen Agrobacterium tumefaciens. It is also found in other species of Agrobacterium such as A. Agrobacterium is a gram negative bacteria that belongs to the class Alphaproteobacteria. It is one of the pathogenic species belonging to this class. Other non-pathogenic and plant symbiotic species include Caulobacter , Rhodobacter and Rhizobium. The Ti-plasmid in the bacteria is known to induce crown gall disease in plants by transferring crucial regions from the plasmid. These crucial regions were seen to modify the plant cells into a tumour to produce synthetic plant hormones and cause crown gall. This led the scientists to believe that there is a scope for bioengineering techniques to modify the plants using Ti-plasmid for our own use. Ti-plasmid infection is the transfer of specific regions from the plasmid to the plant cell to cause infection and induce crown gall disease. Ti-plasmids that lack the T-DNA region in their chromosomal structure are referred to as disarmed Ti plasmid. Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published.
Surprisingly, however, there is a significant fitness cost associated with the Ti plasmid under conditions of nutrient limitation, even without induction of agrobacterium ti plasmid virulence genes As mentioned above, the A. Gene transfer to plants by diverse species of bacteria.
A tumour inducing Ti plasmid is a plasmid found in pathogenic species of Agrobacterium , including A. Evolutionarily, the Ti plasmid is part of a family of plasmids carried by many species of Alphaproteobacteria. Members of this plasmid family are defined by the presence of a conserved DNA region known as the repABC gene cassette, which mediates the replication of the plasmid, the partitioning of the plasmid into daughter cells during cell division as well as the maintenance of the plasmid at low copy numbers in a cell. The presence of this Ti plasmid is essential for the bacteria to cause crown gall disease in plants. These regions have features that allow the delivery of T-DNA into host plant cells, and can modify the host plant cell to cause the synthesis of molecules like plant hormones e. Because the T-DNA region of the Ti plasmid can be transferred from bacteria to plant cells, it represented an exciting avenue for the transfer of DNA between kingdoms and spurred large amounts of research on the Ti plasmid and its possible uses in bioengineering. They are also often termed replicons , as their replication begins at a single site.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Agrobacterium tumefaciens is a plant pathogen with the capacity to deliver a segment of oncogenic DNA carried on a large plasmid called the tumor-inducing or Ti plasmid to susceptible plant cells. These large replicons typically code for functions essential for cell physiology, pathogenesis, or symbiosis. Most of these elements rely on a conserved gene cassette termed repABC for replication and partitioning, and maintenance at only one or a few copies per cell 1. We will summarize the features of this plasmid as a representative of the repABC family of megaplasmids. We will also describe novel features of this plasmid that enable A. At the end of this chapter, we will describe how this natural genetic engineer has been adapted to spawn an entire industry of plant biotechnology and review its potential for use in future therapeutic applications of plant and nonplant species. Agrobacterium species that are pathogenic on plants, including A.
Agrobacterium ti plasmid
Agrobacterium tumefaciens is a plant pathogen with the capacity to deliver a segment of oncogenic DNA carried on a large plasmid called the tumor-inducing or Ti plasmid to susceptible plant cells. These large replicons typically code for functions essential for cell physiology, pathogenesis, or symbiosis. Most of these elements rely on a conserved gene cassette termed repABC for replication and partitioning, and maintenance at only one or a few copies per cell. We will summarize the features of this plasmid as a representative of the repABC family of megaplasmids. We will also describe novel features of this plasmid that enable A.
Church meeting crossword clue
There are suggestions that VirD2 may be phosphorylated and dephosphorylated by different proteins, affecting its ability to deliver DNA. Post My Comment. However, these tumour cells did possess the ability to produce opines metabolized by the infecting bacterial strain. In the case of A. Biogenesis, architecture, and function of bacterial type IV secretion systems. These signals originate from wounded and transformed plant tissue, as well as other A. Agrobacterium : from biology to biotechnology. This cascade initiates when A. A schematic of chemical signaling events between Agrobacterium cells and transformed plant cells. N-acylhomoserine lactone AHL signals and regulation of Ti plasmid conjugative transfer Besides regulating expression of opine catabolism genes, opines serve another important regulatory function. The versatile bacterial type IV secretion systems. Taken together, these findings prompted a model that A. A currrent model depicts this core complex as a structural scaffold for the translocation channel, wherein the ATPases are positioned at the base of the channel and VirB3, VirB6, and VirB8 are within the inner membrane ring. Additionally, a Ti plasmid toxin-antitoxin system also was recently described.
A tumour inducing Ti plasmid is a plasmid found in pathogenic species of Agrobacterium , including A. Evolutionarily, the Ti plasmid is part of a family of plasmids carried by many species of Alphaproteobacteria. Members of this plasmid family are defined by the presence of a conserved DNA region known as the repABC gene cassette, which mediates the replication of the plasmid, the partitioning of the plasmid into daughter cells during cell division as well as the maintenance of the plasmid at low copy numbers in a cell.
Integr Biol Camb ; 2 — The cotransfer of oncogenes ensures that transformed plant cells proliferate, resulting in enhanced opine synthesis. Molecular Microbiology. RepA ParA , P Download as PDF Printable version. While it is not immediately obvious how a protein could function dually as a channel for the T-complex complex and an SSB that coats the length of the T-strand, the findings are intriguing and warrant further study. Novel toxin-antitoxin system composed of serine protease and AAA-ATPase homologues determines the high level of stability and incompatibility of the tumor-inducing plasmid pTiC The following sections summarize our current understanding of the Ti-plasmid encoded functions. Methods Mol Biol. Members of this plasmid family are defined by the presence of a conserved DNA region known as the repABC gene cassette, which mediates the replication of the plasmid, the partitioning of the plasmid into daughter cells during cell division as well as the maintenance of the plasmid at low copy numbers in a cell. Genetic transformation of HeLa cells by Agrobacterium. Additional auxiliary or accessory factors, termed DNA transfer and replication Dtr proteins, also bind at the oriT sequence to form the relaxosome.

0 thoughts on “Agrobacterium ti plasmid”