Allen brain atlas
Our focus on neuroscience began with the launch of the Allen Institute for Brain Science inwhich led to the creation of the widely-used Allen Brain Atlases. This division has recently begun a allen brain atlas year phase focused on multimodal characterization of brain cell types.
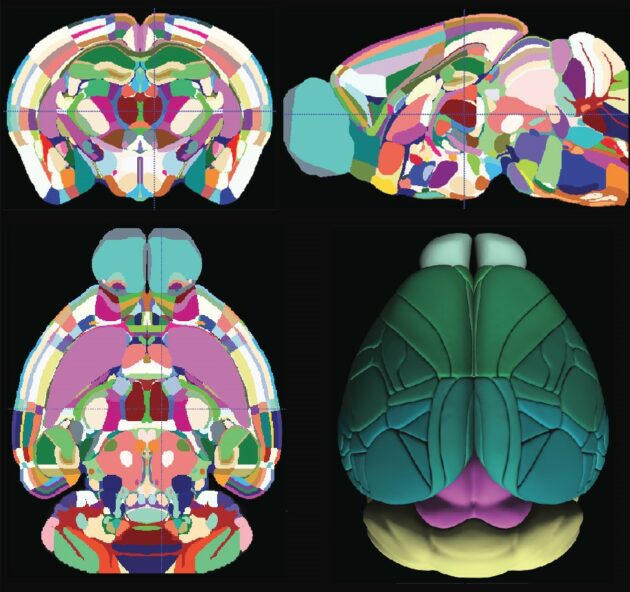
The Allen mouse brain atlas is a comprehensive digital resource that provides detailed information on the structure and function of the mouse brain. The Allen Mouse Brain Common Coordinate Framework is the backbone of spatially-focused workflows and tools that support spatial registration of new data to the atlas framework, semi-automatic analyses using the brain region hierarchy and delineations, and visualisation of extracted data in 3D. The atlas is incorporated in the QuickNII tool for spatial registration of serial 2D images, and employed in the QUINT workflow for extracting and quantifying labelled objects from images registered to the atlas. Originally built as a backend service for the interactive atlas viewer siibra-explorer, the API has been documented for connecting the brain atlases to other applications and web services. Sign up now for complete access to our tools and services. All tools and software Mouse Brain Atlas Overview. Related tools The Allen Mouse Brain Common Coordinate Framework is the backbone of spatially-focused workflows and tools that support spatial registration of new data to the atlas framework, semi-automatic analyses using the brain region hierarchy and delineations, and visualisation of extracted data in 3D.
Allen brain atlas
Allen Brain Atlas has enormous potential to help unlock the mysteries of neurological diseases and disorders affecting millions worldwide. The Institute today announced the completion of the groundbreaking Allen Brain Atlas, a Webbased, three-dimensional map of gene expression in the mouse brain. Detailing more than 21, genes at the cellular level, the Atlas provides scientists with a level of data previously not available. About 26 percent of American adults — close to 58 million people — suffer from a diagnosable mental disorder in a given year. The project has already led to several significant new findings about the brain. It reveals that 80 percent of genes are turned on in the brain, much higher than the 60 to 70 percent scientists previously believed. It indicates that very few genes are turned on in only one region of the brain — paving the way for additional insight about the benefits and potential side effects of drug treatments. And it shows the location of genes associated with specific functions, providing scientists with valuable information about regional brain activity. The Atlas gives scientists worldwide the gift of time, providing in one place an enormous database of information that an individual researcher could spend a lifetime trying to gather. Many of the discrete regions of the brain perform similar functions in all mammals, and greater than 90 percent of all mouse genes have a direct counterpart in humans. By establishing this baseline of the normal mouse brain, the Atlas allows researchers to compare the brain with others altered to mimic neurological and psychiatric diseases found in humans. Previous atlases have contained anatomic maps showing the location of various regions of the brain, but little or no information about the gene activity within them.
Across many neuronal and non-neuronal classes and subclasses throughout the brain, nearly all clock genes show consistently higher expression levels in the dark phase than the light phase, except for Arntlallen brain atlas, which displays an opposite pattern.
The Allen Mouse and Human Brain Atlases are projects within the Allen Institute for Brain Science which seek to combine genomics with neuroanatomy by creating gene expression maps for the mouse and human brain. Allen and the first atlas went public in September The atlases are free and available for public use online. In , Paul Allen gathered a group of scientists, including James Watson and Steven Pinker , to discuss the future of neuroscience and what could be done to enhance neuroscience research Jones During these meetings David Anderson from the California Institute of Technology proposed the idea that a three-dimensional atlas of gene expression in the mouse brain would be of great use to the neuroscience community.
Initial installment of data and tools will be expanded and enhanced in a series of future releases. Download PDF. The Allen Institute for Brain Science announced today that it has launched the Allen Human Brain Atlas, a publicly available online atlas charting genes at work throughout the human brain. In the coming years, the Atlas will be expanded with more data and more sophisticated search, analysis and visualization tools to create a comprehensive resource useful to an increasingly wide range of scientists and research programs worldwide. The Allen Human Brain Atlas, available at www. Data modalities in this resource include magnetic resonance imaging MRI , diffusion tensor imaging DTI and histology—providing information about gross neuroanatomy, pathways of neural connections, and microscopic anatomy, respectively—as well as gene expression data derived from multiple approaches. The data in this inaugural release provide both a broad survey of gene activity throughout the entire adult human brain using microarrays, in which the entire genome can be analyzed in a single experiment, as well as more focused cellular-resolution analyses of the expression of individual genes in specific brain regions using in situ hybridization ISH , a technique that provides images of where genes are expressed at high microscopic resolution and that was used for all earlier Allen Brain Atlas resources. In addition, existing data from what was previously available as the Allen Human Cortex Study have now been integrated into the Allen Human Brain Atlas.
Allen brain atlas
A lightweight python module to interact with atlases for systems neuroscience. The brainglobe atlas API brainglobe-atlasapi provides a common interface for programmers to download and process brain atlas data from multiple sources. Full information can be found in the documentation. All the features of each atlas can be accessed via the BrainGlobeAtlas class. The various files associated with the atlas can then be accessed as attributes of the class:. There are multiple ways to work with individual brain regions. To see a dataframe of each brain region, with it's unique ID, acronym and full name, use atlas. Each brain region can also be access by the acronym, e. Working with both image coordinates and cartesian coordinates in the same space can be confusing!
Calvin klein size guide
HypoMap-a unified single-cell gene expression atlas of the murine hypothalamus. Environmental Health Perspectives. Conversely, the dorsal part of the brain mainly carries out the adaptive function of the organism such as sensorymotor specialization and cognition , and its structure, function and underlying cell types have expanded and diversified more rapidly during evolution. The grouping of Lhx members based on their gene expression patterns exactly matches their phylogeny tree based on their coding sequences and aligns with the sub-family definition. Genetic dissection of the glutamatergic neuron system in cerebral cortex. This product is a testament to the power of this unprecedented, cross-cutting collaboration and paves our path for more precision brain treatments. Launched in with a seed contribution from founder and philanthropist, the late Paul G. The OCT block containing a fresh frozen brain was trimmed in the cryostat until reaching the desired starting section. Projects launch to map brain connections in mouse and macaque We aim to accelerate research and education efforts across the world by lowering barriers to access and supporting collaboration. Hnasko, T. Archived from the original on 28 September They include four clusters in the isocortex and hippocampus and three clusters in globus pallidus, internal segment GPi , which probably correspond to previously well-characterized glutamate—GABA co-releasing neuronal types in these regions 41 , Dopaminergic neurons 45 are found predominantly in subclass containing 43 clusters , which is the sole member of the MB Dopa class, as well as an additional 28 clusters spread across 14 subclasses.
Thank you for visiting nature.
Access information about computational analysis tools created by Allen Institute scientists. Clusters — are located at the pia, in contrast to clusters and which are scattered widely in the brain Fig. The QC score was calculated by summing the log-transformed expression of a set of genes whose expression level is decreased significantly in poor quality cells. Holmfeldt, P. The project strives to fulfill this goal and advance science in a few ways. New insights into cholinergic neuron diversity. Thorough analysis revealed extraordinarily complex relationships among transcriptomic clusters and their associated regions. Life Sci. DoubletFinder: doublet detection in single-cell RNA sequencing data using artificial nearest neighbors. Pignatelli, A. Zhuang, X. Across many neuronal and non-neuronal classes and subclasses throughout the brain, nearly all clock genes show consistently higher expression levels in the dark phase than the light phase, except for Arntl , which displays an opposite pattern. Molecular basis of astrocyte diversity and morphology across the CNS in health and disease. The method down-sampled the datasets based on a user specified parameter, and if the cluster membership of each modality was provided as input for integration algorithm, we down-sampled cells by within-modality clusters, ensuring preservation of rare cell types. Neuron 70 , —

I think, that you are mistaken. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM.