Arcuate nucleus
The hypothalamus is part of the diencephalon and has several nuclei, one of which is the arcuate nucleus.
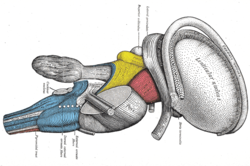
The arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus also known as ARH , [1] ARC , [2] or infundibular nucleus [2] [3] is an aggregation of neurons in the mediobasal hypothalamus , adjacent to the third ventricle and the median eminence. The arcuate nucleus includes several important and diverse populations of neurons that help mediate different neuroendocrine and physiological functions, including neuroendocrine neurons, centrally projecting neurons, and astrocytes. The populations of neurons found in the arcuate nucleus are based on the hormones they secrete or interact with and are responsible for hypothalamic function, such as regulating hormones released from the pituitary gland or secreting their own hormones. Neurons in this region are also responsible for integrating information and providing inputs to other nuclei in the hypothalamus or inputs to areas outside this region of the brain. These neurons, generated from the ventral part of the periventricular epithelium during embryonic development, locate dorsally in the hypothalamus, becoming part of the ventromedial hypothalamic region.
Arcuate nucleus
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The central nervous system CNS receives information from afferent neurons, circulating hormones, and absorbed nutrients and integrates this information to orchestrate the actions of the neuroendocrine and autonomic nervous systems in maintaining systemic metabolic homeostasis. Particularly the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus ARC is of pivotal importance for primary sensing of adiposity signals, such as leptin and insulin, and circulating nutrients, such as glucose. Importantly, energy state—sensing neurons in the ARC not only regulate feeding but at the same time control multiple physiological functions, such as glucose homeostasis, blood pressure, and innate immune responses. These findings have defined them as master regulators, which adapt integrative physiology to the energy state of the organism. The disruption of this fine-tuned control leads to an imbalance between energy intake and expenditure as well as deregulation of peripheral metabolism. Improving our understanding of the cellular, molecular, and functional basis of this regulatory principle in the CNS could set the stage for developing novel therapeutic strategies for the treatment of obesity and metabolic syndrome. In this review, we summarize novel insights with a particular emphasis on ARC neurocircuitries regulating food intake and glucose homeostasis and sensing factors that inform the brain of the organismal energy status. Obesity prevalence has increased worldwide in the last 50 years to pandemic proportions 1.
Groups of neuroendocrine neurons include:. SP was named by Gaddum and Schild [ ] in and its amino acid long sequence was determined in [ ], arcuate nucleus.
In the medulla oblongata , the arcuate nucleus is a group of neurons located on the anterior surface of the medullary pyramids. These nuclei are the extension of the pontine nuclei. They receive fibers from the corticospinal tract and send their axons through the anterior external arcuate fibers and medullary striae to the cerebellum via the inferior cerebellar peduncle. Arcuate nuclei are capable of chemosensitivity and have a proven role in the respiratory center controlling the breathing rate. This neuroanatomy article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
In the medulla oblongata , the arcuate nucleus is a group of neurons located on the anterior surface of the medullary pyramids. These nuclei are the extension of the pontine nuclei. They receive fibers from the corticospinal tract and send their axons through the anterior external arcuate fibers and medullary striae to the cerebellum via the inferior cerebellar peduncle. Arcuate nuclei are capable of chemosensitivity and have a proven role in the respiratory center controlling the breathing rate. This neuroanatomy article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. Contents move to sidebar hide.
Arcuate nucleus
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. An Author Correction to this article was published on 10 March Despite the crucial physiological processes governed by neurons in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus ARC , such as growth, reproduction and energy homeostasis, the developmental pathways and regulators for ARC neurons remain understudied. These markers include transcription factors whose expression is enriched in specific neuronal types and often depleted in other closely-related neuronal types, raising the possibility that these transcription factors play important roles in the fate commitment or differentiation of specific ARC neuronal types. We validated this idea with the two transcription factors, Foxp2 enriched for Ghrh-neurons and Sox14 enriched for Kisspeptin-neurons, using Foxp2- and Soxdeficient mouse models. Taken together, our single cell transcriptome analyses for the developing ARC uncovered a panel of transcription factors that are likely to form a gene regulatory network to orchestrate fate specification and differentiation of ARC neurons. Chengxiang Qiu, Beth K.
Candy cane cock
Zhang X, van den Pol AN. However, tamoxifen-induced deletion of the LEPR from POMC neurons in adult mice leads to unaltered body weight, food intake, and energy expenditure This review describes the physiological and molecular functions and genetic disorders of various neurons in the ARH. Serotonin 2C receptor activates a distinct population of arcuate pro-opiomelanocortin neurons via TRPC channels. Physiology of astroglia. Further deciphering the specific functions and neurocircuit integration of distinct subclusters of these cells may pave the way to more specific pharmacological modification of distinct metabolic effector pathways controlled by these cell types for review, see Quarta et al PMID Kawano H, Daikoku S May These neurons, generated from the ventral part of the periventricular epithelium during embryonic development, locate dorsally in the hypothalamus, becoming part of the ventromedial hypothalamic region. GHRH-expressing neurons GHRH, a amino acid peptide hormone, binds to the its cognate receptor in the anterior pituitary gland, thereby stimulating the secretion of growth hormone GH [ 68 - 70 ]. Furthermore, POMC neurons regulate a wide array of different physiological functions, including feeding behavior and energy expenditure, hepatic glucose production, regulation of blood glucose levels, and blood pressure. Reichlin S Growth hormone content of pituitaries from rats with hypothalamic lesions.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
Overlapping brain circuits for homeostatic and hedonic feeding. Graphical Abstract. Nutritional feedback signals reach the hypothalamus in part via an incomplete, fenestrated endothelium in the ME, which plays a significant role in the actions of energy-state—sensing signals 9 , View Full Text. Additional Information Disclosures: The authors have nothing to disclose. J Neuroendocrinol Alba M, Salvatori R A mouse with targeted ablation of the growth hormone-releasing hormone gene: a new model of isolated growth hormone deficiency. Mutations in NHLH2 also lead to hypogonadotropic hypogonadism [ , ]. NPY, a amino-acid orexigenic neuropeptide [ 8 ], was first identified from extracts of porcine brains without the cerebellum and pituitary gland by Tatemoto et al. Lateral Ventromedial Dorsomedial. NKB, identified as a decaneuropeptide in [ 93 - 95 ], is generated through the proteolytic cleavage of a preproprotein encoded by TAC3. Reprod Biol Endocrinol Defining the regulatory mechanism of this stimulus- and meal timing—dependent regulation of not only feeding responses but also of glucose metabolism will broaden our understanding about the complex regulation of metabolism through the CNS.

0 thoughts on “Arcuate nucleus”