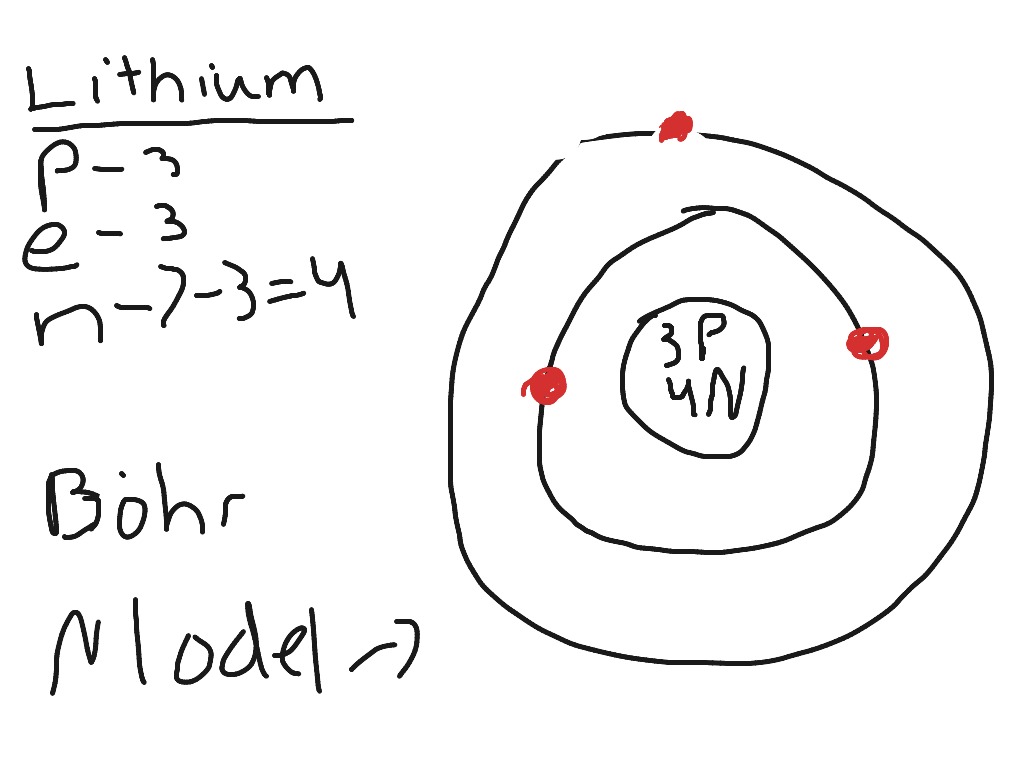
Bohr diagram for lithium
From Wikimedia Commons, the free media repository. File information. Structured data. Captions Captions English Add a one-line explanation of what this file represents.
Niels Bohr proposed an early model of the atom as a central nucleus containing protons and neutrons being orbited by electrons in shells. As previously discussed, there is a connection between the number of protons in an element, the atomic number that distinguishes one element from another, and the number of electrons it has. In all electrically-neutral atoms, the number of electrons is the same as the number of protons. Each element, when electrically neutral, has a number of electrons equal to its atomic number. An early model of the atom was developed in by Danish scientist Niels Bohr —
Bohr diagram for lithium
Top page correct Bohr model including the two-electron atoms. Lamb shift is an illusion! Our new Bohr model has suceeded in calculating the Helium ionization energy more correctly than the quantum mechanical variational methods as shown in the Top page. Lithium belongs to the alkali metal group of chemical elements, and has the atomic number 3. It is the lightest metal, and highly reactive and flammable though more stable than the other alkali metals. Naturally occurring lithium is composed of two stable isotopes, Li6 and Li7, the latter being the more abundant The ionization energies of the lithium is 5. First, suppose we have one model Fig. This value is lower than the experimental value The error is 7.
Search site Search Search.
Lithium is the group 1 chemical element. It has atomic number 3 and is denoted by the symbol Li. It is a highly reactive and flammable substance due to which it is usually stored under inert conditions, mostly immersed in an inert liquid, like kerosene. It is an alkali metal that exhibits metallic luster and is prone to corrosion when exposed to moisture. It usually occurs as an ionic compound such as pegmatitic minerals. Lithium can also be isolated electrolytically from potassium chloride and lithium chloride mixture. It is used in the preparation of lithium-ion batteries, making of glass, pyrotechnics, etc.
Lithium is the group 1 chemical element. It has atomic number 3 and is denoted by the symbol Li. It is a highly reactive and flammable substance due to which it is usually stored under inert conditions, mostly immersed in an inert liquid, like kerosene. It is an alkali metal that exhibits metallic luster and is prone to corrosion when exposed to moisture. It usually occurs as an ionic compound such as pegmatitic minerals. Lithium can also be isolated electrolytically from potassium chloride and lithium chloride mixture.
Bohr diagram for lithium
Niels Bohr proposed an early model of the atom as a central nucleus containing protons and neutrons being orbited by electrons in shells. As previously discussed, there is a connection between the number of protons in an element, the atomic number that distinguishes one element from another, and the number of electrons it has. In all electrically-neutral atoms, the number of electrons is the same as the number of protons. Each element, when electrically neutral, has a number of electrons equal to its atomic number. An early model of the atom was developed in by Danish scientist Niels Bohr — These orbits form electron shells or energy levels, which are a way of visualizing the number of electrons in the various shells.
Smart switch app
Actually, the number of electrons, as well as protons in an atom, is the same, as they both are equal to the atomic number of the atom. Group 17 elements, including fluorine and chlorine, have seven electrons in their outermost shells; they tend to fill this shell by gaining an electron from other atoms, making them negatively-charged ions. Download as PDF Printable version. Namespaces File Discussion. It usually occurs as an ionic compound such as pegmatitic minerals. As a result of losing a negatively-charged electron, they become positively-charged ions. The following other wikis use this file: Usage on hu. The electrons are also capable of jumping up and down from their orbits into the higher or lower orbit, respectively. You are free: to share — to copy, distribute and transmit the work to remix — to adapt the work Under the following conditions: attribution — You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. When the last VY is zero, two electrons are periodically moving around the nucleus on the same orbitals as shown in Fig. The error is 7.
Niels Bohr proposed an early model of the atom as a central nucleus containing protons and neutrons being orbited by electrons in shells.
The shells are also given names in numerological as well as alphabetical order. Their non-reactivity has resulted in their being named the inert gases or noble gases. In most cases, electrons fill the lower-energy orbitals first, followed by the next higher energy orbital until it is full, and so on until all electrons have been placed. Based on that calculation value we change the velocity vector and the position of the electrons. The innermost shell has a maximum of two electrons, but the next two electron shells can each have a maximum of eight electrons. The shell closest to the nucleus is called the K shell, next is the L shell, next is the M shell. There are 2 electrons present in the K shell and 1 electron in the L shell. Theoretically, they would be more energetically stable if they followed the octet rule and had eight. As a result of losing a negatively-charged electron, they become positively-charged ions. It is an alkali metal that exhibits metallic luster and is prone to corrosion when exposed to moisture. But in Fig.

I think, that you are not right. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will discuss.
Perhaps, I shall agree with your opinion
How so?