C2h4 sigma and pi bonds
Pages: [ 1 ] Go Down.
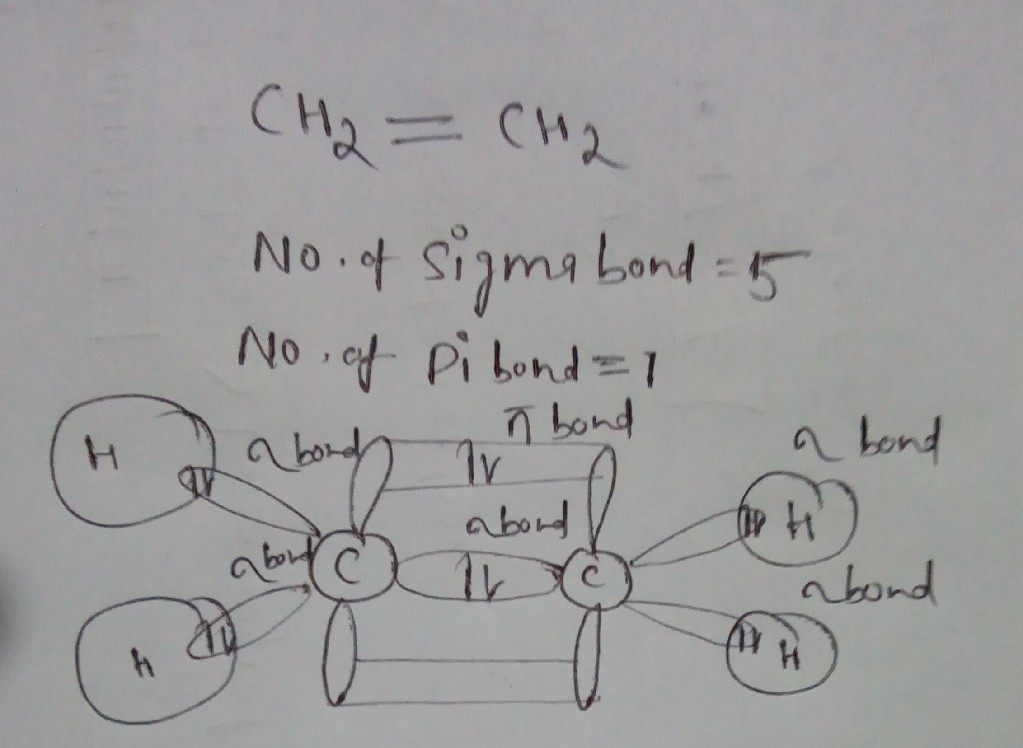
Thus far valence bond theory has been able to describe the bonding in molecules containing only single bonds. However, when molecules contain double or triple bonds the model requires more details. Ethylene commonly knows as ethene , CH 2 CH 2 , is the simplest molecule which contains a carbon carbon double bond. The Lewis structure of ethylene indicates that there are one carbon-carbon double bond and four carbon-hydrogen single bonds. Experimentally, the four carbon-hydrogen bonds in the ethylene molecule have been shown to be identical. Because each carbon is surrounded by three electron groups, VSEPR theory says the molecule should have a trigonal planar geometry.
C2h4 sigma and pi bonds
When you hear the words sigma and pi bond, you might think of Greek life in college. But actually, sigma and pi bonds are types of covalent bonds. Covalent bonds happen when atoms share electrons. They are found in single, double, and triple bonds. They only exist in double and triple bonds. So, what's the difference between sigma and pi bonds? First, sigma bonds are stronger than pi bonds. Second, sigma bonds can exist independently in single bonds, while pi bonds must coexist with a sigma bond and are only found in double and triple bonds. To understand sigma and pi bonds, you need to know a little about atomic orbitals and hybridization. Atomic orbitals are spaces where electrons are likely to be found. There are four types of atomic orbital sets: s, p, d, and f. When two molecules bond, their orbitals usually combine to form hybrid orbitals like sp, sp2, and sp3. In summary, sigma and pi bonds are types of covalent bonds formed by different types of atomic orbital overlap. Sigma bonds are stronger and can exist independently in single bonds, while pi bonds must coexist with a sigma bond and are only found in double and triple bonds.
When considering pi bonds, it's good to think of electrons in a pi orbital not as 2 objects but in terms of their orbitals. Get Started! That's the best I could think about it.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos. About About this video Transcript. Created by Sal Khan. Want to join the conversation? Log in.
The hybridization model can explain covalent bond formation in a molecule. Covalent bonds are formed by overlapping atomic orbitals, resulting in sigma and pi bonds. The two bonds differ in the way in which overlapping occurs. Various bond properties like bond length, bond energy, and bond enthalpy depend on how orbitals overlap. The electron density is concentrated between the nuclei of the bonding atoms. Sigma bond is the strongest covalent bond, owing to the direct overlapping of the contributing orbitals. The bonding electrons are usually referred to as sigma electrons. Generally, all single bonds are sigma bonds. They can be formed via the following combinations of atomic orbitals.
C2h4 sigma and pi bonds
Our minds can handle two electrons interacting with one another in a sphere of space. But then we start putting in double bonds and triple bonds. So we need a more complex picture that works for all these electrons.
Shoes for crews - canada
Who tells carbon to hybridize in sp3 or sp2 or sp? Arrhenius Equation. So this bond right here is this bond. Aldehydes and Ketones. And then we have this hydrogen is sitting right over here. Sponsored Links. With practice, you'll become more confident in identifying and counting sigma and pi bonds in different molecules. Log in. Organic Synthesis. Kinetic Molecular Theory.
Carbon can make single, double, or triple bonds. The number of bonds it makes determines the structure. With four single bonds, carbon has a tetrahedral structure, while with one double bond it's structure is trigonal planar, and with a triple bond it has a linear structure.
In the ethylene molecule, each carbon atom is bonded to two hydrogen atoms. Try Shiken Premium for Free. And then he's got these two hydrogens, so one-- he's got this guy in the back, and then there's one in the front. Arrhenius Equation. Hess' Law. Catalysts Organic Chemistry. Ground State. So it's molecular structure looks like this. Additionally, sigma bonds form single bonds and can exist without a pi bond present; however, a sigma bond must already be formed for a pi bond to form. Ethene, C2H4, has a double bond between Carbons. In this case, one of these, so the first bonds, you can imagine, so these bonds are all sigma bonds. This right here is a sigma bond. So you have this hydrogen there.

I am final, I am sorry, but it not absolutely approaches me.