Carotid massage for svt
A year-old women with a history of palpitations presented to the emergency department with a supraventricular tachycardia; the patient was cardiovascularly stable.
The use of vagal stimulation to halt supraventricular tachycardia is a standard medical therapy. Two methods of vagal stimulation, the Valsalva maneuver and carotid sinus massage, have been used in urgent situations. Lim and associates compared the success rates of these two methods of vagal stimulation in terminating spontaneous supraventricular tachycardia in an emergency department setting. All patients with supraventricular tachycardia whose rhythm did not reveal obvious atrial flutter, atrial fibrillation or sinus tachycardia and who were hemodynamically stable were randomly assigned to undergo either the Valsalva maneuver or carotid sinus massage. Those who had carotid sinus massage were further randomized to undergo either right or left carotid sinus massage first. If the tachycardia was not terminated by the first method of vagal stimulation, the alternative maneuver was attempted.
Carotid massage for svt
Methods: This prospective, randomized case study was performed in the ED of a tertiary care institution. Patients with regular narrow complex tachycardia were randomly assigned to undergo either the Valsalva maneuver or CSM. If the tachycardia was not terminated by the method chosen by randomization, then the alternative method of vagal maneuver was used. If the tachycardia was not converted by both methods of vagal stimulation, patients would undergo either synchronized electrical cardioversion or a pharmacologic method of conversion at the discretion of the treating physician, depending on the patient's hemodynamic status. Results: One hundred forty-eight instances of SVT were studied Sixty-two patients underwent Valsalva maneuver first with conversion in 12 success rate of Eighty-six underwent CSM first with conversion in 9 success rate Carotid sinus massage was used in the 50 cases of SVT in which conversion was not achieved with the Valsalva maneuver. Conversion occurred in 7 cases success rate For the 77 cases of SVT in which initial CSM did not achieve conversion, conversion occurred in 13 with the Valsalva maneuver success rate Conclusion: Vagal maneuvers are efficacious in terminating about one quarter of spontaneous SVT cases.
The management of SVT using vagal maneuvers has relied on a centuries-old procedure, which has undergone only minor modification over time. Latest content Current issue Archive Authors About.
The first explanation behind the process of using a Valsalva Maneuver was described in by Hamilton et al. The pathophysiological basis of action of the four phases of the maneuver is based on the nature of increased refractoriness of AV nodal tissue, particularly on the effect of vagal activity. This occurs through increased intrathoracic pressure leading to baroreceptor stimulation, as demonstrated through the heart rate and blood pressure responses. The best available evidence currently, specifically the work of Taylor and Wong , supports the following three criteria in an evidence-based model of practice of the Valsalva Maneuver for SVT reversion in the emergency-care setting:. Patients should be instructed how to perform VM properly before attempting one.
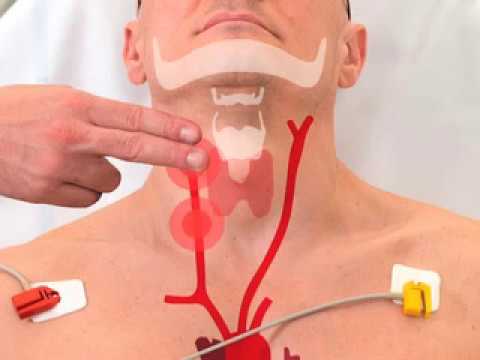
Last Updated: September 16, Fact Checked. This article was medically reviewed by Jennifer Boidy, RN. Jennifer Boidy is a Registered Nurse in Maryland. There are 9 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 99, times. A carotid massage, often called a carotid sinus massage or CSM, is a medical maneuver used to slow down a dangerously rapid heartbeat in patients or to diagnose certain heart rhythm disturbances. The carotid artery carries blood to the brain, and an incorrectly performed CSM can cause serious health repercussions, especially in elderly patients. Do not perform this maneuver on yourself or another person unless you are a physician. National Institutes of Health Go to source.
Carotid massage for svt
The first explanation behind the process of using a Valsalva Maneuver was described in by Hamilton et al. The pathophysiological basis of action of the four phases of the maneuver is based on the nature of increased refractoriness of AV nodal tissue, particularly on the effect of vagal activity. This occurs through increased intrathoracic pressure leading to baroreceptor stimulation, as demonstrated through the heart rate and blood pressure responses. The best available evidence currently, specifically the work of Taylor and Wong , supports the following three criteria in an evidence-based model of practice of the Valsalva Maneuver for SVT reversion in the emergency-care setting:. Patients should be instructed how to perform VM properly before attempting one. In addition, carotid massage is only recommended for select patients and may only be performed by a physician. It is essential to understand that it is not always appropriate to have a patient attempt VM.
Titli full movie download
Email alerts. Further prehospital and emergency department research may provide benefit to VM practice by examining the duration of symptoms and reversion success, an appropriate restitution time between VM attempts, and the number of VM attempts that produce maximum reversion effect before other therapeutic intervention 3. If the tachycardia was not converted by both methods of vagal stimulation, patients would undergo either synchronized electrical cardioversion or a pharmacologic method of conversion at the discretion of the treating physician, depending on the patient's hemodynamic status. The incidence of SVT is approximately 35 cases per , patients with a prevalence of 2. If a physician ensures a patient is an appropriate candidate for VM, the patient can be instructed to perform maneuvers at home in some situations. These conductive accessory pathways pass through the atrioventricular septum and thus provide for a larger re-entry circuit, albeit one that passes through the AV node and is similarly affected by increased vagal tone. Carotid sinus massage was performed in the standard manner for 10 seconds with the head tilted to the opposite side. A total of episodes of supraventricular tachycardia occurred among patients. Instant Provider Card. Shockable Rhythms: Ventricular Tachycardia, Ventricular Fibrillation, Supraventricular Tachycardia According to television, if there's a heart problem, you shock it, right? If there was no recurrence during the observation period, the patient was discharged with an outpatient appointment. This occurs through increased intrathoracic pressure leading to baroreceptor stimulation, as demonstrated through the heart rate and blood pressure responses. Skip to main content. Vagal Maneuvers with Supraventricular Tachycardia Vagal maneuvers are used as a first-line management tool with supraventricular tachycardia.
To diagnose supraventricular tachycardia SVT , a healthcare professional examines you and listens to your heart. A member of your care team takes your blood pressure.
Patient consent: Obtained. Forgot your user name or password? Patients with regular narrow complex tachycardia were randomly assigned to undergo either the Valsalva maneuver or CSM. Those who had carotid sinus massage were further randomized to undergo either right or left carotid sinus massage first. SVT is a rapid heartbeat that originates in the chambers above the ventricles. The Valsalva maneuver was performed by blowing into a mouthpiece with sustained resistance for 30 seconds or more. In some cases, the alternative maneuver was successful when the initial attempt failed. Further prehospital and emergency department research may provide benefit to VM practice by examining the duration of symptoms and reversion success, an appropriate restitution time between VM attempts, and the number of VM attempts that produce maximum reversion effect before other therapeutic intervention 3. Conversion occurred in 7 cases success rate Patients should be instructed how to perform VM properly before attempting one. It can occur due to a variety of reasons, such as structural abnormalities and heart failure. Shockable Rhythms: Ventricular Tachycardia, Ventricular Fibrillation, Supraventricular Tachycardia According to television, if there's a heart problem, you shock it, right? It is essential to understand that it is not always appropriate to have a patient attempt VM. Some potential complications include dizziness and an arrhythmia originating in the ventricles. SVT is a generic term applied to any tachycardia originating above the ventricles and which involves atrial tissue or atrioventricular AV nodal tissue.

Quickly you have answered...
You are not right. I can prove it. Write to me in PM, we will talk.