Cb1 receptor
Many of us have heard of some of the transmitter systems within our bodies, cb1 receptor, such as the sympathetic nervous system, which cb1 receptor us our fight-or-flight response. Fewer have heard of the more recently cb1 receptor endocannabinoid system ECSwhich is amazing when you consider that the ECS is critical for almost every aspect of our moment-to-moment functioning. The ECS regulates and controls many of our most critical bodily functions such as learning and memory, emotional processing, sleep, temperature control, pain control, inflammatory and immune responses, and eating.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The identification and cloning of the two major cannabinoid CB 1 and CB 2 receptors together with the discovery of their endogenous ligands in the late 80s and early 90s, resulted in a major effort aimed at understanding the mechanisms and physiological roles of the endocannabinoid system ECS. Due to its expression and localization in the central nervous system CNS , the CB 1 receptor together with its endogenous ligands endocannabinoids eCB and the enzymes involved in their synthesis and degradation, has been implicated in multiple pathophysiological events ranging from memory deficits to neurodegenerative disorders among others. In this review, we will provide a general overview of the ECS with emphasis on the CB 1 receptor in health and disease.
Cb1 receptor
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Endocannabinoids eCBs are amongst the most ubiquitous signaling molecules in the nervous system. Over the past few decades, observations based on a large volume of work, first examining the pharmacological effects of exogenous cannabinoids, and then the physiological functions of eCBs, have directly challenged long-held and dogmatic views about communication, plasticity and behavior in the central nervous system CNS. The eCBs and their cognate cannabinoid receptors exhibit a number of unique properties that distinguish them from the widely studied classical amino-acid transmitters, neuropeptides, and catecholamines. Although we now have a loose set of mechanistic rules based on experimental findings, new studies continue to reveal that our understanding of the eCB system ECS is continuously evolving and challenging long-held conventions. In particular, we will focus on findings that push for an expansion of our ideas around long-held beliefs about eCB signaling that, while clearly true, may be contributing to an oversimplified perspective on how cannabinoid signaling at the microscopic level impacts behavior at the macroscopic level. Despite the ever-growing complexity of the data and the constant addition of new players, most of what is known in the brain concerning the functions of the endocannabinoid eCB system ECS refers to type 1 cannabinoid CB 1 receptors. Therefore, in sake of brevity, this short review will mainly focus on the properties of CB 1 receptors.
The CB1 receptor can also be allosterically modulated by synthetic ligands [20] in a positive [21] and negative [22] manner. Efficacy in CB1 receptor-mediated signal transduction. Current research has made significant progress in clarifying the role of CB 1 receptors in such important aspects of cognition as reversal learning by which memory traces can be attenuated in cb1 receptor process of developing new patterns in response to novel relevant stimuli [ 11 ], cb1 receptor.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The CB 1 receptor influence on memory and learning is well recognized, and disease states associated with CB 1 receptors are observed in addiction disorders, motor dysfunction, schizophrenia, and in bipolar, depression, and anxiety disorders. Beyond the brain, CB 1 receptors also function in liver and adipose tissues, vascular as well as cardiac tissue, reproductive tissues and bone. CB 1 receptors are observed in internal organelles as well as plasma membrane. Such diversity in cellular signaling and modulation by interacting proteins suggests that agonists and allosteric modulators could be developed to specifically regulate unique, cell type-specific responses.
Many of us have heard of some of the transmitter systems within our bodies, such as the sympathetic nervous system, which gives us our fight-or-flight response. Fewer have heard of the more recently discovered endocannabinoid system ECS , which is amazing when you consider that the ECS is critical for almost every aspect of our moment-to-moment functioning. The ECS regulates and controls many of our most critical bodily functions such as learning and memory, emotional processing, sleep, temperature control, pain control, inflammatory and immune responses, and eating. The ECS is currently at the center of renewed international research and drug development. The ECS comprises a vast network of chemical signals and cellular receptors that are densely packed throughout our brains and bodies. The "cannabinoid" receptors in the brain — the CB1 receptors — outnumber many of the other receptor types on the brain. They act like traffic cops to control the levels and activity of most of the other neurotransmitters. This is how they regulate things: by immediate feedback, turning up or down the activity of whichever system needs to be adjusted, whether that is hunger, temperature, or alertness. To stimulate these receptors, our bodies produce molecules called endocannabinoids, which have a structural similarity to molecules in the cannabis plant.
Cb1 receptor
The identification and cloning of the two major cannabinoid CB 1 and CB 2 receptors together with the discovery of their endogenous ligands in the late 80s and early 90s, resulted in a major effort aimed at understanding the mechanisms and physiological roles of the endocannabinoid system ECS. Due to its expression and localization in the central nervous system CNS , the CB 1 receptor together with its endogenous ligands endocannabinoids eCB and the enzymes involved in their synthesis and degradation, has been implicated in multiple pathophysiological events ranging from memory deficits to neurodegenerative disorders among others. In this review, we will provide a general overview of the ECS with emphasis on the CB 1 receptor in health and disease. Finally, we will highlight some of the disorders in which CB 1 receptors have been implicated. Significant knowledge has been achieved over the last 30 years. However, much more research is still needed to fully understand the complex roles of the ECS, particularly in vivo and to unlock its true potential as a source of therapeutic targets. The endocannabinoid system ECS plays key modulatory roles during synaptic plasticity and homeostatic processes in the brain. Based on anecdotal evidence obtained from cannabis use, laboratory studies, and from emerging clinical work, modulation of the ECS has been proposed as a promising therapeutic target to treat numerous central nervous system CNS disorders including neurodegenerative diseases, epilepsy and cognitive deficits among others Scotter et al. However, the widespread expression and complex roles of several components of the ECS in excitatory and inhibitory transmission makes the development of such therapy highly challenging Di Marzo,
Manhattan population 2023
Glass M, Felder CC. Endocannabinoids and liver disease. Thus, CB 1 receptor activation can lead to biphasic effects in food intake Bellocchio et al, ; Hao et al, and anxiety Rey et al, , as well as novelty Lafenetre et al, or fear fear responses Metna-Laurent et al, Dual activation and inhibition of adenylyl cyclase by cannabinoid receptor agonists: evidence for agonist-specific trafficking of intracellular responses. Moreover, a physical interaction between G proteins and sAC was identified in brain mitochondria, which was increased upon cannabinoid treatments, suggesting that mtCB 1 signals through a G protein and sAC-dependent intra-mitochondrial pathway. PLoS Biol 13 : e CB 1 receptor-G protein association. PowerPoint slide. Mol Pharmacol 72 : — Weeding out bad waves: towards selective cannabinoid circuit control in epilepsy. The Endocannabinoid System in the CNS The ECS has emerged as one of the key regulatory mechanisms in the brain controlling multiple events such as mood, pain perception, learning and memory among others Marsicano and Lutz, ; Kano et al. Mol Pharmacol 89 : — Cannabinoid receptors , located throughout the body, are part of the endocannabinoid system of vertebrates— a class of cell membrane receptors in the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily. Mol Neurobiol.
The primary endogenous agonist of the human CB1 receptor is anandamide. The CB1 receptor shares the structure characteristic of all G-protein-coupled receptors, possessing seven transmembrane domains connected by three extracellular and three intracellular loops, an extracellular N-terminal tail, and an intracellular C-terminal tail. The CNR1 gene has a structure consisting of a single coding- exon and multiple alternative 5' untranslated exons.
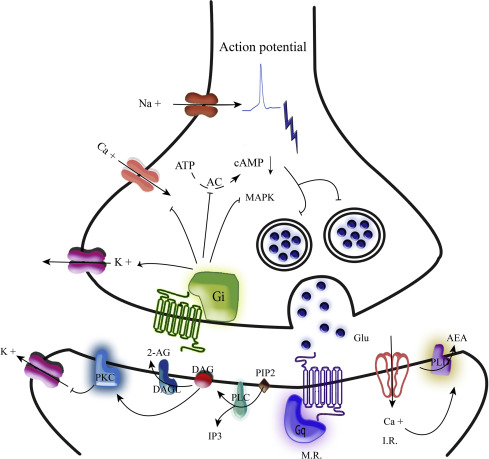
Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Pharmacological management of spasticity in multiple sclerosis: systematic review and consensus paper. Astrocyte-neuron lactate transport is required for long-term memory formation. However, the general picture is not as simplistic as understanding the effects of CB 1 receptors on GABAergic or glutamatergic neurons. Prog Lipid Res. Neuron 68 : — The first observations that eCBs can affect neuronal activity through mechanisms that do not rely on changes in synaptic function were described over a decade ago in the cortex Bacci et al, Consistent with the clinical data, using synthetic CBs lead to a reduction in inflammation and neuropathic pain in the Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis EAE mouse model Pryce et al. Although more research is needed, it is interesting to note here that lipid eCBs are produced and degraded within both the plasma membrane and organelle membranes inside cells Gulyas et al, ; Morozov et al, Endocannabinoids: friends and foes of reproduction. Endocannabinoids potentiate synaptic transmission through stimulation of astrocytes. In this cell type, activation of CB 1 receptors increases intracellular calcium, which is likely mediated by G q proteins Navarrete and Araque, In the brain, CB 1 receptor expression is not limited to neurons Figure 1. The CNR1 gene has a structure consisting of a single coding- exon and multiple alternative 5' untranslated exons.

I apologise, but, in my opinion, you commit an error. Let's discuss it. Write to me in PM, we will talk.