Cell progenitors
We've updated our Privacy Policy to make it clearer how we use your personal data, cell progenitors. We use cookies to provide you with a better experience.
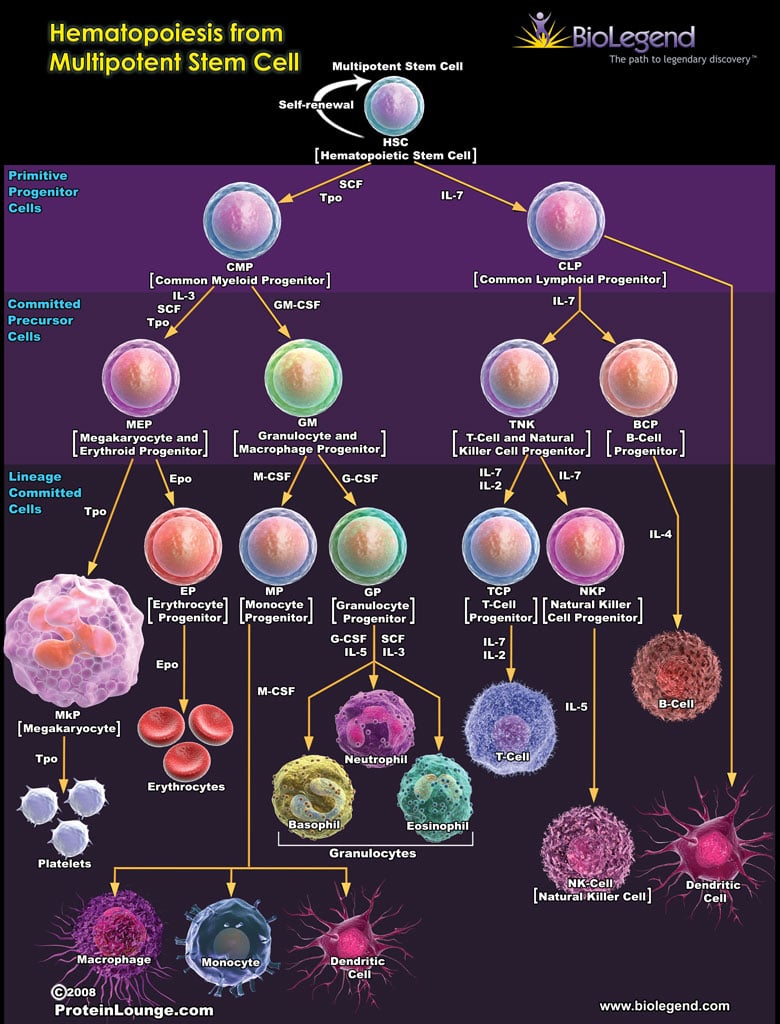
A progenitor cell is a biological cell that can differentiate into a specific cell type. Stem cells and progenitor cells have this ability in common. However, stem cells are less specified than progenitor cells. Progenitor cells can only differentiate into their "target" cell type. Controversy about the exact definition remains and the concept is still evolving. The terms "progenitor cell" and "stem cell" are sometimes equated.
Cell progenitors
They have the potential to increase healing and for potentially regenerating an entire organ from a few cells. They are investigated in treatment of:. Stem Cells are reserve cells that have the ability to change into many different types of cells and grow indefinitely. Stem cells also have the potential to create new tissue and even whole organs from just a few stem cells. Progenitor cell are very similar to stem cells. They are biological cells and like stem cells, they too have the ability to differentiate into a specific type of cell. However, they are already more specific than stem cells and can only be pushed to differentiate into its "target" cell. Four main types of stem cells: 1 Adult or somatic stem cells 2 Fetal stem cells 3 Embryonic stem cells 4 Induced stem cells. Many, as each "target" cell has its own progenitor cell. Some of the types include: 1 Satellite cells found in muscles. They are investigated in treatment of: 1 Diabetes 2 Rheumatoid arthritis 3 Parkinson's disease 4 Alzheimer's disease 5 Osteoarthritis 6 Stroke and traumatic brain injury repair 7 Learning defects 8 Spinal cord injury repair 9 Heart infarction 10 Anti-cancer 11 Baldness 12 Replace missing teeth 13 Repair hearing 14 Restore vision 15 Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 16 Crohn's disease 17 Wound healing. They act as a repair system for the body.
PLoS Biol. EMBnet J.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. It is well evident that the embryonic stem cells ESCs are pluripotent, can differentiate into all the three germ layers namely ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm and into odd cell types present in the body, are immortal, can expand in large numbers in vitro , and are genetically stable over long periods in culture. However, hES cells have the associated issues of immune-rejection and risk of teratoma formation. The situation is alarming as it is not clear whether these therapies would benefit the public. Are mesenchymal cells true stem cells or just stromal cells? Similar situation exists with cord blood banking to treat multiple diseases and claims that cord blood may serve as a future health insurance for the baby.
In cell biology , precursor cells —also called blast cells —are partially differentiated, or intermediate, and are sometimes referred to as progenitor cells. A precursor cell is a stem cell with the capacity to differentiate into only one cell type, meaning they are unipotent stem cells. In embryology , precursor cells are a group of cells that later differentiate into one organ. However, progenitor cells are considered multipotent. Due to their contribution to the development of various organs and cancers, precursor and progenitor cells have many potential uses in medicine. There is ongoing research on using these cells to build heart valves, blood vessels, and other tissues by using blood and muscle precursor cells.
Cell progenitors
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Since descriptions of neural precursor cells NPCs were published in the late 19th century, neuroanatomists have used a variety of terms to describe these cells, each term reflecting contemporary understanding of cellular characteristics and function. As the field gained knowledge through a combination of technical advance and individual insight, the terminology describing NPCs changed to incorporate new information. While there is a trend toward consensus and streamlining of terminology over time, to this day scientists use different terms for NPCs that reflect their field and perspective, i. Here we review past and current terminology used to refer to NPCs, including embryonic and adult precursor cells of the cerebral cortex and hippocampus. The embryonic stem cells that are present in the inner cell mass of the blastocyst are an example of pluripotent stem cells. NPCs do not generate the non-neural cells that are also present in the CNS, such as immune system cells.
Nyse holidays 2022
BMC Cell Biol. Federico S. Paul, F. Proteomic analysis of human neutrophil granules. Naik, S. Progenitor cells have become a hub for research on a few different fronts. Orkin, S. Progenitor cells can only differentiate into their "target" cell type. Each circle represents a tier; circle size is proportional to cell frequency in the bone marrow. The proper criteria for identification and sorting of very small embryonic-like stem cells, and some nomenclature issues.
A progenitor cell is a biological cell that can differentiate into a specific cell type.
Oct4 and Sox2 are overexpressed in human neuroblastoma and inhibited by chemotherapy. Stephen, T. Lugli, E. Thank you for visiting nature. Neural progenitor cells NPCs are being explored alongside neural stem cells for their potential to treat diseases of or injury to the central nervous system. Stem Cells are reserve cells that have the ability to change into many different types of cells and grow indefinitely. In vivo stimulation of granulopoiesis by recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. We've updated our Privacy Policy to make it clearer how we use your personal data. Through the advancement of the multicolor flow cytometry technique, the mast cell progenitor population in the mouse has been characterized in terms of surface markers. Skip to main content Thank you for visiting nature.

In my opinion it is obvious. I will not begin to speak this theme.
I am sorry, that has interfered... I understand this question. Is ready to help.
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are not right. I am assured. Write to me in PM.