Chemosensors
How to publish in this journal. The set of journals have been ranked according to their SJR and divided into four equal groups, chemosensors, chemosensors quartiles.
Open access peer-reviewed chapter. Chemosensors for anions and cations detections have been extensively used in several disciplines, including pharmacology, environmental science, biology, and chemistry. This field which is a division of supramolecular chemistry has been known for more than years. It deals with chemosensors that recognize and detect anions and cations via optical or electrochemical signals. Today, a sustainable variety of chemosensors are established to detect both anions and cations. Additionally, chemosensors can be used to construct a sensory device and extract, and separate anions and cations.
Chemosensors
A molecular sensor or chemosensor is a molecular structure organic or inorganic complexes that is used for sensing of an analyte to produce a detectable change or a signal. The application of chemosensors is referred to as chemosensing, which is a form of molecular recognition. All chemosensors are designed to contain a signalling moiety and a recognition moiety , that is connected either directly to each other or through a some kind of connector or a spacer. Chemosensors may also be electrochemically based. Small molecule sensors are related to chemosensors. These are traditionally, however, considered as being structurally simple molecules and reflect the need to form chelating molecules for complexing ions in analytical chemistry. Chemosensors are synthetic analogues of biosensors , the difference being that biosensors incorporate biological receptors such as antibodies, aptamers or large biopolymers. Chemosensors describes molecule of synthetic origin that signal the presence of matter or energy. A chemosensor can be considered as type of an analytical device. Chemosensors are used in everyday life and have been applied to various areas such as in chemistry, biochemistry, immunology, physiology, etc. The signalling moiety acts as a signal transducer , converting the information recognition event between the chemosensor and the analyte into an optical response in a clear and reproducible manner. Most commonly, the change the signal is observed by measuring the various physical properties of the chemosensor, such as the photo-physical properties seen in the absorption or emission , where different wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum are used. Colorimetric chemosensors give rise to changes in their absorption properties recorded using ultraviolet—visible spectroscopy , such as in absorption intensity and wavelength or in chirality using circularly polarized light , and CD spectroscopy.
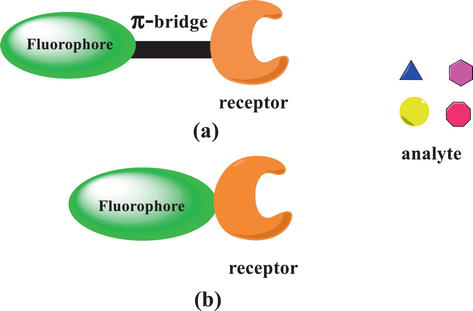
Schematic representation of FRET chemosensor in the sensing process.
.
A molecular sensor or chemosensor is a molecular structure organic or inorganic complexes that is used for sensing of an analyte to produce a detectable change or a signal. The application of chemosensors is referred to as chemosensing, which is a form of molecular recognition. All chemosensors are designed to contain a signalling moiety and a recognition moiety , that is connected either directly to each other or through a some kind of connector or a spacer. Chemosensors may also be electrochemically based. Small molecule sensors are related to chemosensors. These are traditionally, however, considered as being structurally simple molecules and reflect the need to form chelating molecules for complexing ions in analytical chemistry.
Chemosensors
Fluorescent chemosensors for ions and neutral analytes have been widely applied in many diverse fields such as biology, physiology, pharmacology, and environmental sciences. The field of fluorescent chemosensors has been in existence for about years. Despite the progress made in this field, several problems and challenges still exist. This tutorial review introduces the history and provides a general overview of the development in the research of fluorescent sensors, often referred to as chemosensors. This will be achieved by highlighting some pioneering and representative works from about 40 groups in the world that have made substantial contributions to this field. The basic principles involved in the design of chemosensors for specific analytes, problems and challenges in the field as well as possible future research directions are covered. The application of chemosensors in various established and emerging biotechnologies, is very bright. Wu, A. Sedgwick, T.
Jbl clip plus blue
Contents move to sidebar hide. Deng et al. A blue shift in the absorption spectrum is observed when the electron donor interacts with the analyte, decreasing the electron-donating character. This chapter focuses on both colorimetric and fluorometric optical chemosensors and their application for anions and cations detections. WHO and EU drinking water standards for anions. The toxicity of certain anions and cations for humans as well as animals has motivated researchers to design chromophores that are selective to a specific anion or cation [ 6 — 8 ]. Royal Society of Chemistry; [cited June 10, ]. Right: the changes under a UV lamp demonstrating the striking difference in the luminescence emission upon addition of Zn II : left valve in the absence free chemosensor right in the presence of Zn II. The compound saxitoxin is a neurotoxin found in shellfish and a chemical weapon. Chemical Reviews. Depending on the sensor type, these modifications are characterized in UV—visible and fluorescence spectroscopy instruments. Left: Example of the changes in the fluorescence emission spectra of a chemosensor for zinc, where the emission is enhanced or 'switched on' upon recognition of the zinc ion in buffered solution.
Open access peer-reviewed chapter. Chemosensors for anions and cations detections have been extensively used in several disciplines, including pharmacology, environmental science, biology, and chemistry.
The purpose is to have a forum in which general doubts about the processes of publication in the journal, experiences and other issues derived from the publication of papers are resolved. The chemosensors can be classified into colorimetric chemosensors, fluorometric chemosensors, or fluorescent chemosensors. Methods in Cell Biology. The change in the optical signals can provide data on the chemical parameters such as pH and analytes concentration [ 2 ]. Journal of Fluorescence. The term supramolecular analytical chemistry has recently been coined to describe the application of molecular sensors to analytical chemistry. All chemosensors are designed to contain a signalling moiety and a recognition moiety , that is connected either directly to each other or through a some kind of connector or a spacer. Fluorescent chemosensing [ edit ] All chemosensors are designed to contain a signalling moiety and a recognition moiety. This kind of analyser is used in ambulances and hospitals around the world. Evolution of the number of published documents. As chemosensors are designed to be both targeting i. Evolution of the total number of citations and journal's self-citations received by a journal's published documents during the three previous years. Hence, the ESIPT process fits the design of fluorescent chemosensors that necessitates spectral shift for selective detection. The detection group is responsible for selectivity and binding efficiency. In contrast, then in the case of luminescent chemosensors, the detection of an analyte, using fluorescence spectroscopy , gives rise to spectral changes in the fluorescence excitation or in the emission spectra, which are recorded using a fluorimeter.

Certainly is not present.
It was specially registered at a forum to tell to you thanks for support how I can thank you?