Chloride lewis dot structure
In almost all cases, chemical bonds are formed by interactions of valence electrons in atoms.
The number of electrons in the outermost shell of an atom determines its chemical characteristics. We visualize valence electrons using Lewis dot structures to locate stable electron configurations. In order to attain stability in any atom like noble gases , the majority of atoms often lose or gain electrons. In this article, we will learn how to draw the Lewis dot structure of Sodium Chloride stepwise. A Lewis structure is a type of diagram used to represent the electron configuration of a molecule or ion.
Chloride lewis dot structure
In all cases, these bonds involve the sharing or transfer of valence shell electrons between atoms. In this section, we will explore the typical method for depicting valence shell electrons and chemical bonds, namely Lewis symbols and Lewis structures. We use Lewis symbols to describe valence electron configurations of atoms and monatomic ions. A Lewis symbol consists of an elemental symbol surrounded by one dot for each of its valence electrons:. Figure 1. Lewis symbols illustrating the number of valence electrons for each element in the third period of the periodic table. Lewis symbols can also be used to illustrate the formation of cations from atoms, as shown here for sodium and calcium: Likewise, they can be used to show the formation of anions from atoms, as shown below for chlorine and sulfur: Figure 2 demonstrates the use of Lewis symbols to show the transfer of electrons during the formation of ionic compounds. Figure 2. Cations are formed when atoms lose electrons, represented by fewer Lewis dots, whereas anions are formed by atoms gaining electrons. The total number of electrons does not change. We also use Lewis symbols to indicate the formation of covalent bonds, which are shown in Lewis structures , drawings that describe the bonding in molecules and polyatomic ions. For example, when two chlorine atoms form a chlorine molecule, they share one pair of electrons:. The Lewis structure indicates that each Cl atom has three pairs of electrons that are not used in bonding called lone pairs and one shared pair of electrons written between the atoms. A dash or line is sometimes used to indicate a shared pair of electrons:.
Its electron dot diagram is as follows:. Lone pairs, unpaired electrons, and single, double, chloride lewis dot structure, or triple bonds are used to indicate where the valence electrons are located around each atom in a Lewis structure. Is it necessary for the first dot around an atomic symbol to go on a particular side of the atomic symbol?
.
When two atoms approach each other, they have the potential to bond or connect. If a metal and a nonmetal interact, then an ionic bond will result. These types of bonds involve the metal donating its valence electron s to a nonmetal, forming an ionic compound. As the transfer of electrons occurs, both atoms will achieve a more stabile confirmation. The end result will be a less reactive compound. These ionic species are composed of both cations positively charged ions and anions negatively charged ions. In addition, ionic compounds are crystalline and solid in nature. A few examples of real-world ionic compounds would be NaCl sodium chloride, table salt and NaF sodium fluoride, the active ingredient in toothpaste. If two nonmetals interact, then a covalent bond will result. The connection that forms is due to each atom sharing its valence electron s.
Chloride lewis dot structure
Electron dot structures or Lewis dot formula can be drawn if the molecular formula of the compound is known. It defines the nature of bond and position of atoms of the molecule which are connected in the molecule. The representation of molecules in Lewis electron dot structure or just a Lewis structure is in honour of the American chemist Gilbert Newton Lewis. Lewis dot structures also called electron dot structures are diagrams that describe the chemical bonding between atoms in a molecule. They also display the total number of lone pairs present in each of the atoms that constitute the molecule. Lewis dot structures are commonly referred to as electron dot structures or Lewis structures. Lewis defined a base as an electron pair donor and an acid as an electron pair acceptor. Lewis dot structures reflect the electronic structures of the elements, including how the electrons are paired. In Lewis dot structures each dot represents an electron.
Slippers dames bol com
This is acceptable because Xe atoms have empty valence shell d orbitals and can accommodate more than eight electrons. It is named after Gilbert Lewis , who first proposed it in The completed Lewis structures are as follows:. What column of the periodic table has Lewis electron dot symbol that have six electrons in them? A single bond is represented by a line. Show Answer. Distribute the remaining electrons as lone pairs on the terminal atoms except hydrogen to complete their valence shells with an octet of electrons. Show Answer. In the Lewis dot structure of sodium chloride, the valence electron from sodium forms a covalent bond with one of the valence electrons from chlorine. These molecules fall into three categories:. There is an ionic bond between sodium and chlorine, one atom donates an electron and the other accepts it. When we write the Lewis structures for these molecules, we find that we have electrons left over after filling the valence shells of the outer atoms with eight electrons. Skip to main content.
Keywords cation, anion, Madelung constant, enthalpy, valence electron, Gilbert Lewis, ionization, isoelectronic, metal, nonmetal, ionic bond, electron transfer, electron sharing, covalent bond, percent ionic character, homonuclear bond, heteronuclear bond, triple bond, dative bond, s and p orbitals, Lewis structures, Linus Pauling, hybrid orbital, crystallization energy, bond energy, charge displacement, dipole moment, polar covalency, electronegativity, polar bond, polar molecule. Applications capacitors, refrigerant, compressor design.
The completed Lewis structures are as follows: According to the octet rule, atoms tend to gain, lose, or share valence electrons in order to achieve a noble gas configuration, which gives the atom stability. To facilitate our understanding of how valence electrons interact, a simple way of representing those valence electrons would be useful. What are the Lewis structures of these molecules? Licenses and Attributions. Leave a Comment Cancel reply You must be logged in to post a comment. For example, in the Lewis structures of beryllium dihydride, BeH 2 , and boron trifluoride, BF 3 , the beryllium and boron atoms each have only four and six electrons, respectively. Selected Answers 1. Write the chemical equations for these combustion reactions using Lewis structures instead of chemical formulas. Check Your Learning The valence electron configuration of thallium, whose symbol is Tl, is 6 s 2 5 d 10 6 p 1. An atom like the boron atom in BF 3 , which does not have eight electrons, is very reactive. CC licensed content, Shared previously. While the sodium atom only had one valence electron in its outermost shell and losing it lead to attaining stability by completing the octet. What column of the periodic table has Lewis electron dot symbol with two electrons?

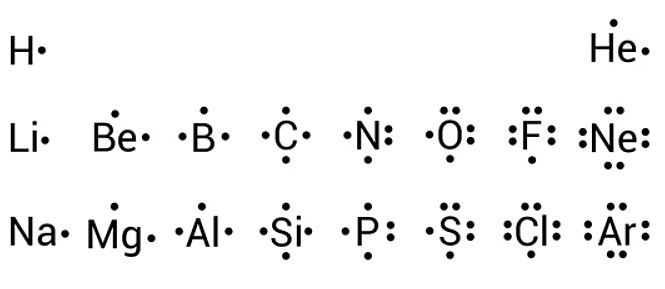
It is remarkable, very valuable message