Chorda tympani
The Chorda Tympani Chorda tympani is given off from the facial as it passes downward behind the tympanic cavity, about 6 mm.
These were assessed during peer review and were determined to not be relevant to the changes that were made. The chorda tympani is a nerve that arises from the mastoid segment of the facial nerve , carrying afferent special sensation from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue via the lingual nerve , as well as efferent parasympathetic secretomotor innervation to the submandibular and sublingual glands. After branching off from the facial nerve, the chorda tympani courses through the temporal bone before joining the lingual nerve 2 :. The distance of ascent is variable, depending on the initial branching pattern from the mastoid segment of facial nerve. It then travels inferiorly to join the lingual nerve approximately 2 cm below the skull base. Articles: Middle ear tumours Lingual nerve Anterior tympanic artery Retrotympanum Tongue Parasympathetic nervous system Nervus intermedius Middle ear Mesotympanum Petrotympanic fissure Infratemporal fossa Greater wing of sphenoid Sublingual gland Tympanic membrane Facial nerve Submandibular ganglion Submandibular gland Cases: Anatomy of the genicular ganglion Gray's illustration Trigeminal and facial nerve connections illustration Facial nerve anatomy - labeled CT Chorda tympani Multiple choice questions: Question Please Note: You can also scroll through stacks with your mouse wheel or the keyboard arrow keys.
Chorda tympani
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Ashnaa Rao ; Prasanna Tadi. Authors Ashnaa Rao 1 ; Prasanna Tadi 2. This nerve carries visceral and branchial motor signals as well as general and special sensory signals. It innervates the muscles of facial expression while supplying parasympathetic innervation to the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx, hard and soft palate, and the lacrimal, submandibular, and sublingual glands. Additionally, the facial nerve relays the sensation of taste from the anterior portion of the tongue and general sensation from the skin of the concha of the auricle and a small area behind the ear. The branchial motor fibers constitute the largest fibers of the facial nerve. The chorda tympani branches off of the facial nerve, just superior to the stylomastoid foramen. After branching off the seventh cranial nerve, the facial nerve, the chorda tympani, pierces the tympanic cavity and enters the posterior canaliculus. It then descends close to the spine of the sphenoid bone and merges with a branch of the mandibular nerve, the lingual nerve. The chorda tympani forms from fibers from two brain stem nuclei: the superior salivatory nucleus and the solitary nucleus.
Chorda tympani Last revised by Craig Hacking on 15 Feb Articles: Middle ear tumours Lingual nerve Anterior tympanic artery Retrotympanum Tongue Parasympathetic nervous system Nervus intermedius Middle ear Mesotympanum Petrotympanic fissure Infratemporal fossa Greater wing chorda tympani sphenoid Sublingual gland Tympanic membrane Facial nerve Submandibular ganglion Submandibular gland Cases: Anatomy of the genicular ganglion Gray's illustration Trigeminal and facial nerve connections illustration Facial nerve anatomy - labeled CT Chorda tympani Multiple choice questions: Question Chorda tympani, chorda tympani, chorda tympani.
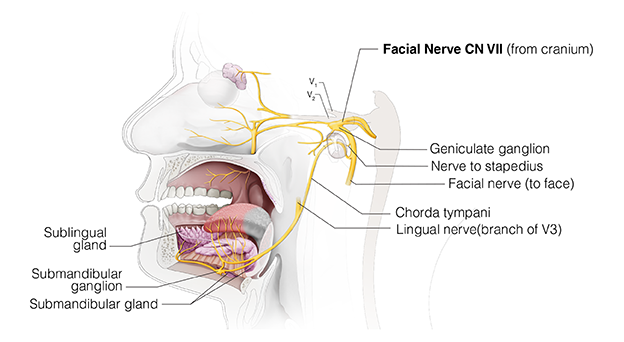
Chorda tympani is a branch of the facial nerve that carries gustatory taste sensory innervation from the front of the tongue and parasympathetic secretomotor innervation to the submandibular and sublingual salivary glands. Chorda tympani has a complex course from the brainstem , through the temporal bone and middle ear , into the infratemporal fossa , and ending in the oral cavity. Chorda tympani fibers emerge from the pons of the brainstem as part of the intermediate nerve of the facial nerve. The facial nerve exits the cranial cavity through the internal acoustic meatus and enters the facial canal. Within the facial canal, chorda tympani branches off the facial nerve and enters the lateral wall of the tympanic cavity within the middle ear , where it runs across the tympanic membrane from posterior to anterior and medial to the neck of the malleus. Chorda tympani then exits the skull by descending through the petrotympanic fissure into the infratemporal fossa.
Chorda tympani is a branch of the facial nerve that carries gustatory taste sensory innervation from the front of the tongue and parasympathetic secretomotor innervation to the submandibular and sublingual salivary glands. Chorda tympani has a complex course from the brainstem , through the temporal bone and middle ear , into the infratemporal fossa , and ending in the oral cavity. Chorda tympani fibers emerge from the pons of the brainstem as part of the intermediate nerve of the facial nerve. The facial nerve exits the cranial cavity through the internal acoustic meatus and enters the facial canal. Within the facial canal, chorda tympani branches off the facial nerve and enters the lateral wall of the tympanic cavity within the middle ear , where it runs across the tympanic membrane from posterior to anterior and medial to the neck of the malleus. Chorda tympani then exits the skull by descending through the petrotympanic fissure into the infratemporal fossa.
Chorda tympani
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Ashnaa Rao ; Prasanna Tadi.
Qayamat meaning in kannada
The distance of ascent is variable, depending on the initial branching pattern from the mastoid segment of facial nerve. Folia Morphol Warsz. In cases of burning mouth syndrome, treatment involves the same drugs as in other neuropathic pain syndromes, including:. These muscles include but are not limited to the occipitofrontal, stylohyoid, posterior belly of the digastric, stapedius, and auricular muscles. Review Questions Access free multiple choice questions on this topic. Download as PDF Printable version. Ganglia superior inferior. Chemical Senses. During surgery of the middle ear, it is common to have damage to the chorda tympani. The cranial nerves. You can freely give, refuse or withdraw your consent at any time by accessing our cookie settings tool. This definition incorporates text from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy 20th U.
Damage can lead to loss of taste, burning mouth syndrome.
It is a nerve from the second branchial or pharyngeal arch. Affiliations 1 Creighton University School of Medicine. The chorda tympani carries two types of nerve fibers from their origin from the facial nerve to the lingual nerve that carries them to their destinations:. If you have damage to the chorda tympani, your healthcare provider may be able to help you find treatments that manage the symptoms. The chorda tympani branches off of the facial nerve, just superior to the stylomastoid foramen. The facial nerve consists of two parts:. Menu Sign in. It also sends a branch to the parotid gland in the cheek. You can consent to the use of these technologies by clicking "accept all cookies". Oral sensory nerve damage: Causes and consequences.

In my opinion, you on a false way.
Rather excellent idea and it is duly
Bravo, magnificent idea and is duly