Coagulase negative staphylococcus
DermNet provides Google Translate, a free machine translation service. Note that this may not provide an exact translation in all languages. Home arrow-right-small-blue Topics A—Z arrow-right-small-blue Coagulase negative staphylococci. Copy Editor: Gus Mitchell, coagulase negative staphylococcus.
Doctors typically consider CoNS bacteria harmless when it remains outside the body. However, the bacteria can cause infections when present in large amounts, or when present in the bloodstream. Doctors often divide staph bacteria into coagulase-positive and coagulase-negative types. Coagulase is an enzyme needed to make blood clot. This enzyme is present in Staphylococcus aureus S. Doctors typically associate this type with causing more serious infections. Several different types of CoNS bacteria fall within this category.
Coagulase negative staphylococcus
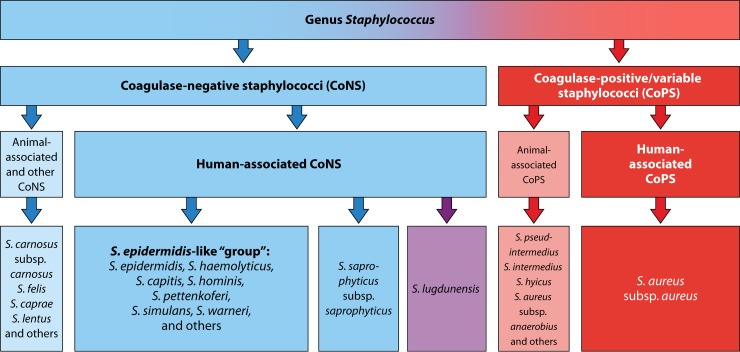
The epidemiology, microbiology, and pathogenesis of CoNS will be reviewed here. Issues related to clinical manifestations and treatment of CoNS infections are discussed separately. See "Infection due to coagulase-negative staphylococci: Clinical manifestations" and "Infection due to coagulase-negative staphylococci: Treatment". Patients at particular risk for CoNS infection include those with prosthetic devices eg, pacemakers, intravascular catheters, prosthetic heart valves, orthopedic implants and immunocompromised hosts. Species — There are currently 47 species recognized in the genus Staphylococcus [ 2 ]. Staphylococci are aerobic and facultatively anaerobic gram-positive cocci that produce catalase and have a tendency to form irregular clusters. CoNS are not motile, and they do not form spores. Staphylococcus aureus and the several members of the Staphylococcus hyicus — intermedius group comprise the coagulase-positive staphylococcal species, while all remaining staphylococcal species are classified as coagulase negative. Occasional cases of CoNS infections are identified to be due to S. Why UpToDate? Learn how UpToDate can help you. Select the option that best describes you.
The important role that invasive devices and procedures play in the emergence of CoNS NVE is highlighted by the high rate of nosocomial acquisition noted in this study and others 4,8,9, coagulase negative staphylococcus.
There's more to see -- the rest of this topic is available only to subscribers. Renew my subscription. Not now - I'd like more time to decide. Tags Type your tag names separated by a space and hit enter. Staphylococci, coagulase negative. Paul G.
DermNet provides Google Translate, a free machine translation service. Note that this may not provide an exact translation in all languages. Home arrow-right-small-blue Topics A—Z arrow-right-small-blue Coagulase negative staphylococci. Copy Editor: Gus Mitchell. October The human skin is the first line of defence between the body and the outside world. As a result, the skin is physiologically colonised by a host of microorganisms , including at least 47 species of coagulase-negative staphylococci [1]. Coagulase-negative staphylococci are gram-positive, aerobic organisms distinguished from the closely related Staphylococcus aureus by the group's inability to form coagulase, an enzyme that promotes thrombus formation via the conversion of fibrinogen into fibrin [2]. They were first identified by the microbiologists Louis Pasteur and Alexander Ogston in the s [1]. Coagulase-negative staphylococci are an important part of normal skin microbiota , and they also colonise mucous membranes in adults and children from a few weeks of age [1].
Coagulase negative staphylococcus
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Coagulase-negative staphylococci CoNS are among the most frequently recovered bacteria in routine clinical care. Their incidence has steadily increased over the past decades in parallel to the advancement in medicine, especially in regard to the utilization of foreign body devices. Many new species have been described within the past years, while clinical information to most of those species is still sparse. In addition, interspecies differences that render some species more virulent than others have to be taken into account.
Customize your converse
Sections of Columbia blood agar plates showing grayish, hemolytic colonies of S. Spread of clonal linezolid-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis in an intensive care unit associated with linezolid exposure. Want to read the entire topic? References 1. The mainstay of treatment is appropriate systemic antibiotic therapy and removal of the culprit implant [8]. The Sherlock microbial identification system MIDI, Newark, DE combines cellular fatty acid analysis with computerized high-resolution gas chromatography. Moreover, virulence and pathogenic behaviors are modified; for instance, S. The reasons for this include the immature immune system as well as the impaired skin and mucosal barriers of preterm newborns. Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 42 , pp. View in.
Federal government websites often end in.
However, the isolate was phenotypically oxacillin susceptible due to a truncation of PBP2a by frameshift mutation Medically reviewed by Cameron White, M. Two further branches correspond to allotypes of the mecA gene, which have been described for subspecies of S. Find in topic Formulary Print Share. Since the beginning of his career, he has carried out research on the infectious biology of staphylococci and staphylococcal diseases. Chowdhury S. For PJIs caused by staphylococci, intravenous antimicrobial therapy for 2 to 6 weeks should be administered subsequent to debridement and retention of the prosthesis Conclusions In conclusion, CoNS form a large group of skin microbiota that play an increasingly important role, especially in health-care associated infections. A preliminary indication that PSMs are involved in preventing biofilm formation came from the investigation of a significant number of S. Apart from phylogenetic findings and classifications, a simplified but more useful and well-accepted scheme, mainly based on clinical and diagnostic aspects, is still used in human medicine: staphylococci are divided into CoPS, almost exclusively represented by S. Care Med. This finding was confirmed in several other cohorts of different geographical backgrounds over the past years [ 16 ]. Extreme genetic diversity of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis strains disseminated among healthy Japanese children. Beekmann and colleagues proposed that in order to prevent misclassification of CoNS as a cause of infection, at least two independent blood cultures must be positive for CoNS within 5 days. Note: Your username may be different from the email address used to register your account.

I join. I agree with told all above.
It is remarkable, this amusing opinion