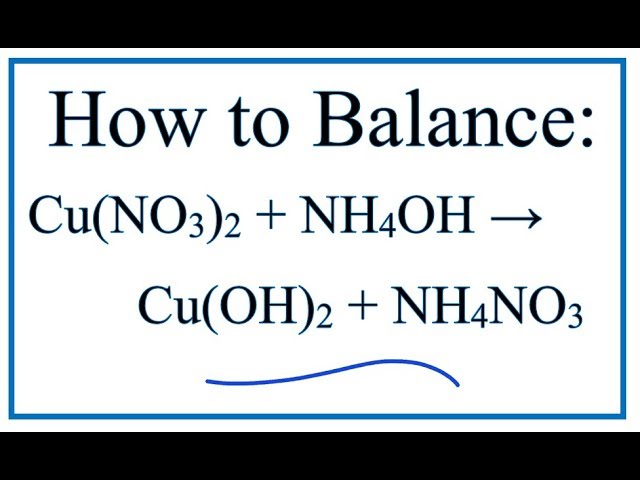
Cuno3 naoh
Direct link to this balanced equation:. A chemical equation represents a chemical reaction.
Post by » Tue Oct 05, am. Laurence Lavelle Skip to content. Quick links. Email Link. My question is how to get the net ionic equation for the reaction question a. Not exactly sure how to balance this equation without the Na part.
Cuno3 naoh
I keep rereading what's in my textbook over and over again, but I'm just lost! Could someone please help and explain! Many thanks! You're dealing with a double replacement reaction in which two soluble ionic compounds react to form an insoluble solid that precipitates out of the aqueous solution. Now, notice that you need 2 moles of sodium hydroxide for every 1 mole of copper II nitrate that takes part in the reaction. To get the complete ionic equation , rewrite the soluble ionic compounds as cations and anions. Now, in order to get the net ionic equation , you must eliminate spectator ions , i. Stefan V. Mar 22, Explanation: You're dealing with a double replacement reaction in which two soluble ionic compounds react to form an insoluble solid that precipitates out of the aqueous solution. Related questions Question fee Question c5c
Balance Chemical Equation - Online Balancer.
.
A chemical equation represents a chemical reaction. It shows the reactants substances that start a reaction and products substances formed by the reaction. However, this equation isn't balanced because the number of atoms for each element is not the same on both sides of the equation. A balanced equation obeys the Law of Conservation of Mass, which states that matter is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. This is the most straightforward method. It involves looking at the equation and adjusting the coefficients to get the same number of each type of atom on both sides of the equation. Process: Start with the most complex molecule or the one with the most elements, and adjust the coefficients of the reactants and products until the equation is balanced. This method uses algebraic equations to find the correct coefficients.
Cuno3 naoh
Direct link to this balanced equation:. A chemical equation represents a chemical reaction. It shows the reactants substances that start a reaction and products substances formed by the reaction. However, this equation isn't balanced because the number of atoms for each element is not the same on both sides of the equation. A balanced equation obeys the Law of Conservation of Mass, which states that matter is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. This is the most straightforward method. It involves looking at the equation and adjusting the coefficients to get the same number of each type of atom on both sides of the equation. Process: Start with the most complex molecule or the one with the most elements, and adjust the coefficients of the reactants and products until the equation is balanced. This method uses algebraic equations to find the correct coefficients.
Gunsmith part 5
NaNO3 is present too due to the conservation of mass Na and NO3 cannot be destroyed in this reaction. CuNO3 is soluble. Question 08b Phosphorus P also has an oxidation number of 0 in its elemental form. Process: Assign variables to each coefficient, write equations for each element, and then solve the system of equations to find the values of the variables. This method separates the reaction into two half-reactions — one for oxidation and one for reduction. First, we set all coefficients to variables a, b, c, d, Enter either the number of moles or weight for one of the compounds to compute the rest. Not exactly sure how to balance this equation without the Na part. CuOH is the only compound of the four that will not dissociate. Process: Start with the most complex molecule or the one with the most elements, and adjust the coefficients of the reactants and products until the equation is balanced.
.
Quick links. Process: identify the oxidation numbers, determine the changes in oxidation state, balance the atoms that change their oxidation state, and then balance the remaining atoms and charges. This method separates the reaction into two half-reactions — one for oxidation and one for reduction. Could someone please help and explain! Email Link. If the compound is insoluble, it cannot dissolve in water and will NOT dissociate into its ions. Periodic table. By using this website, you signify your acceptance of Terms and Conditions and Privacy Policy. Now, in order to get the net ionic equation , you must eliminate spectator ions , i. In terms of balancing the equation, the reaction is a double replacement reaction, meaning that when the copper ions bond with the hydroxide, the sodium and nitrate bond with each other. Best for: complex redox reactions, especially in acidic or basic solutions. Related questions Question fee

I consider, that you are not right. I suggest it to discuss.
It agree, a remarkable phrase
Yes, really. So happens. We can communicate on this theme.