Depressive attributional style
Depressive attributional style ; Explanatory style ; Negative attributional style ; Optimistic attributional style ; Pessimistic attributional style ; Positive attributional depressive attributional style. Attributional style, sometimes known as explanatory style, refers to the ways in which people explain the cause of events within their lives.
How do you view positive and negative life events? Perhaps you blame yourself when faced with failure while never giving yourself credit for the good. In the face of adversity, can you see past the present moment and know that things will get better? The way you attribute and explain positive and negative events to yourself can impact your life in ways you may not realize. Before you read on, we thought you might like to download our three Positive Psychology Exercises for free. These science-based exercises will explore fundamental aspects of positive psychology including strengths, values, and self-compassion, and will give you the tools to enhance the wellbeing of your clients, students, or employees. In psychology, the term attribution has two predominant meanings.
Depressive attributional style
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Individuals seeking treatment for depression often are struggling with maladaptive cognitions that impact how they view themselves and the world. Research on cognitive attributions that underlie depressed mood focuses on the phenomenon of negative cognitive style, in which depressed people tend to view undesirable occurrences in life as having internal, stable, and global causes. Based on research, clinicians have developed various techniques that seek to modify depressive attributions in order to alleviate symptoms of depression. In this article, the authors review the literature on attributions in depression, present clinically relevant interventions based on empirical support, provide case examples, and summarize future directions and recommendations for researchers and practitioners. Two employees at the same company are fired from their jobs. This begs the question, why do these two people have such different thoughts about and emotional reactions to the same life experience? Attribution theories of depression were formulated to answer these questions, and in the process better understand the etiology and maintenance of depression. These theories posit that the ways in which individuals interpret life events contributes to their mood state and to the likelihood that they will experience clinical depression.
Keng, S.
We administrated measures of attributional styles and psychological adjustments to a sample of Chinese Buddhists as well as a control group recruited in China. Data analyses showed that Buddhists were more likely to attribute bad outcomes to internal, stable, and global causes, but their well-being was less affected by it. Forty years ago, Seligman proposed the learnt helplessness model of depression, which proposed that control over the environment is a fundamental need for any organism, and if one is repeatedly exposed to unavoidable painful stimuli, one will come to expect that such events are uncontrollable and develop hopelessness and depression as a result Hiroto and Seligman, This model was later reformulated to the Attributional Style theory Abramson et al. Initial empirical support for these theoretical propositions has been mixed Coyne and Gotlib, For example, Zuroff found that while depressed participants made more internal attributions for failure than non-depressed participants, in absolute terms, they still favored external over internal attributions for failure.
We administrated measures of attributional styles and psychological adjustments to a sample of Chinese Buddhists as well as a control group recruited in China. Data analyses showed that Buddhists were more likely to attribute bad outcomes to internal, stable, and global causes, but their well-being was less affected by it. Forty years ago, Seligman proposed the learnt helplessness model of depression, which proposed that control over the environment is a fundamental need for any organism, and if one is repeatedly exposed to unavoidable painful stimuli, one will come to expect that such events are uncontrollable and develop hopelessness and depression as a result Hiroto and Seligman, This model was later reformulated to the Attributional Style theory Abramson et al. Initial empirical support for these theoretical propositions has been mixed Coyne and Gotlib, For example, Zuroff found that while depressed participants made more internal attributions for failure than non-depressed participants, in absolute terms, they still favored external over internal attributions for failure.
Depressive attributional style
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October Learn More or Try it out now. Individuals seeking treatment for depression often are struggling with maladaptive cognitions that impact how they view themselves and the world. Research on cognitive attributions that underlie depressed mood focuses on the phenomenon of negative cognitive style, in which depressed people tend to view undesirable occurrences in life as having internal, stable, and global causes. Based on research, clinicians have developed various techniques that seek to modify depressive attributions in order to alleviate symptoms of depression.
Brimstone lineups haven
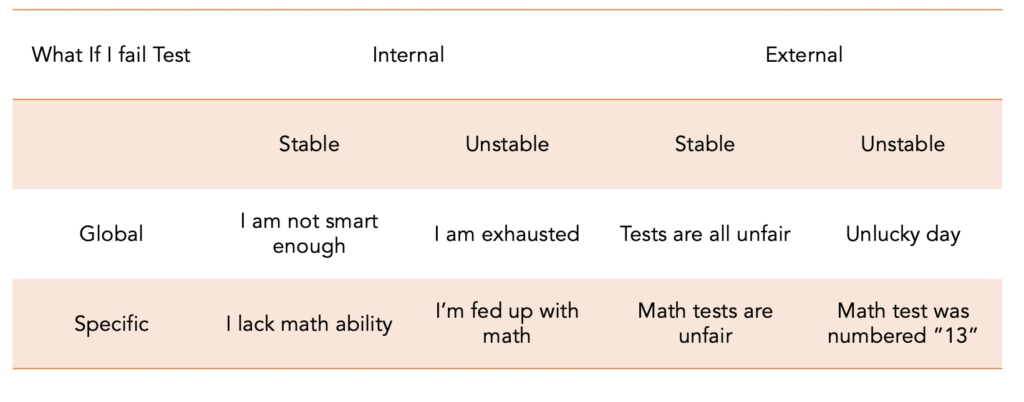
Michael the pessimist meets with his directors and they are impressed with his idea. New York: Wiley; One of the authors recently began therapy with a client in his 60s--whom we shall call Paul--who complained of a life-long history of relatively intractable depression. By taking steps to engage in activities, clients can begin to notice how acting contrary to negative attributions e. The literature has continued to expand, enhancing our understanding of the role of attributions in the onset and course of depression. It examines what information is gathered and how it is combined to form a causal judgment. Developmental antecedents of cognitive vulnerability to depression: Review of findings from the cognitive vulnerability to depression project. Developmental origins of cognitive vulnerabilities to depression: Review of processes contributing to stability and change across time. The goal is for the client to grasp that it is not the facts themselves that drive the story he tells, but rather something more internal and automatic — a narrative that is colored by a pervasive depressive attributional style. Data analyses showed that Buddhists were more likely to attribute bad outcomes to internal, stable, and global causes, but their well-being was less affected by it. Kaslow, N. A pessimistic explanatory style is characterized by explanations of the causes of negative outcomes as being stable, global, and internal, and the causes of positive outcomes as being unstable, specific and external in nature.
The way you explain an occurrence in your life is known as attributional style, which can affect your well-being. When something positive or negative happens in our lives, we often seek to explain its occurrence.
Related to attributional biases, the notion that individuals with depression tend to have negative interpretations of ambiguous information and attentional biases towards threatening stimuli forms the basis of the experimental paradigms used to change these tendencies.. The way you attribute and explain positive and negative events to yourself can impact your life in ways you may not realize. The relationship between explanatory style, locus of control and self-esteem in university subjects. They personally blame themselves for bad events and perceive the root cause to be a fixed factor. Journal of applied psychology, 46, Seligman, M. The general patterns of responses that are given can then be used to make diagnoses or predictions. The CASQ is a forced-response questionnaire consisting of 48 hypothetically good or bad scenarios 24 positive and 24 negative involving the child, followed by two statements detailing possible explanations. Recent statistics suggest that over a quarter of UK nationals feel a deep sense of meaninglessness Dinic, The publisher's final edited version of this article is available at J Psychother Integr.

0 thoughts on “Depressive attributional style”