Draw position time graph for uniform motion
Our study of 1-dimensional kinematics has been concerned with the multiple means by which the motion of objects can be represented.
One of the most elementary forms of graphs in kinematics is the Position-time graph , which helps us to define the motion of a body. In these graphs, the position of the object is represented by the vertical axis, the time elapsed is represented by the horizontal axis, and the dependent variable, that is position, depends on the independent variable, that is time. In this way, the graph expresses to us where the particle can be found after some time. These graphs help us visualise the path of objects. By studying a position-time graph for an object, we can analyse the path and position of an object precisely.
Draw position time graph for uniform motion
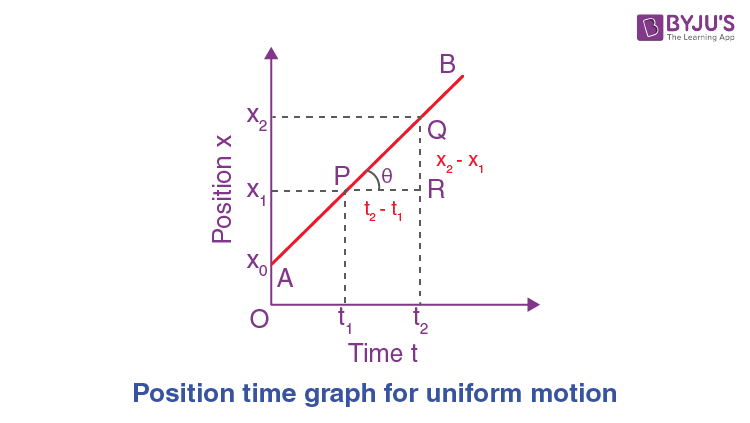
Position time Graph For Uniform Motion. Let us find out displacement for a body moving in uniform motion at a uniform velocity with zero acceleration. To find displacement ref above diagram. Steps to draw a position-time graph for uniform motion. Recommended Read: What is uniform motion? If you are wondering how? Congratulations, you have read the complete article about the position-time graph for uniform motion. If you have any doubts or queries, feel free to comment below. We will respond as soon as possible. Or Email Us At [email protected]. Any topic you want us to cover? Let us know. Your email address will not be published. Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Ferromagnetic Materials Examples.
Show that the slope of the position-time graph gives the velocity of the object. Draw the velocity-time graph for an object in uniform motion. Show that the area under the velocity-time graph gives the displacement of the object in the given time interval. Draw the x-t graph of an object in uniform motion. Draw the position-time graph of a stationary object. Draw the velocity-time graph for uniformly accelerated motion.
Forgot password? New user? Sign up. Existing user? Log in. Already have an account? Log in here. Position-time graphs are the most basic form of graphs in kinematics, which allow us to describe the motion of objects. In these graphs, the vertical axis represents the position of the object while the horizontal axis represents the time elapsed: the dependent variable, position, depends on the independent variable, time. In this way, the graph tells us where the particle can be found after some amount of time.
Draw position time graph for uniform motion
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos. Position-time graphs. About About this video Transcript. Using animations lets learn what position time graphs are, and how they help us figure out which objects are slower and faster. Created by Mahesh Shenoy. Want to join the conversation? Log in.
Common denominator calculator
Both graphs show plotted points forming a curved line. A distance-time graph represents the distance covered, that is the exact length of the actual path followed from the initial point to the final point, with respect to time. Draw the position-time graph of a stationary object. Watch Video Solution. The position-time x-t graph of an object in uniform motion is shown below, the velocity of object is i Positive ii Negative iii Zero iv None of these. For uniformly accelerated motion along a straight line the Position Time relation will be given as,. The object represented by the graph on the right is traveling faster than the object represented by the graph on the left. The given construction as shown in Fig. Draw the velocity-time graph for an object in uniform motion. Once you've practiced the principle a few times, it becomes a very natural means of analyzing position-time graphs. Watch Now.
The learning objectives in this section will help your students master the following standards:. It goes up ft, stops, and then falls back to the earth.
Negative slope of a position-time indicates the velocity of an object moving in the opposite direction. Application Of Rectifier. The position vs. As established earlier, the slope of the x-t graph signifies the velocity of an object. State The Law Of Reflection. Semiconductors Class A vertical line in a position-time graph would mean that an object is occupying more than one position at same time, hence, it is not possible. Both graphs show plotted points forming a curved line. Was this answer helpful? Position time graph for uniform motion starting at some point other than origin.

0 thoughts on “Draw position time graph for uniform motion”