Electrolytic cell diagram
Voltaic cells use a spontaneous chemical reaction to drive an electric current through an external circuit. These cells are important because they are the basis for the batteries that fuel modern society. But they aren't the only kind of electrochemical cell, electrolytic cell diagram. It is also possible to construct a cell electrolytic cell diagram does work on a chemical system by driving an electric current through the system.
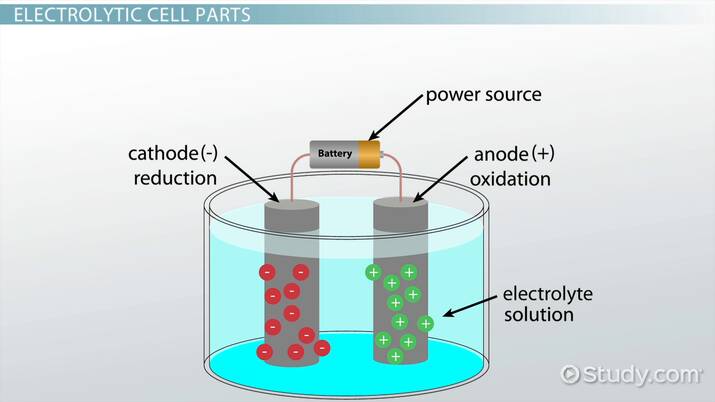
An electrolytic cell can be defined as an electrochemical device that uses electrical energy to facilitate a non-spontaneous redox reaction. Electrolytic cells are electrochemical cells that can be used for the electrolysis of certain compounds. For example, water can be subjected to electrolysis with the help of an electrolytic cell to form gaseous oxygen and gaseous hydrogen. This is done by using the flow of electrons into the reaction environment to overcome the activation energy barrier of the non-spontaneous redox reaction. The electrolyte provides the medium for the exchange of electrons between the cathode and the anode. Commonly used electrolytes in electrolytic cells include water containing dissolved ions and molten sodium chloride. Click here to learn more about the difference between Galvanic cells and electrolytic cells.
Electrolytic cell diagram
A cell is a device capable of producing electrical energy from chemical reactions or employing electrical energy to bring about a chemical reaction. So, cells can be grouped into two major categories: one that produces electrical energy from chemical reactions and another that uses electrical energy to bring about a chemical reaction. While the former is called a galvanic or voltaic cell, the latter is an electrolytic cell. Both electrolytic and galvanic cells operate differently. The following table enumerates the key differences between electrolytic cells vs galvanic cells. However, both cells contain two half-cells for a net-redox reaction with reduction and oxidation. In both cells, oxidation occurs at the anode and reduction at the cathode. An electrolytic cell is a device designed to utilize electrical energy and facilitate a non-spontaneous redox reaction. Thus, electrical energy is converted to chemical energy via the process of electrolysis. The process involving the passage of electric current from an external source into a solution of electrolyte is called electrolysis. An electrolytic cell is suitable for the electrolysis of certain compounds such as water when subjected to electrolysis forms gaseous hydrogen and oxygen. The following electrolytic cell diagram shows the primary components of an electrolytic cell see figure 1. An electrolytic cell has an electrolytic tank made of a non-conducting material such as bakelite or glass. The solution to be electrolysed electrolyte is filled in the tank. The electrolyte can be in the form of a solution or a fused state.
Here, the anode is positive and cathode is the negative electrode. Are you sure you want to logout?
Home 9. Reactions are spontaneous and exothermic. Electrolytic Cells — convert electrical to chemical energy. Non spontaneous. By convention, anode is always of left, and cathode on right. These two are separated, connected only by a salt bride. This is the voltage generated when two different solutions come into contact with each other Salt bridge contains a concentrated solution of a strong electrolyte.
In , two scientists announced that they had achieved "cold fusion", the process of fusing together elements at essentially room temperature to achieve energy production. The hypothesis was that the fusion would produce more energy than was required to cause the process to occur. Their process involved the electrolysis of heavy water water molecules containing some deuterium instead of normal hydrogen on a palladium electrode. The experiments could not be reproduced and their scientific reputations were pretty well shot. However, in more recent years, both industry and government researchers are taking another look at this process.
Electrolytic cell diagram
Voltaic cells are driven by a spontaneous chemical reaction that produces an electric current through an outside circuit. These cells are important because they are the basis for the batteries that fuel modern society. But they are not the only kind of electrochemical cell. The reverse reaction in each case is non-spontaneous and requires electrical energy to occur. It is possible to construct a cell that does work on a chemical system by driving an electric current through the system. These cells are called electrolytic cells. Electrolytic cells, like galvanic cells, are composed of two half-cells--one is a reduction half-cell, the other is an oxidation half-cell. The direction of electron flow in electrolytic cells, however, may be reversed from the direction of spontaneous electron flow in galvanic cells, but the definition of both cathode and anode remain the same, where reduction takes place at the cathode and oxidation occurs at the anode. Because the directions of both half-reactions have been reversed, the sign, but not the magnitude, of the cell potential has been reversed.
Context clues worksheets
So, cells can be grouped into two major categories: one that produces electrical energy from chemical reactions and another that uses electrical energy to bring about a chemical reaction. If all four of these factors are accounted for, we can successfully predict electrode half reactions and overall reactions in electrolysis. Download Now. Sodium Carbonate Formula. Watch Now. Thus, molten sodium chloride can be subjected to electrolysis in an electrolytic cell to generate metallic sodium and chlorine gas as the products. Electrolytic cells are electrochemical cells that can be used for the electrolysis of certain compounds. They move from anode to the cathode in the external circuit. In this equation I represents current and t represents time. The following table enumerates the key differences between electrolytic cells vs galvanic cells. What is an Electrolytic Cell? The reactants may be in nonstandard conditions which means that the voltage for the half cells may be less or more than the standard condition amount. A galvanic cell left transforms the energy released by a spontaneous redox reaction into electrical energy that can be used to perform work. Click here to check your answer to Practice Problem 13 Click here to see a solution to Practice Problem
An electrolytic cell can be defined as an electrochemical device that uses electrical energy to facilitate a non-spontaneous redox reaction.
The direction of electron flow in electrolytic cells, however, may be reversed from the direction of spontaneous electron flow in galvanic cells, but the definition of both cathode and anode remain the same, where reduction takes place at the cathode and oxidation occurs at the anode. Electrochemistry Electrochemical Reactions Electrolytic Cells. What are the criteria for product formation during electrolysis? An electrolytic cell is suitable for the electrolysis of certain compounds such as water when subjected to electrolysis forms gaseous hydrogen and oxygen. The solution to be electrolysed electrolyte is filled in the tank. Here, the anode is positive and cathode is the negative electrode. The potential for oxidation of this ion to the peroxydisulfate ion is Food Chemistry. What would happen if we added an indicator such as bromothymol blue to this apparatus? Following are some useful applications of an electrolytic cell: 1. The zinc half-cell acts as the anode.

I would not wish to develop this theme.
No, opposite.