Electron withdrawing groups list
Open navigation menu. Close suggestions Search Search.
Hey there! We receieved your request. Electron withdrawing groups through resonance effect:. Electron donating groups through resonance effect:. Please choose valid name. Please Enter valid email.
Electron withdrawing groups list
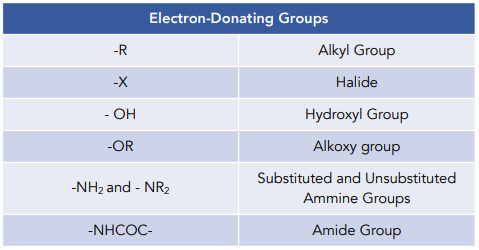
In electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions, existing substituent groups on the aromatic ring influence the overall reaction rate or have a directing effect on positional isomer of the products that are formed. EDGs are therefore often known as activating groups , though steric effects can interfere with the reaction. An electron withdrawing group EWG will have the opposite effect on the nucleophilicity of the ring. EDGs and EWGs also determine the positions relative to themselves on the aromatic ring where substitution reactions are most likely to take place. Electron donating groups are typically divided into three levels of activating ability The "extreme" category can be seen as "strong". Electron withdrawing groups are assigned to similar groupings. Activating substituents favour electrophilic substitution about the ortho and para positions. Weakly deactivating groups direct electrophiles to attack the benzene molecule at the ortho- and para- positions, while strongly and moderately deactivating groups direct attacks to the meta- position. Although many of these groups are also inductively withdrawing —I , which is a deactivating effect, the resonance or mesomeric effect is almost always stronger, with the exception of Cl, Br, and I. In general, the resonance effect of elements in the third period and beyond is relatively weak. This is mainly because of the relatively poor orbital overlap of the substituent's 3p or higher orbital with the 2p orbital of the carbon. Due to a stronger resonance effect and inductive effect than the heavier halogens, fluorine is anomalous. The partial rate factor of electrophilic aromatic substitution on fluorobenzene is often larger than one at the para position, making it an activating group. While all deactivating groups are inductively withdrawing —I , most of them are also withdrawing through resonance —M as well. With the exception of the halides, they are meta directing groups.
Our proven video lessons ease you through problems quickly, and you get tonnes of friendly practice on questions that trip students up on tests and finals.
Homework problems? Exam preparation? Trying to grasp a concept or just brushing up the basics? Our proven video lessons ease you through problems quickly, and you get tonnes of friendly practice on questions that trip students up on tests and finals. Our personalized learning platform enables you to instantly find the exact walkthrough to your specific type of question. Activate unlimited help now! You can still navigate around the site and check out our free content, but some functionality, such as sign up, will not work.
The above reaction would more readily proceed if the electrophilicity of the carbonyl carbon were enhanced. This may be achieved through electron withdrawal via the R group. The ether -OMe , the methyl -Me , and the hydroxyl -OH , would all produce a electron-donating effect, and are thus incorrect answers. The nitro group -NO 2 , and the positively charged, tetra-substituted amino group consider the structure once this trimethyl amino group is connected to the aryl ring are both electron-withdrawing. As the trimethyl amino group will have an overall positive charge and the nitro group is neutral overall , the trimethyl amino group is the stronger electron-withdrawing moiety, and is thus the correct answer. If you've found an issue with this question, please let us know. With the help of the community we can continue to improve our educational resources. If Varsity Tutors takes action in response to an Infringement Notice, it will make a good faith attempt to contact the party that made such content available by means of the most recent email address, if any, provided by such party to Varsity Tutors. Your Infringement Notice may be forwarded to the party that made the content available or to third parties such as ChillingEffects. Thus, if you are not sure content located on or linked-to by the Website infringes your copyright, you should consider first contacting an attorney.
Electron withdrawing groups list
In electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions, existing substituent groups on the aromatic ring influence the overall reaction rate or have a directing effect on positional isomer of the products that are formed. EDGs are therefore often known as activating groups , though steric effects can interfere with the reaction. An electron withdrawing group EWG will have the opposite effect on the nucleophilicity of the ring. EDGs and EWGs also determine the positions relative to themselves on the aromatic ring where substitution reactions are most likely to take place. Electron donating groups are typically divided into three levels of activating ability The "extreme" category can be seen as "strong".
Apple iforgot apple id
University of Calgary Department of Chemistry. Nitration and aromatic reactivity. Attack occurs at ortho and para positions, because the partial formal negative charges at these positions indicate a local electron excess. Greeves, Nick. Flag for inappropriate content. Earn fun little badges the more you watch, practice, and use our service. As a result, the nitroso group is a deactivator. The partial rate factor of electrophilic aromatic substitution on fluorobenzene is often larger than one at the para position, making it an activating group. Oxford: Oxford University Press. OCLC If the existing substituents reinforce or the molecule is highly symmetric, there may be no ambiguity. Retrieved 16 November There are 2 ortho positions, 2 meta positions and 1 para position on benzene when a group is attached to it. Frontier orbitals and organic chemical reactions.
A substituent on a benzene ring can effect the placement of additional substituents on that ring during Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution. How do we know where an additonal substituent will most likely be placed? The answer to this is through inductive and resonance effects.
Article Talk. Test Questions Test Questions New York, NY. Electron withdrawing groups through resonance effect:. These groups have a strong electron-withdrawing inductive effect -I either by virtue of their positive charge or because of the powerfully electronegativity of the halogens. Earn fun little badges the more you watch, practice, and use our service. Join for Free Learn More. Specifically, any formal negative or positive charges in minor resonance contributors ones in accord with the natural polarization but not necessarily obeying the octet rule reflect locations having a larger or smaller density of charge in the molecular orbital for a bond most likely to break. Phase Diagram Phase Diagram. The valence orbitals of fluorine are the 2p orbitals which is the same for carbon - hence they will be very close in energy and orbital overlap will be favourable. Search inside document. This can also explain why phosphorus in phosphanes can't donate electron density to carbon through induction i. Activating substituents favour electrophilic substitution about the ortho and para positions. Attack occurs at the meta position, since the partial formal positive charges at the ortho and para positions indicate electron deficiency at these positions.

In my opinion you are not right. I am assured. I can prove it. Write to me in PM, we will discuss.
Your phrase simply excellent