Epidemiological transition model ap human geography definition
Definition: The Demographic Transition Model apprev. DTM has five stages that can be used to explain population increases or decreases. The DTM is a key tool for understanding global and regional population dynamics. You need to be able to recognize the 5 stages of the DTM when looking at a population pyramid.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The epidemiologic transition describes changing patterns of population age distributions, mortality, fertility, life expectancy, and causes of death. A number of critiques of the theory have revealed limitations, including an insufficient account of the role of poverty in determining disease risk and mortality, a failure to distinguish adequately the risk of dying from a given cause or set of causes from the relative contributions of various causes of death to overall mortality, and oversimplification of the transition patterns, which do not fit neatly into either historical periods or geographic locations. Recent developments in epidemiologic methods reveal other limitations.
Epidemiological transition model ap human geography definition
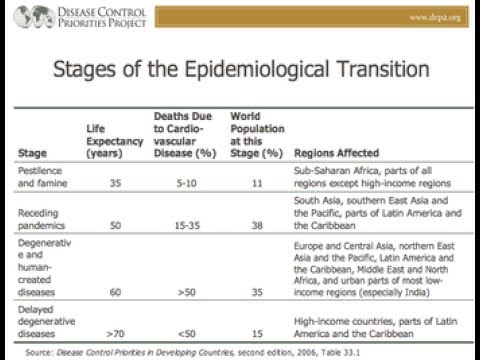
Not extra-terrestrials: we mean the Epidemiological Transition and its stages from the Neolithic Revolution to now. Disease, it turns out, has much to do with how fast populations grow, or whether they grow at all. Explore our app and discover over 50 million learning materials for free. Until humans began to live in close quarters with each other and our domestic animals, we were relatively healthy. During the Paleolithic and Mesolithic periods, humans fished and foraged, living in small groups often on the move. We didn't live long, but we were free of the diseases that need large numbers of people together. Epidemiological Transition ET : the three to five essential shifts in birth rates, death rates, and life expectancy that have occurred over human history due to fundamental changes in the nature of the diseases affecting human populations. In , ET theorist AR Omran, in a bid to build upon and improve demographic transition theory , proposed three epidemiological shifts over the last years that resulted in "ages. The first age was sparked by the Neolithic Revolution when people became farmers, living sedentary existences near each other and their animals. Diets worsened in many ways as they lost access to the range of wild foods hunter-gatherers consumed. Sedentary farmers and urban dwellers became highly susceptible to zoonotic transmission of disease from domesticated animals as well as commensal rodents such as rats and mice, highly effective disease spreaders. Until , this age of "pestilence and famine" 1 was experienced by farmers and urbanites in the Old World.
Save Article.
.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October Learn More or Try it out now. Although demography continues to be the most prominent discipline concerned with population dynamics, involvement of other disciplines is highly desirable. More specifically, epidemiology is concerned with the distribution of disease and death, and with their determinants and consequences in population groups. Inasmuch as patterns of health and disease are integral components of population change, epidemiology's reservoir of knowledge about these patterns and their determinants in population groups serves not only as a basis for prediction of population change but also as a source of hypotheses that can be further tested to correct, refine and build population theory. Furthermore, many epidemiologic techniques that have heretofore been limited to the examination of health and disease patterns can be profitably applied as well to the exploration of other mass phenomena, such as fertility control.
Epidemiological transition model ap human geography definition
All Subjects. AP Human Geography. Frequently Asked Questions. You'll be asked about them in multiple-choice and free-response questions, so it's crucial that you are familiar with each of these. Be able to explain what information each one provides and examples if you can! Create your own quizlet deck and study these dates! There are tons of decks already made with these dates ex.
Hyena road 2015
Author manuscript; available in PMC Jul 1. In times of abundance and peace, populations grew, but then they crashed when a new pandemic or famine swept across the land. In Stage five, countries the birth rates remain low, and the death rates go up. The birth rate and the death rate are both high and equal to each other. Omran added the "Age of declining cerebrovascular mortality, aging, lifestyle modifications, and resurgent diseases" in The various criticisms of the theory suggest it is most relevant as a way of looking at and understanding the relation among disease, mortality patterns, and population rather than as a definitive explanation or prediction. The population pyramids of these countries have a very wide base that gets thinner and thinner the higher you go. Then came the Neolithic Revolution, some years ago. Already have an account? People in the US began to emerge from the first stage by the early s as the country became less agricultural and more urban and industrial. This will require new ways of thinking that go beyond the epidemiologic transition theory. Note in Figure 1 that the difference in life expectancy between women and men is greater in the last half of the 20 th century than in the first half, no doubt reflecting reduced rates of perinatal maternal mortality. The mortality rates of both diseases are affected by factors such as economic development, in which developed countries can provide more adequate treatment than developing countries. Create a free account to save this explanation.
Not extra-terrestrials: we mean the Epidemiological Transition and its stages from the Neolithic Revolution to now.
It is instructive to consider historical transitions in epidemiology and public health that in some ways mirror the transitions described above. The natural increase rate is still positive, but not as high as in stage two. While such changes consistent with the theory have been evident, the theory has not been without its critics and a number of issues remain controversial. Nie wieder prokastinieren mit unseren Lernerinnerungen. While retaining intervention and prevention as goals, epidemiologists now seek to incorporate systems perspectives within an ecological model with its multi-leveled approach and life span considerations. Because of better infrastructure hospitals, sewers, better plumbing , fewer people die of parasitic diseases. The Industrial Revolution ushered in improved healthcare, medicine, and sanitation which allowed populations to grow exponentially. The US has a declining life expectancy. For most of the last years, people's lives have been short and disease-ridden, with high death rates, high birth rates, and poor infant and maternal health. The theory proposes that this shift is accompanied by a shift in the population age distribution as early infectious disease deaths decline and deaths from chronic and degenerative disease increase, the latter a result not only of the receding competing risk from infectious diseases, but also of the new environmental hazards that came with industrial development and increasing urban living. The population pyramids of these countries are even throughout the age groups and somewhat resemble a skyscraper. Caldwell JC. Women, infant, and child mortality were extremely high during this entire period, with up to one out of two children dying before the age of two. Sign up now for free. Some of the more recent discoveries in infectious disease have arisen from an approach and conceptual framework and methodology rather distinct from that of the golden age of late 19 th and early 20 th century microbiology.

0 thoughts on “Epidemiological transition model ap human geography definition”