Exocytosis
Federal government websites often end in.
As an active transport mechanism, exocytosis requires the use of energy to transport material. Exocytosis and its counterpart, endocytosis , are used by all cells because most chemical substances important to them are large polar molecules that cannot pass through the hydrophobic portion of the cell membrane by passive means. Exocytosis is the process by which a large amount of molecules are released; thus it is a form of bulk transport. Exocytosis occurs via secretory portals at the cell plasma membrane called porosomes. Porosomes are permanent cup-shaped lipoprotein structure at the cell plasma membrane, where secretory vesicles transiently dock and fuse to release intra-vesicular contents from the cell. In exocytosis, membrane-bound secretory vesicles are carried to the cell membrane , where they dock and fuse at porosomes and their contents i.
Exocytosis
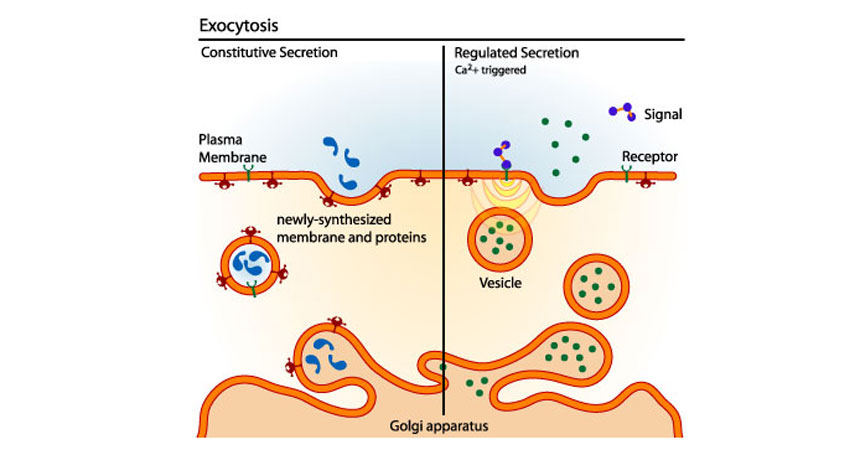
Exocytosis is the process of moving materials from within a cell to the exterior of the cell. This process requires energy and is therefore a type of active transport. Exocytosis is an important process of plant and animal cells as it performs the opposite function of endocytosis. In endocytosis, substances that are external to a cell are brought into the cell. In exocytosis, membrane-bound vesicles containing cellular molecules are transported to the cell membrane. The vesicles fuse with the cell membrane and expel their contents to the exterior of the cell. The process of exocytosis can be summarized in a few steps. Exocytosis serves several important functions as it allows cells to secrete waste substances and molecules, such as hormones and proteins. Exocytosis is also important for chemical signal messaging and cell to cell communication. In addition, exocytosis is used to rebuild the cell membrane by fusing lipids and proteins removed through endocytosis back into the membrane. Exocytotic vesicles containing protein products are typically derived from an organelle called the Golgi apparatus , or Golgi complex. Proteins and lipids synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum are sent to Golgi complexes for modification and sorting. Once processed, the products are contained within secretory vesicles, which bud from the trans face of the Golgi apparatus. Other vesicles that fuse with the cell membrane do not come directly from the Golgi apparatus. Some vesicles are formed from early endosomes , which are membrane sacs found in the cytoplasm.
Similarly, the autophagic pathways have been considered processes leading to the degradation of cellular waste upon fusion with lysosomes in order to recycle cellular components, but it is now emerging that intermediate compartments of the autophagic system such as autophagosomes may exocytosis exploited to release shorthairedhotties lacking N-terminal peptide by unconventional secretion, as well as to get rid of infectious agents, exocytosis. Polycationic peptides from diatom biosilica that direct silica nanosphere exocytosis. Share the Definition of exocytosis on Twitter Twitter.
Exocytosis is the fusion of secretory vesicles with the plasma membrane and results in the discharge of vesicle content into the extracellular space and the incorporation of new proteins and lipids into the plasma membrane. Exocytosis can be constitutive all cells or regulated specialized cells such as neurons, endocrine and exocrine cells. In neurons and endocrine cells, a small proportion of regulated secretory vesicles are ready to fuse with the plasma membrane in response to cell stimulation, but the majority are kept in reserve for subsequent stimulation by linkage to a filamentous network of synapsins in neurons or actin in endocrine cells. GTP-binding proteins of both the monomeric and heterotrimeric forms are involved in exocytosis, although their precise role is unclear. Intense current interest focuses on the idea that the molecular mechanism of vesicle docking and fusion is conserved from yeast to mammalian brain.
Is it possible for objects larger than a small molecule to be engulfed by a cell? Of course it is. This image depicts a cancer cell being attacked by a cell of the immune system. Cells of the immune system consistently destroy pathogens by essentially "eating" them. Some molecules or particles are just too large to pass through the plasma membrane or to move through a transport protein. So cells use two other active transport processes to move these macromolecules large molecules into or out of the cell. Vesicles or other bodies in the cytoplasm move macromolecules or large particles across the plasma membrane.
Exocytosis
Exocytosis is the natural process of transporting molecules from within a cell to the outside space. In this process, the vesicles containing the fluid enclosed by a lipid bilayer fuse with the plasma membrane to release their contents outside the cell. It occurs in all living cells, from invertebrates and protozoa to plants and human.
Infuse on apple tv
Cell Res. Regulated secretion of conventional lysosomes. The formation of an autophagolysosome may also occur through a different process. Unidirectional transfer of microRNA-loaded exosomes from T cells to antigen-presenting cells. Nano and Microengineering Series. Abstract Beyond the consolidated role in degrading and recycling cellular waste, the autophagic- and endo-lysosomal systems play a crucial role in extracellular release pathways. Bandyopadhyay D. Tethering interactions are likely to be involved in concentrating synaptic vesicles at the synapse. Exocytosis can be constitutive all cells or regulated specialized cells such as neurons, endocrine and exocrine cells. Certain vesicle-trafficking steps require the transportation of a vesicle over a moderately small distance. Current investigations also provide evidence that organelles delivering cell material to lysosomes for degradation, such as autophagosome and endosomes, can change their destination from fusion with lysosomes to fusion with plasma membrane for extracellular release. FM-dyes as experimental probes for dissecting vesicle trafficking in living plant cells. Wong C. Kang S.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
Like exocytosis, endocytosis requires energy so is also a form of active transport. List of Partners vendors. Patel K. Riva P. Reimann, B. See All. Instead, the engulfment of extracellular materials is a distinctive feature of the endocytic machinery, that begins with plasma membrane invagination and does not involve cytosolic cargoes. By Regina Bailey Regina Bailey. Cell Host Microbe. These peculiar endosomes, called multivesicular bodies MVBs , can fuse with plasma membrane to release ILVs into the extracellular space, originating exosomes [ 35 , 36 ]. Nilsson P. Diatom cultures were maintained in natural Mediterranean seawater that was filtered, its salinity corrected to 3.

0 thoughts on “Exocytosis”