Formal charge of nitrogen
It is more important that students learn to easily identify atoms that have formal charges of zero, than it is to actually calculate the formal charge of every atom in an organic compound.
Too much emphasis can easily be placed on the concept of formal charge, and the mathematical approach is hard to justify. In this course, you will certainly need to be able to recognize whether a given species carries a charge i. A formal charge compares the number of electrons around a "neutral atom" an atom not in a molecule versus the number of electrons around an atom in a molecule. Formal charge is assigned to an atom in a molecule by assuming that electrons in all chemical bonds are shared equally between atoms, regardless of relative electronegativity. To calculate formal charges, we assign electrons in the molecule to individual atoms according to these rules:.
Formal charge of nitrogen
Too much emphasis can easily be placed on the concept of formal charge, and the mathematical approach used in the textbook is hard to justify. In this course, you will certainly need to be able to recognize whether a given species carries a charge i. It is sometimes possible to write more than one Lewis structure for a substance that does not violate the octet rule, as we saw for CH 2 O, but not every Lewis structure may be equally reasonable. In these situations, we can choose the most stable Lewis structure by considering the formal charge on the atoms, which is the difference between the number of valence electrons in the free atom and the number assigned to it in the Lewis electron structure. The formal charge is a way of computing the charge distribution within a Lewis structure; the sum of the formal charges on the atoms within a molecule or an ion must equal the overall charge on the molecule or ion. A formal charge does not represent a true charge on an atom in a covalent bond but is simply used to predict the most likely structure when a compound has more than one valid Lewis structure. To calculate formal charges, we assign electrons in the molecule to individual atoms according to these rules:. A neutral nitrogen atom has five valence electrons it is in group Substituting into the formula, we obtain. A neutral hydrogen atom has one valence electron. Using Equation 4. The hydrogen atoms in ammonia have the same number of electrons as neutral hydrogen atoms, and so their formal charge is also zero. Adding together the formal charges should give us the overall charge on the molecule or ion.
C Predict which structure is preferred based on the formal charge on each atom and its electronegativity relative to the other atoms present. Lisa C. Evelyn Shkraba.
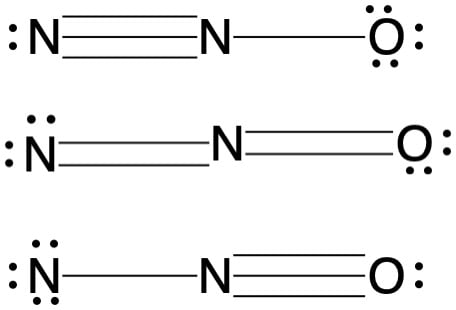
How do you calculate the formal charge of all atoms in NO 3 -? Formal charges are represented as the actual charges on any atom within a molecule, for which we can use the formula as;. Step 2: Structure of NO 3 - , for understanding bonding within it For NO 3 - , the formal charges on each atom can be depicted by analyzing its structure given by;. From the structure, we can see Nitrogen has 5 valence electrons and 8 bonding electrons, hence its formal charge is counted as:.
In the previous section, we discussed how to write Lewis structures for molecules and polyatomic ions. As we have seen, however, in some cases, there is seemingly more than one valid structure for a molecule. We can use the concept of formal charges to help us predict the most appropriate Lewis structure when more than one is reasonable. The formal charge of an atom in a molecule is the hypothetical charge the atom would have if we could redistribute the electrons in the bonds evenly between the atoms. Another way of saying this is that formal charge results when we take the number of valence electrons of a neutral atom, subtract the nonbonding electrons, and then subtract the number of bonds connected to that atom in the Lewis structure. We can double-check formal charge calculations by determining the sum of the formal charges for the whole structure. The sum of the formal charges of all atoms in a molecule must be zero; the sum of the formal charges in an ion should equal the charge of the ion. We must remember that the formal charge calculated for an atom is not the actual charge of the atom in the molecule. Formal charge is only a useful bookkeeping procedure; it does not indicate the presence of actual charges. The arrangement of atoms in a molecule or ion is called its molecular structure.
Formal charge of nitrogen
It is more important that students learn to easily identify atoms that have formal charges of zero, than it is to actually calculate the formal charge of every atom in an organic compound. Students will benefit by memorizing the "normal" number of bonds and non-bonding electrons around atoms whose formal charge is equal to zero. A formal charge compares the number of electrons around a "neutral atom" an atom not in a molecule versus the number of electrons around an atom in a molecule. Formal charge is assigned to an atom in a molecule by assuming that electrons in all chemical bonds are shared equally between atoms, regardless of relative electronegativity. To calculate formal charges, we assign electrons in the molecule to individual atoms according to these rules:. The formal charge of each atom in a molecule can be calculated using the following equation:. A neutral nitrogen atom has five valence electrons it is in group From the Lewis structure, the nitrogen atom in ammonia has one lone pair and three bonds with hydrogen atoms. Substituting into Equation 2. A neutral hydrogen atom has one valence electron.
16 january 2017 tithi
The hydrogen atoms in ammonia have the same number of electrons as neutral hydrogen atoms, and so their formal charge is also zero. Two other possibilities are carbpon radicals and carbenes, both of which have a formal charge of zero. For example, carbon with four covalent bonds and no lone pairs has a formal charge of zero. As an example of how formal charges can be used to determine the most stable Lewis structure for a substance, we can compare two possible structures for CO 2. Over here on the right, same idea. In other words, carbon is tetravalent , meaning that it commonly forms four bonds. A neutral nitrogen atom has five valence electrons it is in group Your end bit sounds like rambling, it doesn't make sense. So nitrogen has a formal charge of zero. Standard XII Chemistry. It would be exceptionally tedious to determine the formal charges on each atom in 2'-deoxycytidine one of the four nucleoside building blocks that make up DNA using equation 2. Thus the symmetrical Lewis structure on the left is predicted to be more stable, and it is, in fact, the structure observed experimentally. You should certainly use the methods you have learned to check that these formal charges are correct for the examples given above. When summed the overall charge is zero, which is consistent with the overall charge on the NH 3 molecule. So let's look at some examples where nitrogen has a formal charge of plus one.
Sigma bonds come in six varieties: Pi bonds come in one. The calculation is pretty straightforward if all the information is given to you. So part of the trick for you will be to calculate the formal charge in situations where you have to take account of implicit lone pairs and C-H bonds.
Carbon, the most important element for organic chemists. Draw two possible structures, assign formal charges on all atoms in both, and decide which is the preferred arrangement of electrons. Example 2. So let's assign a formal charge to the nitrogen in this molecule. More importantly, you will need, before you progress much further in your study of organic chemistry, to simply recognize these patterns and the patterns described below for other atoms and be able to identify carbons that bear positive and negative formal charges by a quick inspection. Formal Charge. Why can't we assume that Nitrogen has H bonds as we did with Carbon in the previous video instead of lone pairs? Sign in. Chapter 1: Structure and Bonding. Chemistry: Structure and Properties, 3rd ed.

Talently...
I do not doubt it.
Brilliant idea and it is duly