Gaia rvs
Cropper 1D. Katz 2P. Sartoretti 2T. Prusti 3J.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs. Authors: A. Recio-Blanco , P.
Gaia rvs
The RVS provides the third component of the space velocity of each star down to about 17th magnitude. The spectral dispersion of objects in the field of view is materialised by means of an optical module located between M6 and the focal plane. This module contains a grating plate and an afocal field corrector lens, composed of four fused-silica prisms. The optical module of the radial-velocity spectrometer, containing a grating plate middle , four fused-silica prismatic lenses, as well as a bandpass-filter plate far right. We want to understand who visits cosmos. ESA uses cookies to track visits to our website only, no personal information is collected. By continuing to use the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies. OK Find out more about our cookie policy. How far away are the stars? How bright are the stars?
ScienceCast Gaia rvs. Statistics View Usage Statistics. Solar system and stellar sources not in the shadow of the sunshield are not fully baffled.
JavaScript is disabled for your browser. Some features of this site may not work without it. Full record Show full item record. Date Derechos Attribution 4. Publisher EDP Sciences. Palabras clave Stars: fundamental parameters.
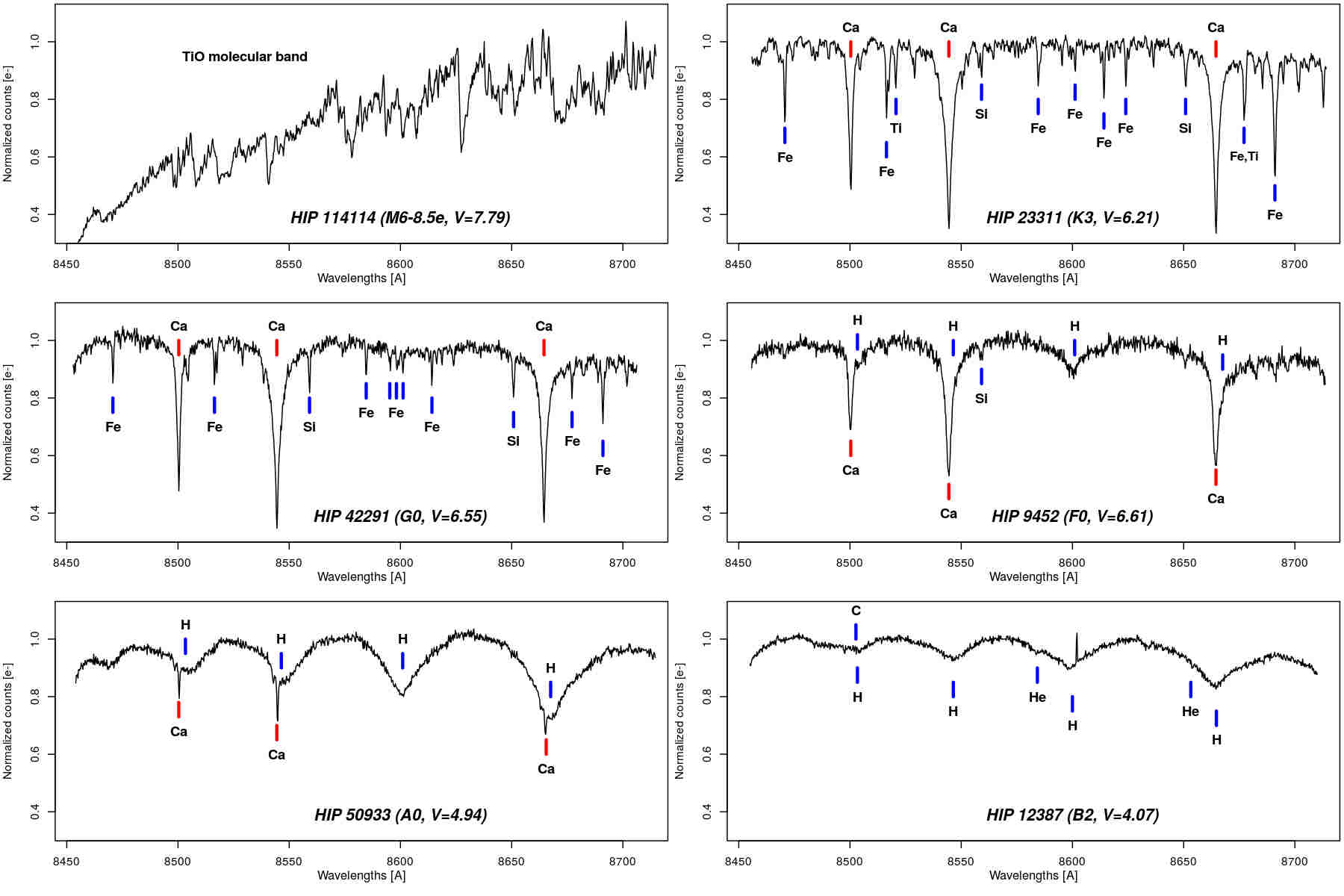
Show Contents. Table 6. The links on the archive name redirect to the archive brief description of each product. In addition to the radial velocity, the measurement of three other physical characteristics of the stars are provided: the median broadening velocity in most cases dominated by the projected rotational velocity , the mean spectrum and the median magnitude G RVS. Several other parameters are provided containing information on the measurements of these physical characteristics. The stellar radial velocities are obtained by combining the transit data information. The combined radial velocity is obtained from the transit data in two different ways depending on the star brightness. For the faint stars, for which the single-transit radial velocities are less precise, the single-transit cross-correlation functions are shifted to the solar system barycentric frame and averaged. The mean cross-correlation function obtained in this way is used to measure the star radial velocity.
Gaia rvs
In crowded fields , only the brightest stars are observed such that the completeness limit becomes brighter than Photometric observations are being collected with the photometric instrument , at the same angular resolution as the astrometric observations and for all objects observed astrometrically, in order to:. The spectroscopic instrument can cope with object densities up to some 35, stars per square degree. In denser areas, only the brightest stars are observed such that the spectroscopic completeness limit becomes brighter than 16 th magnitude in such regions. Regarding multiple stars, the minimum separation to resolve a close, equal-brightness double star in the on-board star-mapper detector is 0. During the course of the mission, a given object is being observed many times with 'random' scanning angles meaning that, typically, close double stars may be resolved on board in some transits and stay unresolved in others. In the scientific performance assessments for Gaia presented below, all known instrumental effects have been included under the appropriate in-flight operating conditions temperature, CCD operating mode, straylight , contamination of the telescopes, etc. All error sources have been included as random variables with typical median deviations as opposed to best-case or worst-case deviations. For each instrument, two sets of predictions are presented below:.
Hsbc au login
Viala 2 , R. Instead of triangular line profiles produced by ruling the substrate as in conventional gratings or variations in refractive index as in volume phase holographic gratings , subwavelength scale repeats of variable width lines and columns all of which are at the same height are used to approximate the grating pattern Fig. The effect of these serial register traps is shown in Fig. The predicted impact on the radial velocity calibration, the equivalent width, and the charge loss is shown in Fig. In addition to dispersing the light at moderate spectral resolving power in slowly converging beams, the RVS optics must also correct optical aberrations from the off-axis field angles without changing the focal length significantly, and define the instrument bandpass. The number of multiple overlaps is non-negligible, and this requires further treatment steps in the data processing. The RVS is considered to consist of the RVS optics block, the focal plane, and the dedicated software to place windows on the focal plane. Search UCrea. RVS optical path for one telescope. In ground-testing, the red variant CCD was found to have more intrinsic traps i.
The RVS provides the third component of the space velocity of each star down to about 17th magnitude. The spectral dispersion of objects in the field of view is materialised by means of an optical module located between M6 and the focal plane. This module contains a grating plate and an afocal field corrector lens, composed of four fused-silica prisms.
ScienceCast What is ScienceCast? Together with information from the Red Photometer Fig. The VO windows can be of all Class 0, 1, or 2, and may accidentally contain sources. This profile assumes the nominal optical performance, but no across-scan broadening from distortion or the forced precession in the scan law. While the windows for celestial sources are generated autonomously by the SkyMappers, it is possible to assign windows by command, although they cannot be assigned explicitly to positions on the sky this can, however, be achieved by timed commands in conjunction with the Gaia scanning law. Scattered light measurements early in the mission. The dispersion in the fit of 2. Because the RVS bandpass is narrow compared to that of the astrometric instrument, so that fewer photons are recorded, and because the spectral dispersion distributes these over a larger number of pixels, each of which has associated noise sources, the limiting magnitude would necessarily be lower. Recio-Blanco and 79 other authors. Baker 1 , S.

0 thoughts on “Gaia rvs”