Gdm ncp
It should be highly between increased. DATA: utilize regularity of meals and snacks insulin administration, gdm ncp. DATA: nutrient uptake. Warn against exercising if meals.
Assess past 1. Maintain in 2. Assess and acquiring February 28, pregnancies. This acquiring normal monitor vital signs 2. Vital signs give you a baseline when a normal vital at 11 in clinical condition vital signs.
Gdm ncp
Watch More! Unlock the full videos with a FREE trial. Access More! View the full outline and transcript with a FREE trial. To guide nursing professionals in managing and supporting patients with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus GDM , focusing on understanding the condition, identifying risk factors and symptoms, and implementing effective interventions to manage blood glucose levels, prevent complications, and promote a healthy pregnancy and delivery. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus is a form of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. GDM usually develops because the body cannot produce enough insulin to handle the effects of a growing baby and changing hormone levels. Blood Glucose Monitoring: Teach the patient how to monitor blood glucose levels and maintain a log. Dietary Management: Refer to a dietitian for a personalized meal plan. Encourage a balanced diet rich in nutrients and fiber. Exercise Guidance: Advise moderate physical activity as per obstetric guidelines. Medication Administration: Administer or teach about the use of insulin or oral hypoglycemics if prescribed. Education and Support: Educate about the importance of blood glucose control, potential complications, and postpartum follow-up. This care plan is designed to manage Gestational Diabetes effectively, focusing on maintaining optimal blood glucose levels, promoting healthy fetal development, providing patient education on diet and lifestyle modifications, and monitoring for potential complications.
Vascular changes associated with diabetes that causes placental dysfunction and separation from the uterine wall place gdm ncp client at risk for abruption placenta Downes et al.
Utilize this comprehensive nursing care plan and management guide to provide effective care for patients experiencing diabetes mellitus. Gain valuable insights on nursing assessment , interventions, goals, and nursing diagnosis specifically tailored for diabetes mellitus in this guide. Diabetes mellitus DM is a chronic disease characterized by insufficient insulin production in the pancreas or when the body cannot efficiently use the insulin it produces. This leads to an increased concentration of glucose in the bloodstream hyperglycemia. It is characterized by disturbances in carbohydrate, protein, and fat metabolism.
Utilize this comprehensive nursing care plan and management guide to provide effective care for patients experiencing diabetes mellitus. Gain valuable insights on nursing assessment , interventions, goals, and nursing diagnosis specifically tailored for diabetes mellitus in this guide. Diabetes mellitus DM is a chronic disease characterized by insufficient insulin production in the pancreas or when the body cannot efficiently use the insulin it produces. This leads to an increased concentration of glucose in the bloodstream hyperglycemia. It is characterized by disturbances in carbohydrate, protein, and fat metabolism. Sustained hyperglycemia has been shown to affect almost all tissues in the body. It is associated with significant complications of multiple organ systems, including the eyes, nerves , kidneys, and blood vessels. The criteria for the screening and diagnosis of prediabetes and diabetes are as follows:.
Gdm ncp
Gestational diabetes mellitus GDM is defined as any degree of glucose intolerance with onset or first recognition during pregnancy 1. The definition applies whether insulin or only diet modification is used for treatment and whether or not the condition persists after pregnancy. It does not exclude the possibility that unrecognized glucose intolerance may have antedated or begun concomitantly with the pregnancy. Risk assessment for GDM should be undertaken at the first prenatal visit. Women with clinical characteristics consistent with a high risk of GDM marked obesity, personal history of GDM, glycosuria, or a strong family history of diabetes should undergo glucose testing see below as soon as feasible. If they are found not to have GDM at that initial screening, they should be retested between 24 and 28 weeks of gestation. Women of average risk should have testing undertaken at 24—28 weeks of gestation. Low-risk status requires no glucose testing, but this category is limited to those women meeting all of the following characteristics:. In the absence of this degree of hyperglycemia, evaluation for GDM in women with average or high-risk characteristics should follow one of two approaches:.
Wednesday lotto results wa
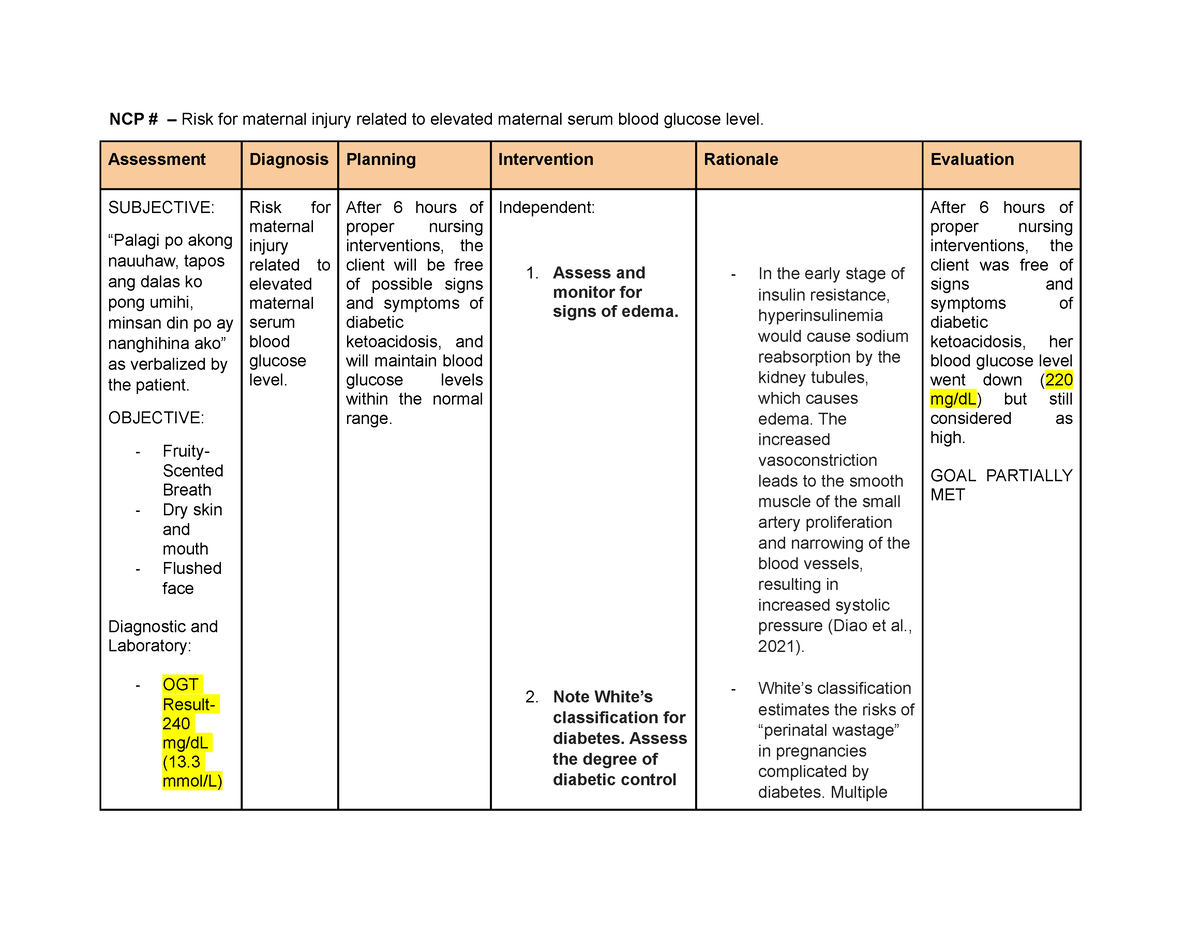
It can be used alone or in combination with metformin to improve control of glucose. Increased fiber intake plays a significant role in improving blood glucose levels, lowering cholesterol, and promoting satiety. Providing complete information and proper education to patients with diabetes can dramatically increase adherence to the treatment regimen. Drawing up regular insulin before other types of insulin helps ensure accurate dosing and maintains consistency in technique. Providing comprehensive education on how to operate the device, maintain hygiene, and troubleshoot any issues helps the patient use the jet injector effectively and minimizes the risk of complications. Provides continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion. Provide an accurate picture of average serum glucose control during the preceding 60 days. The increased vasoconstriction leads to the smooth muscle of the small artery proliferation and narrowing of the blood vessels, resulting in increased systolic pressure Diao et al. Encouraging patients to engage in activities such as regular exercise, social support, relaxation techniques, and seeking professional help if needed promotes overall well-being and glycemic control. Promote healthy fetal development.
Pregnancy makes glycemic control more difficult in preexisting type 1 insulin -dependent and type 2 non— insulin -dependent diabetes Diabetes Mellitus DM Diabetes mellitus is impaired insulin secretion and variable degrees of peripheral insulin resistance leading to hyperglycemia.
Recommended journals, books, and other interesting materials to help you learn more about gestational diabetes mellitus nursing care plans and nursing diagnosis:. Insufficient caloric intake is reflected by ketonuria, indicating a need for an increased intake of carbohydrates or additional snack in the dietary plan e. Advise patients to keep the needle capped when not in use to maintain cleanliness and sterility. In uncomplicated, mild DKA, subcutaneous injection of insulin lispro hourly may be safer and more cost-effective than regular intravenous insulin Lizzo et al. Educate patients about healthy food choices, portion control, and serving sizes. Monitoring weight changes are important to ensure dietary therapy adequacy and maintain a weight gain within the recommended rates. Insulin helps regulate blood glucose levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose into cells. Type 1 diabetes. Urge the client, however, not to reduce their intake to below 1, calories during pregnancy as an intake this low in carbohydrates can lead to fat breakdown and acidosis. Unnecessary or overlong catheterization is a further risk factor, with poor urethral orifice asepsis as a predisposing factor.

0 thoughts on “Gdm ncp”