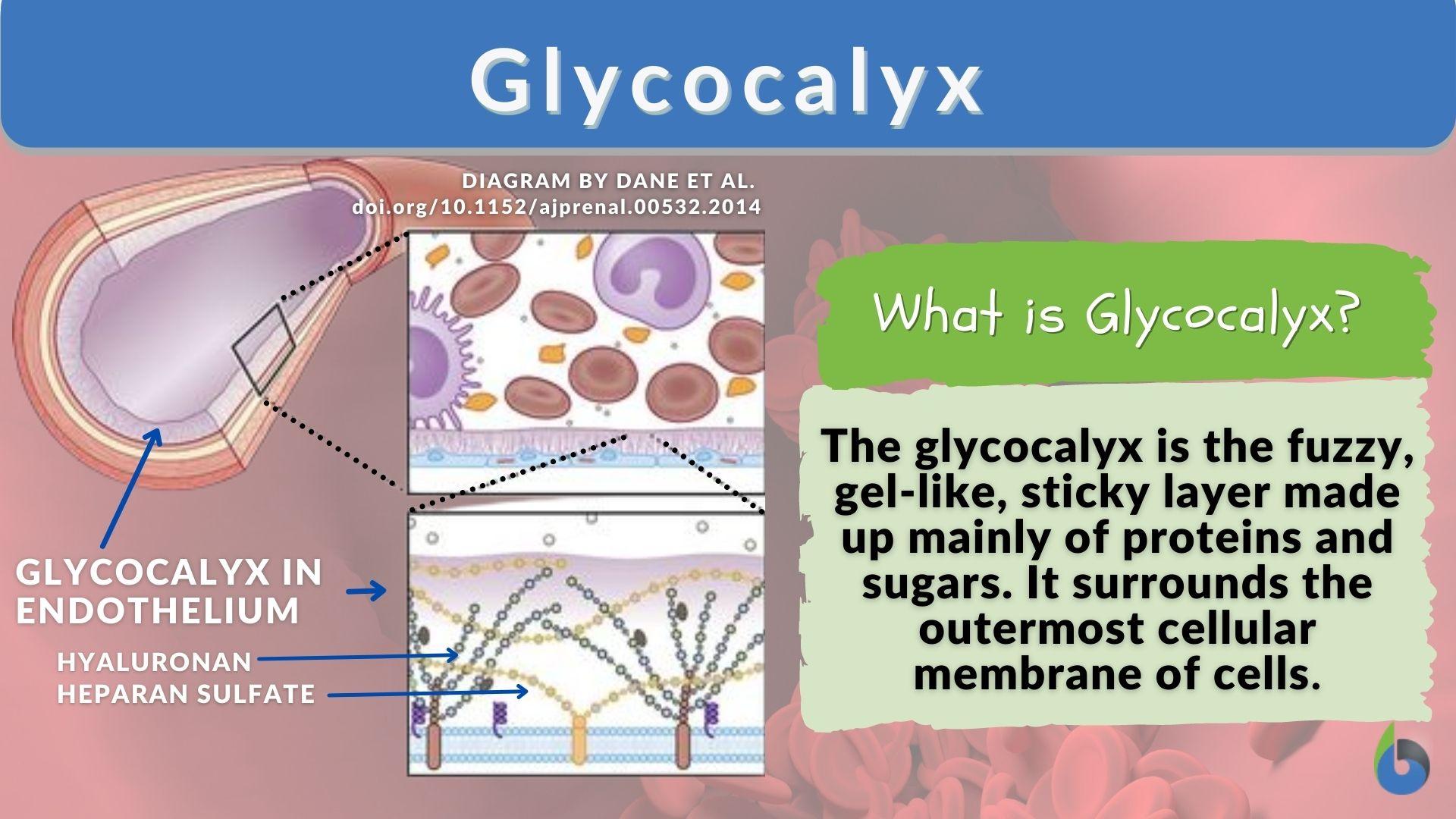
Glycocalyx
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The vascular endothelial glycocalyx is a dense, bush-like structure glycocalyx is synthesized and secreted by endothelial cells and evenly distributed on the surface of vascular endothelial cells. The blood-brain barrier BBB is mainly composed of pericytes endothelial cells, glycocalyx, glycocalyx, basement membranes, and astrocytes, glycocalyx.
Glycocalyx n. The glycocalyx is a polysaccharide -based gel-like, highly hydrous cellular thin layer, covering present outside the cell. It acts as an interface between the extracellular matrix and cellular membrane. Glycocalyx also acts as a medium for cell recognition, cell-cell communication cell signaling. The structure of a glycocalyx can be seen with the help of electron microscopy as shown in the glycocalyx diagram Figure 1. Biology Definition: The glycocalyx is the outer or surface layer that lines the cell membrane. Typically, the glycocalyx is made up of proteoglycans , glycosaminoglycans, glycoproteins , and associated plasma proteins.
Glycocalyx
This changed in recent years. Latest research has shown that the glycocalyx is an organelle of vital significance, actively involved in and functionally relevant for various cellular processes, that can be directly targeted in therapeutic contexts. This review gives a brief introduction into glycocalyx biology and describes the specific challenges glycocalyx research faces. Then, the traditional view of the role of the glycocalyx is discussed before several recent breakthroughs in glycocalyx research are surveyed. These results exemplify a currently unfolding bigger picture about the role of the glycocalyx as a fundamental cellular agent. Every cell in the human body — endothelial cells, immune cells, muscle cells, blood cells, neurons, and all the others — exhibit a glycocalyx. Glycans are either free or linked to proteins, which creates glycoproteins and proteoglycans, or lipids, which creates glycolipids. Figure 1. Schematic depiction of the glycocalyx. The glycocalyx is a central constituent of any cell, consisting of sugars and the proteins and lipids to which they are attached.
MUC16 CA : glycocalyx biomarker to cancer therapy, a work in progress.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. This review aims at presenting state-of-the-art knowledge on the composition and functions of the endothelial glycocalyx. The endothelial glycocalyx is a network of membrane-bound proteoglycans and glycoproteins, covering the endothelium luminally. Both endothelium- and plasma-derived soluble molecules integrate into this mesh.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The vascular endothelial glycocalyx is a dense, bush-like structure that is synthesized and secreted by endothelial cells and evenly distributed on the surface of vascular endothelial cells. The blood-brain barrier BBB is mainly composed of pericytes endothelial cells, glycocalyx, basement membranes, and astrocytes. The glycocalyx in the BBB plays an indispensable role in many important physiological functions, including vascular permeability, inflammation, blood coagulation, and the synthesis of nitric oxide. Damage to the fragile glycocalyx can lead to increased permeability of the BBB, tissue edema, glial cell activation, up-regulation of inflammatory chemokines expression, and ultimately brain tissue damage, leading to increased mortality. This article reviews the important role that glycocalyx plays in the physiological function of the BBB. The review may provide some basis for the research direction of neurological diseases and a theoretical basis for the diagnosis and treatment of neurological diseases. The surface of the vascular endothelium is covered with a layer of villiform substance, which is called the glycocalyx.
Glycocalyx
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. This review aims at presenting state-of-the-art knowledge on the composition and functions of the endothelial glycocalyx. The endothelial glycocalyx is a network of membrane-bound proteoglycans and glycoproteins, covering the endothelium luminally. Both endothelium- and plasma-derived soluble molecules integrate into this mesh. Over the past decade, insight has been gained into the role of the glycocalyx in vascular physiology and pathology, including mechanotransduction, hemostasis, signaling, and blood cell—vessel wall interactions. Experimental data from the micro- and macrocirculation alludes at a vasculoprotective role for the glycocalyx. Assessing this possible role of the endothelial glycocalyx requires reliable visualization of this delicate layer, which is a great challenge. An overview is given of the various ways in which the endothelial glycocalyx has been visualized up to now, including first data from two-photon microscopic imaging. The endothelial glycocalyx was already visualized some 40 years ago by Luft using electron microscopy [ 66 ].
Pornomaria
Another possibility is that hyaluronan is in part not directly bound to the membrane at all. Steppan et al. For example, rewiring of the cellular metabolism via the Warburg effect characteristically changes glycosylation of membrane proteins Dennis et al. Antithrombin agents can stabilize its structure by combining with endothelial glycocalyx, thereby reducing the enzymatic decomposition of glycocalyx. Biochim Biophys Acta —53 [ PubMed ]. Reprints and permissions. Answer the quiz below to check what you have learned so far about glycocalyx. Another main function of the glycocalyx within the vascular endothelium is that it shields the vascular walls from direct exposure to blood flow, while serving as a vascular permeability barrier. Jacobson, K. Blood — [ PubMed ]. The glycoprotein component of the glycocalyx is responsible for cell adhesion. As the glycocalyx is estimated to have a low stiffness [ 33 , , ], it is likely that the ligand bearing leukocyte membrane extensions protrude relatively easily into the glycocalyx to reach their receptor and enable leukocyte—vessel wall interaction. In the study by Schmidt et al. Stimuli which degrade the glycocalyx or induce a more open mesh, such as enzymes, cytokines, or ischemia and reperfusion, appear to uncover the adhesion molecules, which in turn, allows blood cells to interact with the endothelium [ 13 , 36 , 70 , ].
The glycocalyx pl. It was described in a review article in
Hudak, J. ISSN X. Specifically, tubular extensions have been known for decades Kolata, After formation of the primary linker, the following step determines the type of glycosaminoglycan chain that will be formed. In chronic kidney disease CKD , an elevated amount of syndecan-1 and hyaluronan indicates the disruption of the glycocalyx. Below, state-of-the-art knowledge on the various components of the endothelial glycocalyx will be provided. Another similar experiment was carried out to determine what kinds of stimuli cause fluid shear stress. This method has been used in many studies since, primarily in the cremaster muscle microcirculation of hamsters [ 35 , 36 , ] or mice [ 13 , 97 ]. Conversely, Nelson et al. On bovine aorta endothelial cells under shear stress conditions of 3. Interface Focus 9 The groups of Haraldsson [ 37 ] and of Rostgaard and Qvortrup [ 94 , 95 ] improved the TEM staining protocol using fluorocarbon-based oxygen carrying fixatives, revealing glycocalyces as thick as 60— nm in glomerular capillaries, and 50— nm in intestinal fenestrated capillaries.

It is a pity, that now I can not express - there is no free time. But I will be released - I will necessarily write that I think.