Glycogen synthase
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Glycogen synthase kinase 3 GSK3glycogen synthase, a constitutively acting multi-functional serine threonine kinase is involved in diverse physiological pathways ranging from metabolism, cell cycle, gene expression, development and oncogenesis to neuroprotection.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Glycogen is the major glucose reserve in eukaryotes, and defects in glycogen metabolism and structure lead to disease. Glycogenesis involves interaction of glycogenin GN with glycogen synthase GS , where GS is activated by glucosephosphate G6P and inactivated by phosphorylation.
Glycogen synthase
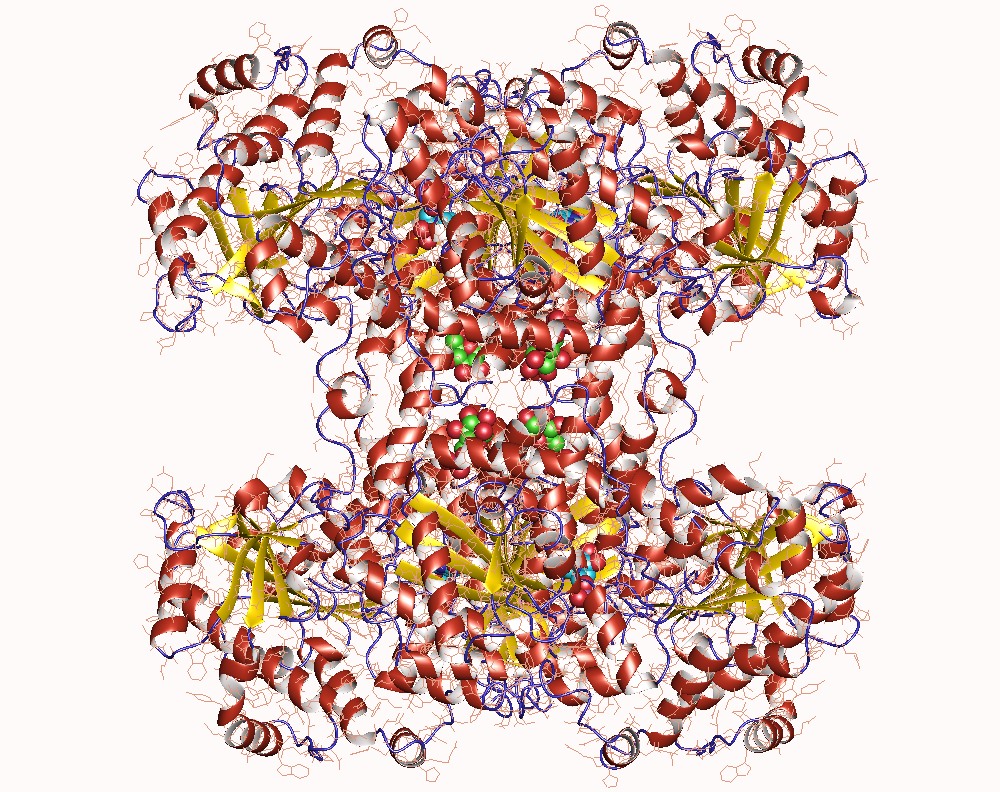
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Glycogen synthase GYS1 is the central enzyme in muscle glycogen biosynthesis. GYS1 activity is inhibited by phosphorylation of its amino N and carboxyl C termini, which is relieved by allosteric activation of glucosephosphate Glc6P. We present cryo-EM structures at 3. Phosphorylations of specific terminal residues are sensed by different arginine clusters, locking the GYS1 tetramer in an inhibited state via intersubunit interactions. The Glc6P activator promotes conformational change by disrupting these interactions and increases the flexibility of GYS1, such that it is poised to adopt a catalytically competent state when the sugar donor UDP-glucose UDP-glc binds. We also identify an inhibited-like conformation that has not transitioned into the activated state, in which the locking interaction of phosphorylation with the arginine cluster impedes subsequent conformational changes due to Glc6P binding. Our results address longstanding questions regarding the mechanism of human GYS1 regulation.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar.
Glycogen synthase UDP-glucose-glycogen glucosyltransferase is a key enzyme in glycogenesis , the conversion of glucose into glycogen. It is a glycosyltransferase EC 2. Much research has been done on glycogen degradation through studying the structure and function of glycogen phosphorylase , the key regulatory enzyme of glycogen degradation. The crystal structure of glycogen synthase from Agrobacterium tumefaciens , however, has been determined at 2. This structural property, among others, is shared with related enzymes, such as glycogen phosphorylase and other glycosyltransferases of the GT-B superfamily. Since the structure of eukaryotic glycogen synthase is highly conserved among species, glycogen synthase likely forms a tetramer in humans as well.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Salah A. Daghlas ; Shamim S. Authors Salah A.
Glycogen synthase
Although glucose is the primary fuel for cells, it is not an efficient molecule for long-term storage in complex i. Therefore, in both plants and animals, the glucose molecules are linked together to form polysaccharides known as glucans. The average size of a glycogen unit is a cytoplasmic granule containing over glucose molecules. The addition of a glucosephosphate to another or to a glycogen chain is energetically unfavorable, so it must be coupled with a sufficiently exergonic reaction to proceed. The phosphoanhydride exchange reaction catalyzed by UDP-glucose phosphorylase is minimally exergonic. However, the pyrophosphate released is quickly hydrolyzed by inorganic pyrophosphatase, a ubiquitous cytosolic enzyme, in a highly exergonic reaction.
Hl select uk income shares
Inset shows the EM density of both termini, along with arginine residues from the neighbouring subunit that would interact with phosphorylation sites 2 and 2a. Conflict of interest None. This removed intersubunit contacts at the minor interfaces B—D and A—C between the N-terminal Rossmann domain 1 of one subunit and the tetramerization domain of the neighbouring subunit Extended Data Fig. Methods 14 , — Antibody validation is shown in Supplementary Fig. Selective glycogen synthase kinase 3 inhibitors potentiate insulin activation of glucose transport and utilization in vitro and in vivo. Ryu, J. All other chemicals if not noted otherwise are from Sigma Aldrich. Inhibition of GSK-3 selectively reduces glucosephosphatase and phosphatase and phosphoenolypyruvate carboxykinase gene expression. Download citation. From the seminal discovery of proteoglycogen and glycogenin to emerging knowledge and research on glycogen biology. Diabetes 60 , —
Glycogen synthase UDP-glucose-glycogen glucosyltransferase is a key enzyme in glycogenesis , the conversion of glucose into glycogen. It is a glycosyltransferase EC 2.
The first family GT3 , which is from mammals and yeast, is approximately 80 kDa, uses UDP-glucose as a sugar donor, and is regulated by phosphorylation and ligand binding. Subsequently, the activation of phosphoinositol 3 kinase converts phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate to phosphatidylinositol triphosphate, which in turn stimulates and activates PKB. We observed density at the sugar donor site, which fit better as individual UDP and glucose moieties, suggesting that UDP-glc was hydrolysed Fig. Interactions with Glc6P in the lower-resolution map without substrate were the same. Suppression of glycogen synthesis as a treatment for Lafora disease: establishing the window of opportunity. Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase Uracil phosphoribosyltransferase Amidophosphoribosyltransferase. Cite this article Marr, L. Identification of a novel mutation in GYS1 muscle-specific glycogen synthase resulting in sudden cardiac death, that is diagnosable from skin fibroblasts. Berg or Wyatt W. Potential role of protein kinase B in insulin-induced glucose transport, glycogen synthesis, and protein synthesis. Insulin promotes glycogen synthesis in the absence of GSK3 phosphorylation in skeletal muscle. The kinase chiefly responsible for phosphorylating the site 3 has been identified as GSK3. Furthermore, our structures provide opportunities for rational inhibitor design in the development of new GSD therapies.

0 thoughts on “Glycogen synthase”