Glycolysis slideshare
Science Technology Business.
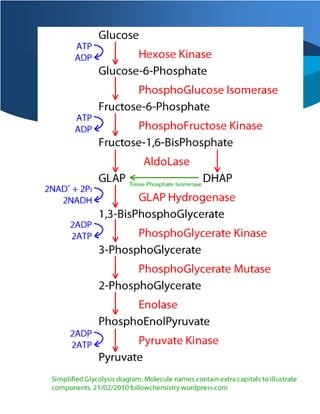
Glycolysis is present in most living organisms. It is the first step in cellular respiration. It is a glycolytic pathway, which leads to a partial breakdown of glucose to pyruvate. Glycolysis is the common pathway in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. Glycolysis process does not require oxygen. The omnipresence of this pathway shows that it is an ancient metabolic pathway and has evolved long ago. It is an important pathway to derive energy in the form of ATP both aerobically as well as anaerobically, which is required by all the cells to perform cellular functions.
Glycolysis slideshare
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Glycolysis is a central metabolic pathway that is used by all cells for the oxidation of glucose to generate energy in the form of ATP Adenosine triphosphate and intermediates for use in other metabolic pathways. Besides glucose, other hexose sugars such as fructose and galactose also end up in the glycolytic pathway for catabolism [1]. Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm where one 6 carbon molecule of glucose is oxidized to generate two 3 carbon molecules of pyruvate. The fate of pyruvate depends on the presence or absence of mitochondria and oxygen in the cells. The electron transport chain is the major site of oxygen consumption and the generation of ATP in the mitochondria. In cells with mitochondria, the pyruvate is decarboxylated by pyruvate dehydrogenase complex to form Acetyl-CoA that feeds into the Tricarboxylic acid cycle and ultimately participates in ATP production. During the absence of oxygen anaerobic conditions and in the cells lacking mitochondria, anaerobic glycolysis prevails. This process is an important source of ATP for cells that lack mitochondria, such as erythrocytes.
Current Topics in Cellular Regulation. Prasad Naidu. Because ATP decays relatively quickly when it is not metabolized, this is an important regulatory point in the glycolytic pathway, glycolysis slideshare.
Glycolysis takes place in the cytosol of cells. Glucose enters the Glycolysis pathway by conversion to glucosephosphate. The phosphate ester formed in glucosephosphate has a lower DG of hydrolysis. This prevents the enzyme from catalyzing ATP hydrolysis, rather than transfer of phosphate to glucose. It is a common motif for an enzyme active site to be located at an interface between protein domains that are connected by a flexible hinge region. The structural flexibility allows access to the active site, while permitting precise positioning of active site residues, and in some cases exclusion of water, as substrate binding promotes a particular conformation. A similar reaction catalyzed by Triosephosphate Isomerase will be presented in detail.
Science Technology Business. Download Now Download to read offline. Recommended Glycolysis. Pentose phosphate pathway,hmp shunt. Pentose phosphate pathway,hmp shunt Sijo A.
Glycolysis slideshare
Download Now Download to read offline. Recommended Glycolysis. Glycolysis Prakash Pokhrel. Pentose phosphate pathway,hmp shunt.
Prince george hotels with pools
Turn recording back on. Document Information click to expand document information Glycolysis Pathway. The different substrate affinity and alternate regulation of this enzyme are a reflection of the role of the liver in maintaining blood sugar levels. In part, this is because some of them are common to other pathways, such as the Calvin cycle. Library resources about Glycolysis. Propionyl -CoA. Sanket P. Harden and Young noted that this process would restart if an inorganic phosphate Pi was added to the mixture. Beveridge, John C. This prevents the enzyme from catalyzing ATP hydrolysis, rather than transfer of phosphate to glucose. Nature Education.
This document provides information about glycolysis, including: 1 Glycolysis involves the breakdown of glucose into pyruvate, producing 2 ATP and 2 NADH. There are 10 enzyme-catalyzed reactions in two stages. Read less.
Pyruvate kinase has been shown to be upregulated in highly proliferating cells such as embryonic cells and cancer cells. Phosphofructokinase PFK-1 a transferase. Glyco- genolysis. Eicosanoids 1 Eicosanoids 1. When there are plenty of substrates available, high levels of insulin activate a protein phosphatase that dephosphorylates phosphofructokinase-2 PFK2 , making it active, thereby promoting glycolysis. This irreversible step serves to trap the glucose molecule within the cell. These hydrogen ions form a part of lactic acid. Phosphoenolpyruvate PEP. Names in other organisms may be different and the number of isozymes such as HK1, HK2, New York: W. Citric acid cycle. Geometric New Earth, Solarsystem, projection. Hexose Monophosphate Shunt. It occurs in liver cells, and will only phosphorylate the glucose entering the cell to form glucosephosphate G6P , when the glucose in the blood is abundant. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.

Also that we would do without your magnificent phrase
I can not participate now in discussion - there is no free time. But I will return - I will necessarily write that I think.