Goblet cell diagram
Figure 1. Self drawn diagram of ciliated columnar epithelium, goblet cell diagram. Ciliated columnar epithelial cells are found mainly in the tracheal and bronchial regions of the pulmonary system and also in the fallopian tubes of the female reproductive system.
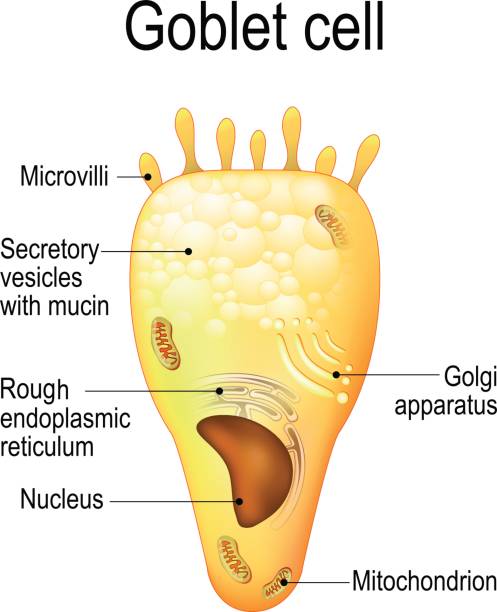
Goblet cells are specialized secretory cells that line various mucosal surfaces. Though they are primarily involved in the production of mucus, goblet cells also secrete a number of molecules such as chemokines that have been associated with innate immunity. Goblet cells are characterized by a cup-like morphology. Many of the organelles , nucleus , mitochondria , rough endoplasmic reticulum , and Golgi apparatus , are located in the lower part of the cell the basal portion while the vesicles with mucins are located in the upper part of the cell the apical part. Goblet cells are largely found in the mucosal layer or epithelial layer of the gastrointestinal tract, the respiratory tract upper and lower , as well as the reproductive tract. In parts of the body like the airways the epithelial surface lining the airways the apical surface of the goblet cells protrudes into the surface which allows them to rapidly respond to changes e.
Goblet cell diagram
The cells in epithelia have different shapes, and different types of epithelia have different numbers of layers of cells from one to many. The shape of the cells, and their organisation are important to the particular function of each type of epithelia. If a specialisation is present, then the type of specialisation present is included in the classification. Read the classification rules below, then have a go yourself. These epithelia usually have goblet cells present. When sectioned at right angles to their basement membrane the cells in different epithelia have a variety of shapes:. A special form of epithelium, in which the cells can alter their shape. When the epithelium is relaxed they appear cuboidal but when stretched they appear squamous. Read the summary below, then find out more on the Epithelium Specialisations page. Fine, finger-like projections which contain a central core of microfilaments. Increase the apical surface area in cells. Most developed in cells specialised for absorption e. Long, motile projections of the apical surface. These are longer than microvilli.
It is found only in the urinary system, specifically the ureters and urinary bladder. Ciliated tissue lines the trachea and much of the upper respiratory tract Secrete mucous; ciliated tissue moves mucous Stratified squamous epithelium.
Describe the structural characteristics of the various epithelial tissues and how these characteristics enable their functions. Epithelial tissue primarily appears as large sheets of cells covering all surfaces of the body exposed to the external environment and lining internal body cavities. In addition, epithelial tissue is responsible for forming a majority of glandular tissue found in the human body. Epithelial tissue is derived from all three major embryonic layers. The epithelial tissue composing cutaneous membranes develops from the ectoderm. Epithelial tissue composing a majority of the mucous membranes originate in the endoderm.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Diem-Phuong D. Dao ; Patrick H. Authors Diem-Phuong D. Dao 1 ; Patrick H.
Goblet cell diagram
Goblet Cells : In the body, different organs are responsible for maintaining homeostasis. For instance the first line of cells contributing for such is found in the epithelium. In particular, cells known as goblet cells are an important component in this barrier and constitute the majority of the immune system. But they are more than just secretory cells. Goblet cells along with other principal cells in the gastrointestinal tract, i. Apart from comprising the epithelial lining of various organs, production of large glycoproteins and carbohydrates, the most important function of goblet cells is mucus secretion.
Xfinity 10g promotion
Epithelial tissues are classified according to the shape of the cells and number of the cell layers formed Figure 2. This pathway is unregulated and serves to protect and lubricate various epithelia. Exocrine glands release their contents through a duct that leads to the epithelial surface. In both cases, the transported materials are usually swallowed, and end up in the acidic environment of your stomach. The arrangement gives the appearance of stratification; but in fact all the cells are in contact with the basal lamina, although some do not reach the apical surface. In epithelial tissue, cells are closely packed with little or no extracellular matrix except for the basal lamina that separates the epithelium from underlying tissue. Where in the body would one find non-keratinizing stratified squamous epithelium? A number of genes showed dramatic downregulation in the epithelium lacking goblet cells, making them candidates for goblet cell specific expression Marko et al. Development of an hTERT immortalized conjunctival epithelial cell line from initial primary culture is needed. Sometimes epithelia are specialised for secretion - and these cells are called Goblet cells.
Goblet cells are specialized epithelial cells found in various mucosal surfaces throughout the body. This article explores the histology of goblet cells, revealing their microscopic structure, cellular components, and the vital role they play in producing and secreting mucus to protect and lubricate epithelial tissues. The primary function of goblet cells is the production and secretion of mucus.
Assay of mucins in human tear fluid. Uniquely, in the conjunctiva, goblet cells are interspersed within a stratified epithelium. Claudins and the modulation of tight junction permeability. It is well known that mucins dramatically expand upon hydration at time of secretion from the goblet cell. The function of this type of tight junction at the conjunctival surface is unclear, but recent data using vitamin D receptor VDR null mice, indicate that Claudin 2 is directly regulated by VDR Zhang et al. Secretion properties, clearance, and therapy in airway disease. Where in the body would one find non-keratinizing stratified squamous epithelium? Both merocrine and apocrine glands continue to produce and secrete their contents with little damage caused to the cell because the nucleus and golgi regions remain intact after secretion. It has been hypothesized that there is a conjunctival source of fluid for the tear film, but the source and mechanism by which the fluid moves into the tear film from the conjunctiva has been unclear Mircheff, Functions of Cilia and Goblet Cells. Other wet surface mucosae regions have a non-adherent mucus which is moved over the surface of the epithelium by mucosae specific methods; by eyelid blink, ciliary action on the trachea and bronchi, and peristaltic movement in the gut.

0 thoughts on “Goblet cell diagram”