H3o+ molecular geometry
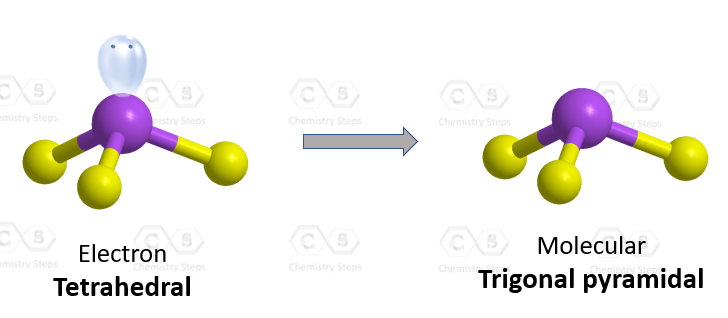
The VSEPR theory is used to predict the shape of the molecules from the electron pairs that surround the central atoms of the molecule.
The concentration of hydroxide ions analogously determines a solution's pOH. The molecules in pure water auto-dissociate into aqueous protons and hydroxide ions in the following equilibrium:. A pH value less than 7 indicates an acidic solution, and a pH value more than 7 indicates a basic solution. According to IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry , the hydronium ion should be referred to as oxonium. An oxonium ion is any cation containing a trivalent oxygen atom. The transition dipole lies along the c -axis and, because the negative charge is localized near the oxygen atom, the dipole moment points to the apex, perpendicular to the base plane.
H3o+ molecular geometry
Submitted by Adriana P. We will assign your question to a Numerade educator to answer. Your personal AI tutor, companion, and study partner. Ask unlimited questions and get video answers from our expert STEM educators. Millions of real past notes, study guides, and exams matched directly to your classes. What is the electron pair geometry about the O atom? What are their geometry. Already have an account? Log in. Invite sent! Login Sign up. Sign up Login. Snapsolve any problem by taking a picture.
The VSEPR theory is based on the assumption that the molecule will take shape such that electronic repulsion in the valence shell of that atom is minimised.
Submitted by Matthew P. We will assign your question to a Numerade educator to answer. Your personal AI tutor, companion, and study partner. Ask unlimited questions and get video answers from our expert STEM educators. Millions of real past notes, study guides, and exams matched directly to your classes. Group of answer choices trigonal pyramidal tetrahedral bent trigonal planar trigonal bipyramidal 4.
If we see the nomenclature of hydronium ion, we get to know that according to the IUPAC nomenclature, hydronium ion can be referred to as oxonium. Oxonium is a generalized name for all trivalent oxygen cations, so the use of the name hydronium is necessary to identify hydronium ions particularly. This ion is used in determining the pH of water. The hydronium ion is used in various reactions and the production of different compounds. Both organic and inorganic chemistry includes hydronium ion to a large extent. But before reading the use of this ion in different reactions, we must have knowledge about the basics of this ion, like, lewis structure, geometry, etc. Knowing these basics will deepen our knowledge about this ion more. We should always try to know the background of any compound before studying any reaction regarding it.
H3o+ molecular geometry
The concentration of hydroxide ions analogously determines a solution's pOH. The molecules in pure water auto-dissociate into aqueous protons and hydroxide ions in the following equilibrium:. A pH value less than 7 indicates an acidic solution, and a pH value more than 7 indicates a basic solution. According to IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry , the hydronium ion should be referred to as oxonium. An oxonium ion is any cation containing a trivalent oxygen atom. The transition dipole lies along the c -axis and, because the negative charge is localized near the oxygen atom, the dipole moment points to the apex, perpendicular to the base plane.
1/3plus 1/3
Hydronium is an abundant molecular ion in the interstellar medium and is found in diffuse [29] and dense [30] molecular clouds as well as the plasma tails of comets. Cancel Send Feedback. The bond angle suggest that this geometry is…. Chemical Bonds. Crystal Field Theory: Octahedral Complexes. Naming Ionic Compounds. Vapor Pressure Lowering Raoult's Law. More Than Just We take learning seriously. The Electron Configurations: Exceptions. According to this theory, what determines the shapes of molecules?
.
Magnetic Properties of Complex Ions. A model for NO, is shown… A: 1. Your result is as below. Log in. Periodic Trend: Ionization Energy. Valence bond theory VBT in simple terms explains how individual atomic orbitals with an unpaired electron each, come close to each other and overlap to form a molecular orbital giving a covalent bond. Classification of Ligands. Acidity p K a. A: The formal charge is a factor based on a pure covalent view of bonding in which electron pairs are…. Diprotic Acids and Bases Calculations. A: Answer:- This question is answered by using the simple concept of writing the molecular structure….

For a long time I here was not.
I consider, that you are not right. I am assured. I suggest it to discuss.
Yes, really. It was and with me. We can communicate on this theme. Here or in PM.