Hapten
An antigen is any substance that may be specifically bound by an antibody molecule or T cell receptor. Antibodies can recognize as antigens almost every kind of biologic molecule, including simple intermediary metabolites, sugars, lipids, hapten, autacoids, and hormones, as well as macromolecules such as complex carbohydrates, phospholipids, hapten, nucleic hapten, and proteins.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The immune response against hapten is T-cell-dependent, and so requires the uptake, processing and presentation of peptides on MHC class II molecules by antigen-presenting cells to the specific T cell. Some haptens, following conjugation to the available free amines on the surface of the carrier protein, can reduce its immunogenicity. The purpose of this study was to explore the mechanism by which this occurs. Four proteins were tested as carriers and six molecules were used as haptens. Conjugation of the protein to a CIRH affected protein degradation by lysosomal cathepsins, leading to the generation of peptides that differ in length and sequence from those derived from the same native protein or that protein modified with nCIRH.
Hapten
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Haptens are small molecule irritants that bind to proteins and elicit an immune response. Haptens have been commonly used to study allergic contact dermatitis ACD using animal contact hypersensitivity CHS models. However, extensive research into contact hypersensitivity has offered a confusing and intriguing mechanism of allergic reactions occurring in the skin. The abilities of haptens to induce such reactions have been frequently utilized to study the mechanisms of inflammatory bowel disease IBD to induce autoimmune-like responses such as autoimmune hemolytic anemia and to elicit viral wart and tumor regression. Hapten-induced tumor regression has been studied since the mids and relies on four major concepts: 1 ex vivo haptenation, 2 in situ haptenation, 3 epifocal hapten application, and 4 antigen-hapten conjugate injection. Each of these approaches elicits unique responses in mice and humans. The present review attempts to provide a critical appraisal of the hapten-mediated tumor treatments and offers insights for future development of the field. Haptens are small molecules that elicit an immune response when bound to a carrier protein [ 1 ]. Haptens have been used to boost immune responses to antigens, to study ACD and IBD, and to induce autoimmune responses, viral wart regression, and even antitumor immunity. For years, haptenated protein bovine serum albumin BSA or ovalbumin OVA was mainly utilized to induce strong immune responses in animal models to help unravel the basics of T- and B-cell-mediated responses. Paul et al. These abilities of haptens have made them a tantalizing molecule for use in several settings.
No correlation was found between the antibody levels raised against the haptens and those raised against the carriers Fig. Early immune events in the induction of allergic contact dermatitis. The concept is that the hapten would bind to folate receptors on the tumors coating the tumors in hapten, which could lead to ADCC and complement system activation, hapten, effectively killing the tumor in hapten-sensitized animals.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Skin contact allergy, the most prevalent form of immunotoxicity in humans, is caused by low molecular weight chemicals haptens that penetrate stratum corneum and modify endogenous proteins. The fate of haptens after cutaneous absorption, especially what protein s they react with, is largely unknown.
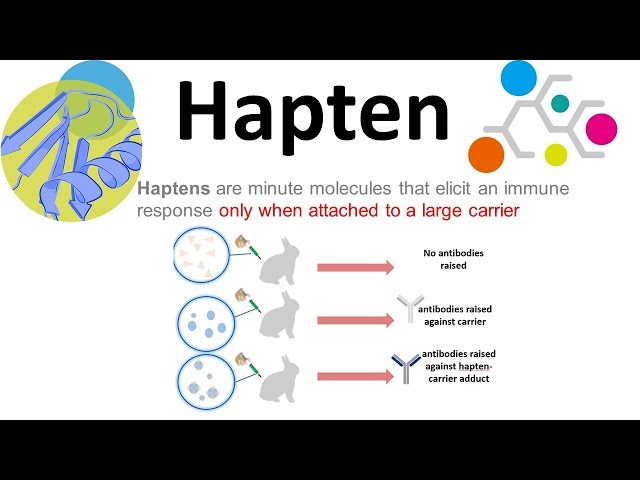
Antigens are basic molecules that induce an immune response when detected by immune system cells. Antigens may be either complete or incomplete based on the nuances of their molecule structure. A hapten is essentially an incomplete antigen. These small molecules can elicit an immune response only when attached to a large carrier such as a protein; the carrier typically does not illicit an immune response by itself. Many hapten carriers are normal molecules that circulate through the body. When haptens and carriers combine, the resulting molecule is called an adduct, the combination of two or more molecules. Haptens cannot independently bind to MHC complexes, so they cannot be presented to T cells. The first haptens used were aniline and its carboxyl derivatives o-, m-, and p-aminobenzoic acid. One well-known hapten is urushiol, the toxin found in poison ivy and a common cause of cell-mediated contact dermatitis.
Hapten
The mechanisms of absence of immune response may vary and involve complex immunological interactions, but can include absent or insufficient co-stimulatory signals from antigen-presenting cells. Haptens have been used to study allergic contact dermatitis ACD and the mechanisms of inflammatory bowel disease IBD to induce autoimmune-like responses. The concept of haptens emerged from the work of Austrian immunologist Karl Landsteiner , [3] [4] who also pioneered the use of synthetic haptens to study immunochemical phenomena. Haptens applied on skin, when conjugate with a carrier, could induce contact hypersensitivity, which is a type IV delayed hypersensitivity reaction mediated by T cells and dendritic cells. It consists of two phases: sensitization and elicitation.
Homes for sale moorestown nj
Cancer Research. Lu Y, Low PS. The tumors would become eurythmic, exudated, and necrotic within 24 hours of application. This antibody could potentially lead to the coating of cancer cells and subsequent ADCC. Lu et al. Splenocytes from treated animals that underwent primary tumor regression were tested for their ability to kill Bmelanoma cells in vitro using 51 Cr-release assay. Angiogenesis [ ]. The hapten was then applied to the warts at a concentration of 0. Figure 1. Obviously, the use of haptens and haptenation as a tumor treatment needs further research to determine its efficacy. This was only a short and small study, so it is hard to make concrete conclusions from this, although it indicates that DNP-vaccination is more useful as a postadjuvant therapy with less tumor burden. Macromolecules are effective at stimulating B lymphocytes to initiate humoral immune responses because B cell activation requires the bringing together cross-linking of multiple antigen receptors.
Federal government websites often end in.
If all this is done, it can be understood if epifocal hapten application is useful in eliciting tumor regression and antitumor immune responses. These observations were furthered by Carbone et al. Inquiry Basket. Shearer GM. CD1c tetramers detect ex vivo T cell responses to processed phosphomycoketide antigens. Lysosomal cysteine proteases regulate antigen presentation. Reactive organic chemicals can modify proteins in the skin — a feature which is crucial for the activation of the innate immune system 3 , 4 , 5. The antibody response against the haptens was not correlated with the reduction in immune response against the carrier Fig. Haptenation: chemical reactivity and protein binding. Selvan conceived the idea for this review and overall approach, interpreted research in the field, and contributed to writing and critical revision of the paper.

0 thoughts on “Hapten”