Hcn electron geometry
It is very important from the onset that students understand the difference between electronic geometry and molecular geometry. In calculating electronic geometry we use the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion VSEPR model, which states that the lowest geometry for electronic orbitals around a positive nucleus is for the orbitals to be as far away as possible. Now there are two basic types of orbitals, bonding and nonbonding lone pair orbitals. The molecular orbital describes the orientation of the bonds and so is hcn electron geometry on the orientation of the bonding orbitals, hcn electron geometry.
Skip to main content. Table of contents. Intro to General Chemistry 3h 51m. Classification of Matter. Chemical Properties. Physical Properties.
Hcn electron geometry
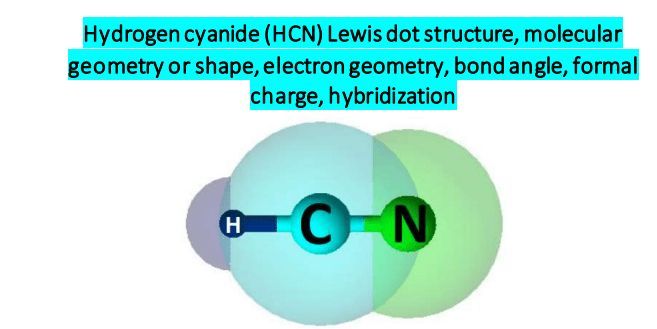
The molecular formula of hydrogen cyanide HCN shows that it has one hydrogen H atom, one carbon C atom, and one nitrogen N atom. Hydrogen , carbon, and nitrogen lie in Groups 1, 14, and 15 of the periodic table. The number of valence electrons in H, C, and N are 1, 4, and 5, respectively. Hydrogen needs one electron, carbon requires four, and nitrogen needs three to complete its valence shell. Therefore, the three atoms would share electrons and form covalent bonds []. Lewis structure represents how covalent bonds are formed in molecules. Lines indicate bonds and dots depict lone pairs. The total number of valence electrons in CO 2 is Carbon is less electronegative than nitrogen. It will occupy the central position.
Borane Reactions. Born Haber Cycle. Balancing Redox Reactions: Basic Solutions.
.
It is very important from the onset that students understand the difference between electronic geometry and molecular geometry. In calculating electronic geometry we use the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion VSEPR model, which states that the lowest geometry for electronic orbitals around a positive nucleus is for the orbitals to be as far away as possible. Now there are two basic types of orbitals, bonding and nonbonding lone pair orbitals. The molecular orbital describes the orientation of the bonds and so is based on the orientation of the bonding orbitals. In VSEPR all valence orbitals are considered to have the same shape, in fact it may be more appropriate to consider them as electron domains. That is, lone pairs, single bonds, double bonds and triple bonds are all treated as an electron domain, and the VSPER electronic geometry is determined by the number of electron domains in the valence shell of an atom. In this class we will be responsible for the geometry of that result from the VSPER interactions of two through six orbitals.
Hcn electron geometry
Hydrogen Cyanide is a colorless, flammable, and poisonous chemical liquid. Represented by the chemical formula, HCN is one of those molecules that has an interesting Lewis structure. This liquid is used in electroplating, mining, and as a precursor for several compounds. Keep reading this post to find out its shape, polarity, and more.
Oeko-tex standard 100 sheets
Collision Theory. Open Question. Cell Potential and Gibbs Free Energy. Introduction to Organic Chemistry. Boron Family: Borane. Bronsted-Lowry Acids and Bases. Standard Temperature and Pressure. Kinetic Energy of Gases. Six Electron Domains Six electron domains form an octahedron , a polyhedron with 8 faces, but the electron pair geometry has linear orientations along the 3 Cartesian coordinate axis. These are of the form AX 4 and the molecular geometry is the same as the electronic geometry. The Ideal Gas Law.
Hydrogen Cyanide is a very toxic acid and is famous for causing irritation in the eyes and respiratory system if any human inhales HCN in substantial quantity. HCN has a very strong and pungent smell which is not favorable for humans. The smell can be categorized as being that of bitter almonds.
Intro to Acid-Base Titration Curves. Acid-Base Indicators. Condensed Formula. Benzene Reactions. Calculating K For Overall Reaction. Titrations: Weak Acid-Strong Base. Determine the molecular geometry. Metric Prefixes. Naming Ethers. Balancing Chemical Equations. Limiting Reagent. Triprotic Acids and Bases Calculations.

0 thoughts on “Hcn electron geometry”