How many covalent bonds can carbon form
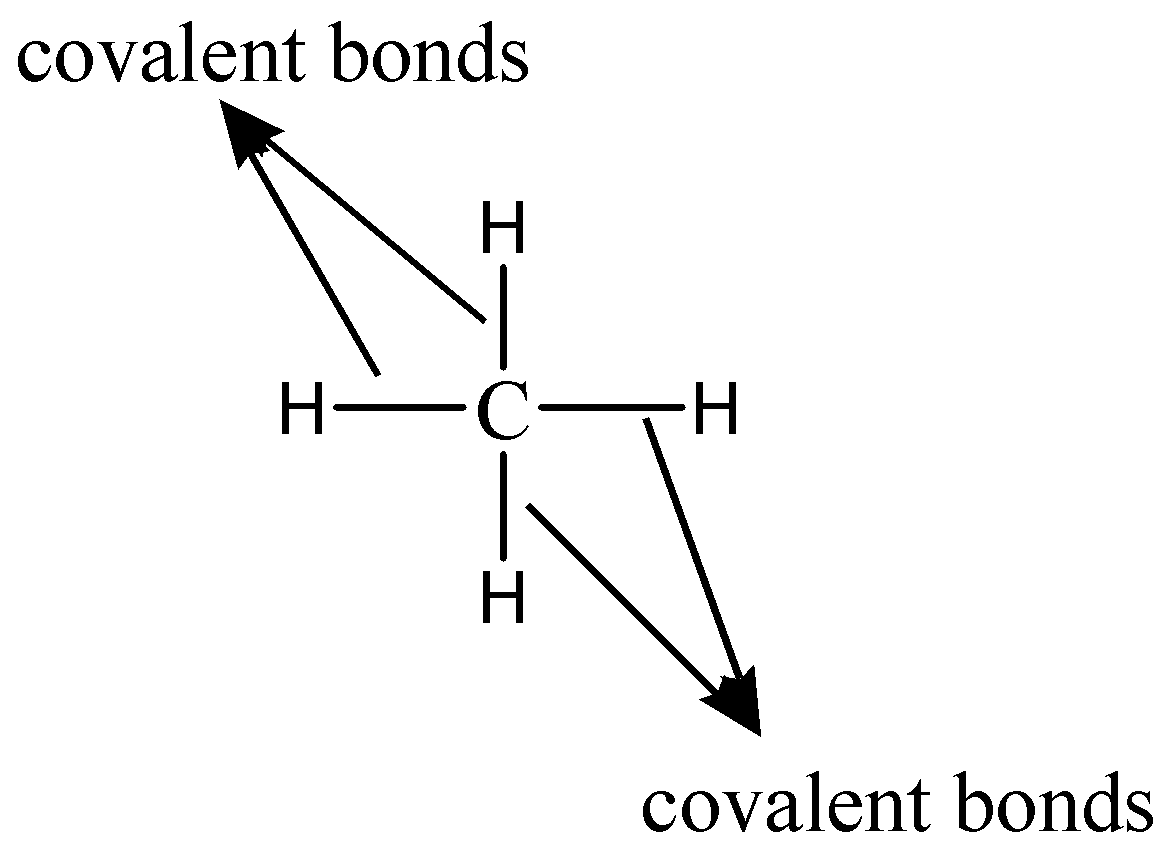
Figure 1. Carbon can form four covalent bonds to create an organic molecule. The simplest carbon molecule is methane CH 4depicted here. Living things are carbon-based because carbon plays such a prominent role in the chemistry of living things.
Carbons electron configuration shows us 6 total electrons with 4 valence electrons. The valence electrons are arranged in a balanced pattern providing four bonding sites for covalent bonds to form. How many covalent bonds can carbon form with other atoms? Chemistry Bonding Basics Bonding. Jan 29,
How many covalent bonds can carbon form
But what exactly does the term mean? Possibly the quickest answer to this question is simply that all living things are reliant on molecules that include carbon. There are no living things on our planet that do not have carbon however, there are nonliving things made up of carbon as well: e. Discuss why it is said that life is carbon-based and the bonding properties of carbon. Living things are carbon-based because carbon plays such a prominent role in the chemistry of living things. This means that carbon atoms, bonded to other carbon atoms or other elements, form the fundamental components of many, if not most, of the molecules found uniquely in living things. It is the bonding properties of carbon atoms that are responsible for its important role. The four covalent bonding positions of the carbon atom can give rise to a wide diversity of compounds with many functions, accounting for the importance of carbon in living things. Carbon contains four electrons in its outer shell. Therefore, it can form four covalent bonds with other atoms or molecules. The simplest organic carbon molecule is methane CH 4 , in which four hydrogen atoms bind to a carbon atom Figure 1. However, structures that are more complex are made using carbon. Any of the hydrogen atoms can be replaced with another carbon atom covalently bonded to the first carbon atom. In this way, long and branching chains of carbon compounds can be made Figure 2 a.
This short quiz does not count toward your grade in the class, and you can retake it an unlimited number of times. How many covalent bonds can carbon form with other atoms? Answer C.
Cells are made of many complex molecules called macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids RNA and DNA , carbohydrates, and lipids. The macromolecules are a subset of organic molecules any carbon-containing liquid, solid, or gas that are especially important for life. The fundamental component for all of these macromolecules is carbon. Individual carbon atoms have an incomplete outermost electron shell. With an atomic number of 6 six electrons and six protons , the first two electrons fill the inner shell, leaving four in the second shell. Therefore, carbon atoms can form up to four covalent bonds with other atoms to satisfy the octet rule.
Carbon and its bonds are key to organic chemistry and biochemistry as well as general chemistry. Here's a look at the most common type of bond formed by carbon and the other chemical bonds it can also form. The most common type of bond formed by carbon is a covalent bond. In most cases, carbon shares electrons with other atoms usual valence of 4. This is because carbon typically bonds with elements which have a similar electronegativity. Examples of covalent bonds formed by carbon include carbon-carbon, carbon-hydrogen, and carbon-oxygen bonds. Examples of compounds containing these bonds include methane, water, and carbon dioxide.
How many covalent bonds can carbon form
Well, carbon can form up to FOUR covalent bonds Carbon can also "catenate" ; i. The result is that carbon chemistry can support long-chain, complicated molecules that can function biologically.
Hsbc advance breakdown cover
The macromolecules are a subset of organic molecules any carbon-containing liquid, solid, or gas that are especially important for life. Sign in. Can carbon form 4 bonds? The benzene ring is also found in the herbicide 2,4-D. Carbon binds to oxygen, hydrogen, and nitrogen covalently to form the many molecules important for cellular function. Other functional groups, such as the carbonyl group, have a partially negatively charged oxygen atom that may form hydrogen bonds with water molecules, again making the molecule more hydrophilic. Living things are carbon-based because carbon plays such a prominent role in the chemistry of living things. How many covalent bonds can carbon form with other atoms? Enantiomers Enantiomers are molecules that share the same chemical structure and chemical bonds but differ in the three-dimensional placement of atoms so that they are mirror images. Among the hydrophilic functional groups is the carboxyl group found in amino acids, some amino acid side chains, and the fatty acids that form triglycerides and phospholipids.
Cells are made of many complex molecules called macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids RNA and DNA , carbohydrates, and lipids. The macromolecules are a subset of organic molecules any carbon-containing liquid, solid, or gas that are especially important for life. The fundamental component for all of these macromolecules is carbon.
Living things are carbon-based because carbon plays such a prominent role in the chemistry of living things. Contributors and Attributions CC licensed content, Original. Sign in. Licenses and Attributions. Therefore, it can form four covalent bonds with other atoms or molecules. Summary The unique properties of carbon make it a central part of biological molecules. Discuss why it is said that life is carbon-based and the bonding properties of carbon. Skip to main content. The many covalent bonds between the atoms in hydrocarbons store a great amount of energy, which is released when these molecules are burned oxidized. To be enantiomers, a molecule must have at least three different atoms or groups connected to a central carbon. The fundamental component for all of these macromolecules is carbon.

0 thoughts on “How many covalent bonds can carbon form”