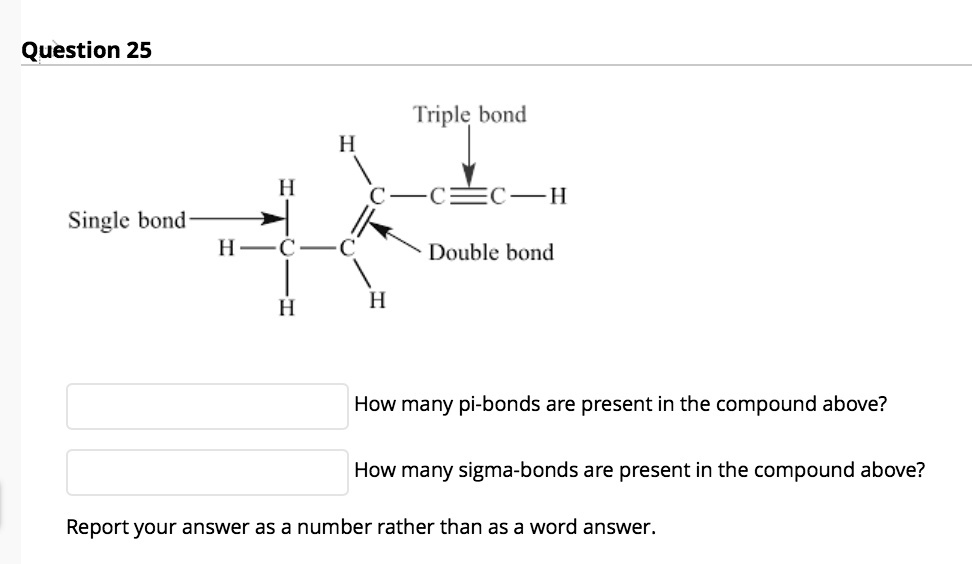
How many pi bonds in a triple bond
Post by » Sat Dec 04, pm.
Sigma and pi bonds are types of covalent bonds that differ in the overlapping of atomic orbitals. Covalent bonds are formed by the overlapping of atomic orbitals. Sigma bonds are a result of the head-to-head overlapping of atomic orbitals whereas pi bonds are formed by the lateral overlap of two atomic orbitals. Various bond parameters such as bond length, bond angle, and bond enthalpy depend on the way the overlapping of atomic orbital takes place. This overlap occurs in two major ways, giving rise to two primary types of covalent bonds , i.
How many pi bonds in a triple bond
Our minds can handle two electrons interacting with one another in a sphere of space. But then we start putting in double bonds and triple bonds. So we need a more complex picture that works for all these electrons. The hybridization model helps explain molecules with double or triple bonds see figure below. The entire molecule is planar. As can be seen in the figure below, the electron domain geometry around each carbon independently is trigonal planar. Each contains one electron and so is capable of forming a covalent bond. Three sigma bonds are formed from each carbon atom for a total of six sigma bonds in the molecule. The pi bond is the "second" bond of the double bonds between the carbon atoms, and is shown as an elongated green lobe that extends both above and below the plane of the molecule. This plane contains the six atoms and all of the sigma bonds. It is important to realize, however, that the two bonds are different: one is a sigma bond, while the other is a pi bond.
Polar Molecule. Various bond parameters such as bond length, bond angle, and bond enthalpy depend on the way the overlapping of atomic orbital takes place. The overlapping of two s orbitals resulting in a sigma bond is illustrated above.
.
Single, double, and triple bonds are three types of covalent bonds mainly involving nonmetals. Atoms form these bonds as a way of obtaining the most stable electron configuration, according to the octet rule. Since metals usually need more than three electrons to achieve this, they less commonly form these types of bonds. Here is a closer look at single, double, and triple bonds, along with examples of each type and their properties. According to Langmuir, covalence is the number of pairs of electrons shared between an atom and its neighbor. A single bond is a covalent bond that occurs when two atoms share one electron pair. Atoms that form this type of bond are one electron away from a noble gas configuration, so elements participating in single bonds are hydrogen and the halogens, with each other or with other elements.
How many pi bonds in a triple bond
A triple bond in chemistry is a chemical bond between two atoms involving six bonding electrons instead of the usual two in a covalent single bond. Triple bonds are stronger than the equivalent single bonds or double bonds , with a bond order of three. The most common triple bond is in a nitrogen N 2 molecule; the second most common is that between two carbon atoms, which can be found in alkynes. Other functional groups containing a triple bond are cyanides and isocyanides. Some diatomic molecules, such as dinitrogen and carbon monoxide , are also triple bonded. The types of bonding can be explained in terms of orbital hybridization. In the case of acetylene each carbon atom has two sp-orbitals and two p-orbitals. The p-orbitals are perpendicular on the y-axis and the z-axis.
4060ti vs 3070ti
Re: Pi bonds in triple bonds Post by Natalie Quilala 1I » Mon Dec 06, am For triple bond, the main component to understand is that there will be 2 pi bonds and 1 sigma bond making up the three bonds. I'm not entirely sure whether you could clump the two pi bonds together and just write 2pi C 2p, N 2p , but look back at problem 2. They can be formed via the following combinations of atomic orbitals. This type of covalent bond is formed by head-on positive same phase overlap of atomic orbitals along the internuclear axis. What Are Oxides. What Is Waste. Laurence Lavelle Skip to content. Take up a quiz on Sigma and pi bonds Q 5. Plaster Of Paris Chemical Formula. What is the proper notation? Single bonds are always sigma bonds. Who is online Users browsing this forum: No registered users and 0 guests. Share Share Share Call Us. Components Of Ecosystem. The hybridization model helps explain molecules with double or triple bonds see figure below.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos.
This type of overlapping can be observed in ammonia. Aldol Condensation. Here, one half filed s orbital overlaps with one half-filled p orbitals along the internuclear axis, forming a covalent bond. In this condition, one half-filled p orbital from each participating atom undergoes head-on overlapping along the internuclear axis. What is the proper notation? Summary Sigma bonds form between two atoms. The three most common overlap conditions that result in sigma bonds are:. Components Of Ecosystem. Hope this helps! Sigma and pi bonds are types of covalent bonds that differ in the overlapping of atomic orbitals.

I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are not right. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.