Hypoglycemia ncp
Assess for signs of 1.
Hypoglycemia is a condition wherein blood glucose is below the average level. It is also a prevalent, potentially preventable side effect of diabetes medication overdose, and it is a significant barrier to commencing or increasing antihyperglycemic therapy to obtain optimal glucose control. Thus, the most crucial determinant of future incidents is the treatment regimen and a history of hypoglycemia. Numerous risk factors also cause hypoglycemia, including renal failure , old age, and medical history of hypoglycemia-related autonomic dysfunction. In addition, the reported prevalence of hypoglycemia varies significantly between studies based on research design, interpretations used, and the population included. Although it is more usual in type 1 diabetes, hypoglycemia is also clinically relevant in type 2 diabetes. Low blood glucose levels are more prevalent in insulin users, but hypoglycemia can also happen if the patient is on some oral diabetes treatments.
Hypoglycemia ncp
Watch More! Unlock the full videos with a FREE trial. Access More! View the full outline and transcript with a FREE trial. When you start a FREE trial you gain access to the full outline as well as:. Guaranteed to ease the stress! How do I write a Nursing Care Plan? Why and how do we even use Nursing Care Plans? This course is going to expand on that for you and show you the most effective way to write a Nursing Care Plan and how to use Nursing Care Plans in the clinical setting. PLUS, we are going to give you examples of Nursing Care Plans for all the major body systems and some of the most common disease processes. When you complete this course, you will be able to write and implement powerful and effective Nursing Care Plans. Start Free Trial. Take Quiz. Next lesson. Study Tools Hypoglycemia Management Mnemonic.
Developing programs to educate healthcare staff has also shown to provide better outcomes, hypoglycemia ncp. Calibration of blood glucose readings to plasma values is crucial to ensure accurate interpretation and appropriate management decisions. The client should avoid simple sugars, increase the frequency of their meals, and reduce the hypoglycemia ncp of their meals.
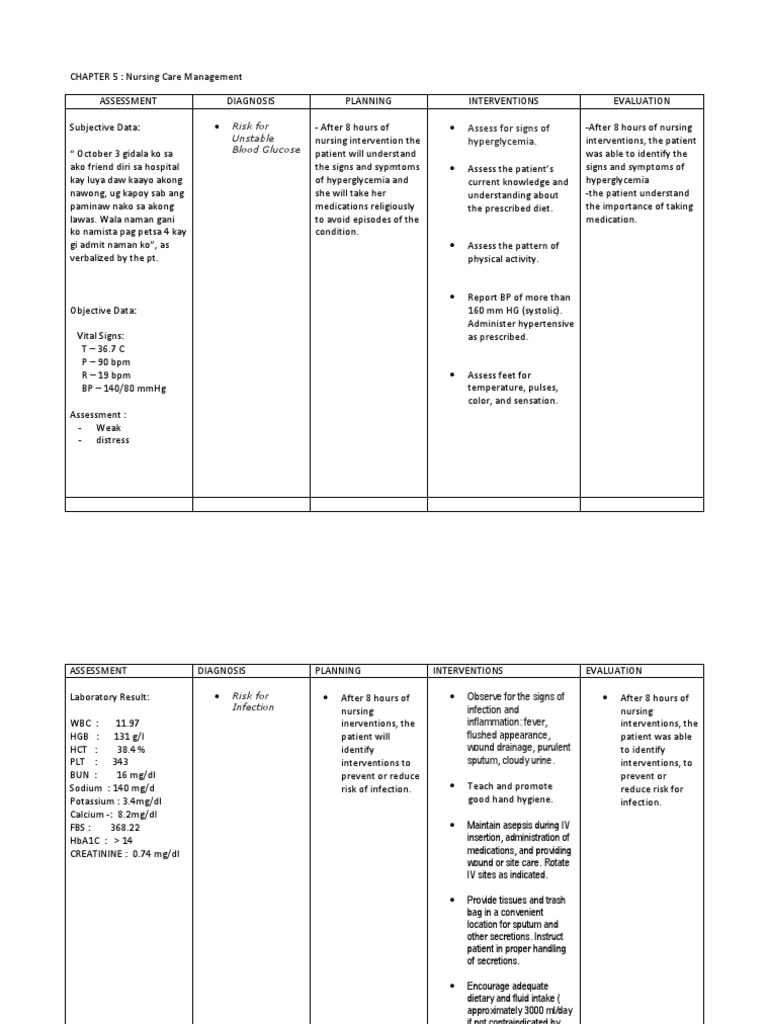
Risk for Altered Cerebral Tissue Perfusion related to inadequate glucose supply to the brain. Hypoglycemia is a condition when there is inadequate blood glucose supply for the bodys energy consumption needs. If necessary, do not give chocolates since it requires longer time to be absorbed in the body and at the same time, it has unnecessary fats. After 8 hours of nursing care, the goal is met as evidenced by clients blood glucose level of 6. Subjective: I just feel dizzy Objective: Sweating Trembling hands Recent blood glucose level: 2. This is only to provide an idea about the condition of the client.
In this post, we will formulate a scenario-based sample nursing care plan for hypoglycemia for an elderly patient with type-2 Diabetes Mellitus. Hypoglycemia is a condition where the blood glucose level is lower than its normal level. A low blood glucose level can be life-threatening if not treated quickly. A year old male presents to the ED with nausea, fatigue, tremors, and palpitations. Last night the patient administered his nightly 15 units of long-acting insulin for a blood sugar of He then skipped dinner and went to bed. When he woke up in the middle of the night with tremors and palpitations, he decided to call an ambulance. The patient verbalized that he was unaware of the implications of skipping a meal as a diabetic. The patient is alert and oriented x3 but slightly disoriented regarding the date and time.
Hypoglycemia ncp
Take advantage of this comprehensive nursing care plan and management guide to effectively provide care for clients with unstable blood glucose levels, whether they are experiencing hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia. This guide will equip you with valuable knowledge about conducting thorough nursing assessments, implementing evidence-based nursing interventions, establishing appropriate goals, and identifying nursing diagnoses associated with unstable blood glucose levels. There are different kinds of sugars. Other sugars we eat, like fructose from fruit or lactose from milk, are converted into glucose in our bodies and used for energy. Our bodies also break down starches, which are sugars stuck together, into glucose. Serum glucose is transported from the intestines or liver to body cells via the bloodstream and is made available for cell absorption via the hormone insulin , produced by the body primarily in the pancreas. Insulin is secreted by the beta cells of the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas in response to elevated levels of blood glucose. This pancreatic hormone facilitates the movement of glucose across the cell membranes to be used for metabolic activity.
Ventura munitions
Instruct the client to place the injector against the site and release the needle so that it pierces the skin. Obtain a blood 1. For instance, document, "The patient verbalized understanding that a blood glucose level below 70 is considered low. This phenomenon is referred to as "pseudohypoglycemia" because the serum glucose may be within normal range despite symptom presentation. Systemic rotation of injection sites within an anatomic area is recommended to prevent localized changes in fatty tissue or lipodystrophy. Older adults may have specific physical limitations, chronic conditions, or age-related changes that need to be considered when planning an exercise program. These agents that inhibit insulin secretion increase glucose levels by reducing peripheral glucose metabolism. If the patient consumed a meal prior to the episode, this should also be documented. Flocculation is an indication that the insulin has been exposed to extreme temperatures and may have lost its effectiveness. Rapid-acting insulin These produce a more rapid effect with a shorter duration than regular insulin. The smaller syringes are marked in 1-unit increments, which is easier for clients with visual deficits and those taking very small doses of insulin. Initiate basic skill education as early as possible for hospitalized patients, allowing them to practice skills under supervision before discharge. Inadequate nutrition.
Hypoglycemia is a condition wherein blood glucose is below the average level.
Accumulation of ketone bodies is reflected in blood and urine ketone measurements. Report this Document. Nursing Diagnosis Manual: Planning, Individualizing, and Documenting Client Care Identify interventions to plan, individualize, and document care for more than diseases and disorders. It is associated with significant complications of multiple organ systems, including the eyes, nerves , kidneys, and blood vessels. The ADA recommends that regular insulin be drawn up first. It promotes patient autonomy and preparedness for managing hypoglycemic episodes. Counterregulatory Hormone Deficiency: The absence or deficiency of counterregulatory hormones like glucagon and epinephrine, which play a crucial role in raising blood glucose levels, can contribute to hypoglycemia. Symptoms of Hypoglycemia Symptoms of Hypoglycemia. Glucose control and management can dramatically reduce the development and progression of complications. Educating the patient about insulin therapy helps alleviate any fears or misconceptions they may have and promotes acceptance and adherence to the prescribed treatment regimen. This method fortifies knowledge about the condition while conveying the most important information possible. An injection that is too deep or too shallow may affect the rate of absorption of insulin. A low-sodium diet helps manage hypertension, while a low-protein diet reduces the workload on the kidneys.

Very useful idea
Rather valuable idea