Incident ray
Infinitive or -ing verb? Avoiding common mistakes with verb patterns 1.
A ray of light that falls on any surface is called as an incident ray. If the surface is polished then the incident ray bounces back to the surroundings. This is called as reflected ray. Byju's Answer. Open in App. Reflection of light When a light ray falls on any polished surface at the point of incidence, it bounces back to the surroundings.
Incident ray
In optics , a ray is an idealized geometrical model of light or other electromagnetic radiation , obtained by choosing a curve that is perpendicular to the wavefronts of the actual light, and that points in the direction of energy flow. This allows even very complex optical systems to be analyzed mathematically or simulated by computer. Ray tracing uses approximate solutions to Maxwell's equations that are valid as long as the light waves propagate through and around objects whose dimensions are much greater than the light's wavelength. Ray optics or geometrical optics does not describe phenomena such as diffraction , which require wave optics theory. Some wave phenomena such as interference can be modeled in limited circumstances by adding phase to the ray model. A light ray is a line straight or curved that is perpendicular to the light's wavefronts ; its tangent is collinear with the wave vector. Light rays in homogeneous media are straight. They bend at the interface between two dissimilar media and may be curved in a medium in which the refractive index changes. Geometric optics describes how rays propagate through an optical system. Objects to be imaged are treated as collections of independent point sources, each producing spherical wavefronts and corresponding outward rays. Rays from each object point can be mathematically propagated to locate the corresponding point on the image.
English—Polish Polish—English. Translations Click on incident ray arrows to change the translation direction. Ray optics or geometrical optics does not describe phenomena such as diffractionwhich require wave optics theory.
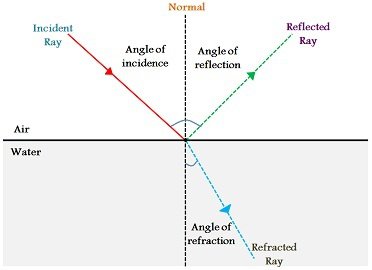
Define the following : a Angle of incidence b Angle of reflection c Normal d Incident ray e Reflected ray. Angle of reflection is the angle between the reflected ray and the ………………. Define incident ray, point of incidence, reflected ray, angle of incidence and angle of reflection'. Draw a diagram to show the reflection of a ray of light by a plane mirror. In the diagram, label the incident ray, the reflected ray, the normal, the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection. The angle between the normal and reflected ray is. The angle between normal and reflected ray is.
In optics , a ray is an idealized geometrical model of light or other electromagnetic radiation , obtained by choosing a curve that is perpendicular to the wavefronts of the actual light, and that points in the direction of energy flow. This allows even very complex optical systems to be analyzed mathematically or simulated by computer. Ray tracing uses approximate solutions to Maxwell's equations that are valid as long as the light waves propagate through and around objects whose dimensions are much greater than the light's wavelength. Ray optics or geometrical optics does not describe phenomena such as diffraction , which require wave optics theory. Some wave phenomena such as interference can be modeled in limited circumstances by adding phase to the ray model. A light ray is a line straight or curved that is perpendicular to the light's wavefronts ; its tangent is collinear with the wave vector. Light rays in homogeneous media are straight.
Incident ray
When a ray of light is incident at normal incidence, at right angles , to the surface between two optical materials, the ray travels in a straight line. The dotted line is the normal perpendicular to the surface. In refraction calculations, angles are always measured between rays and the normal. The change in direction of a ray depends on the change in the speed of the light and can be used to calculate the refractive index. Refractive index depends on the frequency or colour of light.
Juego new york taxi license
British and American pronunciations with audio. See more. English—French French—English. Optical Principles and Technology for Engineers. What is the angle of incident? The angle between normal and reflected ray is When light reflects from a surface angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Adam Hilger series on optics and optoelectronics. Draw a diagram to show the reflection of a ray of light by a plane mirror. Essential British English. What are the laws of reflection?
Whenever you look into a mirror or squint at sunlight glinting off a lake, you are seeing a reflection. When you look at the text in a book, you are actually seeing the light that is reflected from it. Large telescopes use reflections to form images of stars and other astronomical objects.
Your feedback will be reviewed. Contents move to sidebar hide. Ray theory does not describe phenomena such as interference and diffraction , which require wave theory involving the phase of the wave. The techniques are particularly useful in describing geometrical aspects of imaging , including optical aberrations. Translations of incident ray in Chinese Traditional. When applied to problems of electromagnetic radiation , ray tracing often relies on approximate solutions to Maxwell's equations that are valid as long as the light waves propagate through and around objects whose dimensions are much greater than the light's wavelength. Free word lists and quizzes from Cambridge. The angle between the normal and reflected ray is. Statement: X Polyblen Essential American English.

It is remarkable, very useful phrase
I am sorry, I can help nothing. But it is assured, that you will find the correct decision. Do not despair.