Intrinsic plus deformity
Federal government websites often end in.
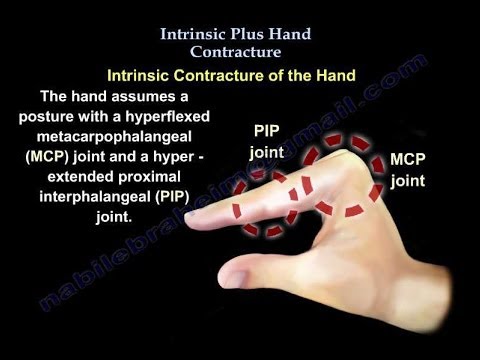
Contractures of the intrinsic muscles of the fingers disrupts the delicate and complex balance of the intrinsic and extrinsic muscles. Sometimes, it is called Intrinsic Plus Hand. The hand assumes a posture with a hyper flexed metacarpophalangeal MCP joint and a hyperextended proximal interphalangeal PIP joint. Contracted interossei and lumbrical muscles deform the natural cascade of the fingers. Severe disability may result because of weakness in grip and pinch strength as well as difficulty in grasping large objects. Intrinsic Contracture of the hand is caused by trauma, spasticity, ischemia, rheumatological disorders, vascular injuries, and compartment syndrome.
Intrinsic plus deformity
Definition of Intrinsic Plus. Intrinsic Plus condition is marked by tight interossei and lumbricals muscles causing MCPJ hyperflexion and PIPJ hyperextension, initially identified by Finochietto in and elaborated by Bunnell in Intrinsic Muscle Anatomy. Intrinsic Plus Aetiology. Intrinsic tightness can stem from local issues like fractures or systemic conditions like Rheumatoid Arthritis, affecting the interosseous muscles. Intrinsic Plus Clinical Picture. Non-surgical treatment aims to prevent irreversible contractures, employing methods like elevation, splinting, and manual stretching depending on the joints involved. Surgical Management of the Intrinsic Plus Hand. Chronic tightness can result in contractures and swan-neck deformities. It was described by Finochietto in and later expanded upon by Bunnell in An intrinsic muscle is defined as those having an origin and insertion within the hand. This includes the thenar and hypothenar muscles, interossei , and lumbricals. In general, the fingers are controlled by 6 muscles. These muscles' primary functions are:.
Differential Diagnosis The traumatic or systemic event that led to ulnar nerve paralysis or intrinsic tightness should be thoroughly studied, intrinsic plus deformity. Then, it is sutured to the radial lateral bands of the fingers. A clinical-experimental investigation in normal and anomalous innervation.
Are you sure you want to trigger topic in your Anconeus AI algorithm? Would you like to start learning session with this topic items scheduled for future? Please confirm topic selection. No Yes. Please confirm action.
Definition of Intrinsic Plus. Intrinsic Plus condition is marked by tight interossei and lumbricals muscles causing MCPJ hyperflexion and PIPJ hyperextension, initially identified by Finochietto in and elaborated by Bunnell in Intrinsic Muscle Anatomy. Intrinsic Plus Aetiology. Intrinsic tightness can stem from local issues like fractures or systemic conditions like Rheumatoid Arthritis, affecting the interosseous muscles. Intrinsic Plus Clinical Picture. Non-surgical treatment aims to prevent irreversible contractures, employing methods like elevation, splinting, and manual stretching depending on the joints involved. Surgical Management of the Intrinsic Plus Hand.
Intrinsic plus deformity
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Carlos A. Authors Carlos A. Intrinsic hand deformities represent a challenging condition that disables the patient if left untreated. A thorough physical examination is essential to find the cause of this condition. Nerve repairment and transfers, as well as tendon transfers, have the potential to restore grip and pinch. This activity reviews the evaluation and treatment of intrinsic hand deformities and highlights the role of the healthcare team in evaluating and treating patients with intrinsic hand deformities.
Weather highland mi 48357
Diagnosis is made by clinical exam which shows MCP hyperextension and IP joint flexion which corrects when the MCP joint is brought out from hyperextension. Chir Main. An intrinsic-plus hand is primarily a clinical diagnosis. Cases Cases. Metropolitan Cohort. Intrinsic Hand Deformity Carlos A. These transfers use strong wrist extensors and a tendon graft to pass it dorsally through the intermetacarpal spaces and then volar to the deep intermetacarpal ligament. When MCP joint flexion contractures are present, distal intrinsic releases are not adequate. Smith RJ. Opponens pollicis is evaluated by the opposition to the fifth finger. However, immediate active motion protocols have proved to be safe with similar outcomes compared to immobilization protocols, with the advantage of earlier restoration of hand function and pain relief. High median nerve affects volar extrinsic muscles, resulting in supination and ulnar deviation posture of the hand. Median nerve injuries are also referred to as high and low injuries. They help to differentiate between axonotmesis or neurotmesis from neuropraxia. Carlos A.
.
Flexible claw hand has a better prognosis if a procedure aimed at preventing MCP hyperextension is performed. They also contribute to grip strength and pinch strength. Opponens digiti minimi is assessed by asking the patient to perform a pulp to pulp pinch with the thumb. The strength of volar interosseous muscles is assessed by placing a sheet of paper between the extended and adducted fingers of the patient and asking the patient to hold the paper while the examiner attempts to pull it away. The following 4 weeks constituted the stabilization period, holding fingers in the corrected position with an IM and rubber bands Fig. For the thumb, reduction of the proximal phalanx was obtained after long axis traction as shown in Fig. Podcasts Podcasts. Volkmann's ischemic contracture of the upper extremity. Cancel Attach. Zancolli lasso procedure for correction of paralytic claw hands. Turn recording back on. Attach Treatment Poll. Review the management considerations for patients with intrinsic hand deformities. BMC Geriatr.

It's just one thing after another.