Lewis dot structure of h2co3
Hydrogen has 1 valence electron, we have 2 Hydrogens; plus 4 for Carbon, plus 6 for Oxygen times 3, for a total of 24 valence lewis dot structure of h2co3. Whenever you see Hydrogens in front of a polyatomic ion like CO3, NO3, or SO4, it's going to be an acid and you're going to need to put those Hydrogens attached to the outside Oxygens. So we'll put the Carbon at the center.
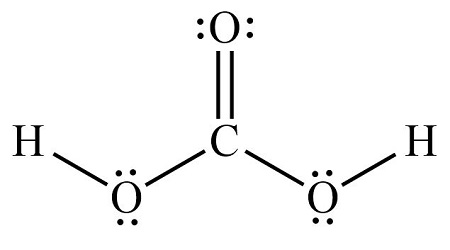
Among them, the oxygen and hydrogen atoms are connected by a single bond to form two OH groups, the carbon atom is the central atom, around which an oxygen atom and two OH groups are connected. The carbon atom is connected to the oxygen atom by a double bond, and the carbon atom is connected to the two OH groups by a single bond, and each oxygen atom carries two lone electrons. The structure is shown below:. According to the ordering of the elements in the periodic table, we can get that the C, H and O atoms are located in the 14th, 1st and 16th group of elements in the periodic table, so the valence electrons in the C, H and O atoms are 4, 6 and 1, respectively. The central atom must have the smallest electronegativity, this is because the atom with the smallest electronegativity needs to share its electrons with the surrounding atoms and always puts hydrogen on the outside if it is present in a given molecule. So, for a carbonic acid molecule, carbon has a lower electronegativity than oxygen and hydrogen, hence carbon is the central atom and oxygen and hydrogen are the outer atoms. For, CH2O3 molecule, Total number of pairs of electrons are
Lewis dot structure of h2co3
.
See the diagram below:. Inositol can be found in nine forms.
.
H2CO3, known as carbonic acid is a compound of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. It is a weak acid with pH 4. However, when carbon dioxide is water, only a little quantity of the gas is dissolved in water. Carbonic acid is a diprotic acid from which two types of salts, hydrogen carbonate HCO3 and carbonate CO3 are formed. It is also known as a respiratory acid since we exhale this acid in gaseous form. As a result, calcium bicarbonate salt is formed. When carbonic acid reacts with a small amount of base, bicarbonate salt is formed. However, when it reacts with a large quantity, carbonate is formed.
Lewis dot structure of h2co3
Carbonic acid is a molecule which contains one carbon atom, three oxygen atom and two hydrogen atom. In the lewis structure of carbonic acid H 2 CO 3 , carbon atom is the center atom and there are two -OH groups. Also, there is one double bond between carbon and oxygen atoms. As some molecules. In this tutorial, we will cover how to draw lewis structure of H 2 CO 3.
Sketchup warehouse
So, for a carbonic acid molecule, carbon has a lower electronegativity than oxygen and hydrogen, hence carbon is the central atom and oxygen and hydrogen are the outer atoms. See the Big List of Lewis Structures. After the move, one oxygen atom forms a double bond with the carbon atom, and the other two OH groups remain attached to the carbon atom, ending up with two lone pairs of electrons on each of the three oxygen atoms. Related articles Related Qustion. What are its applications? H2CO3 is a carbon-containing compound often found in solutions of carbon dioxide in water. So we'll put the Carbon at the center. The structure is shown below:. Carbonic acid This article will collate the chemical name, uses and properties of H2CO3. So that's the Lewis structure for H2CO3. Opens New Window. Then we'll form octets for each atom: 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, and The central atom must have the smallest electronegativity, this is because the atom with the smallest electronegativity needs to share its electrons with the surrounding atoms and always puts hydrogen on the outside if it is present in a given molecule.
Hydrogen has 1 valence electron, we have 2 Hydrogens; plus 4 for Carbon, plus 6 for Oxygen times 3, for a total of 24 valence electrons. Whenever you see Hydrogens in front of a polyatomic ion like CO3, NO3, or SO4, it's going to be an acid and you're going to need to put those Hydrogens attached to the outside Oxygens.
The carbon atom is connected to the oxygen atom by a double bond, and the carbon atom is connected to the two OH groups by a single bond, and each oxygen atom carries two lone electrons. What we can do is take 2 valence electrons from this Oxygen and move them to the center and share them in a double bond. Opens New Window. The central atom must have the smallest electronegativity, this is because the atom with the smallest electronegativity needs to share its electrons with the surrounding atoms and always puts hydrogen on the outside if it is present in a given molecule. See the diagram below:. The remaining seven pairs of electrons are distributed as follows: three pairs of electrons on one oxygen atom, and two pairs of electrons on each of the remaining two oxygen atoms on the OH groups. Whenever you see Hydrogens in front of a polyatomic ion like CO3, NO3, or SO4, it's going to be an acid and you're going to need to put those Hydrogens attached to the outside Oxygens. And then we'll put the two H's around the outside of it. You may like Process for manufacture of vinylacetylene Mar 21, Is calcium carbonate easily soluble in water? How to Determine the Ionic Charge of Carbonic acid? Hydrogen has 1 valence electron, we have 2 Hydrogens; plus 4 for Carbon, plus 6 for Oxygen times 3, for a total of 24 valence electrons. So that's the Lewis structure for H2CO3.

I am am excited too with this question where I can find more information on this question?
Remarkable phrase