Lipoxygenase
Thank you lipoxygenase visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS.
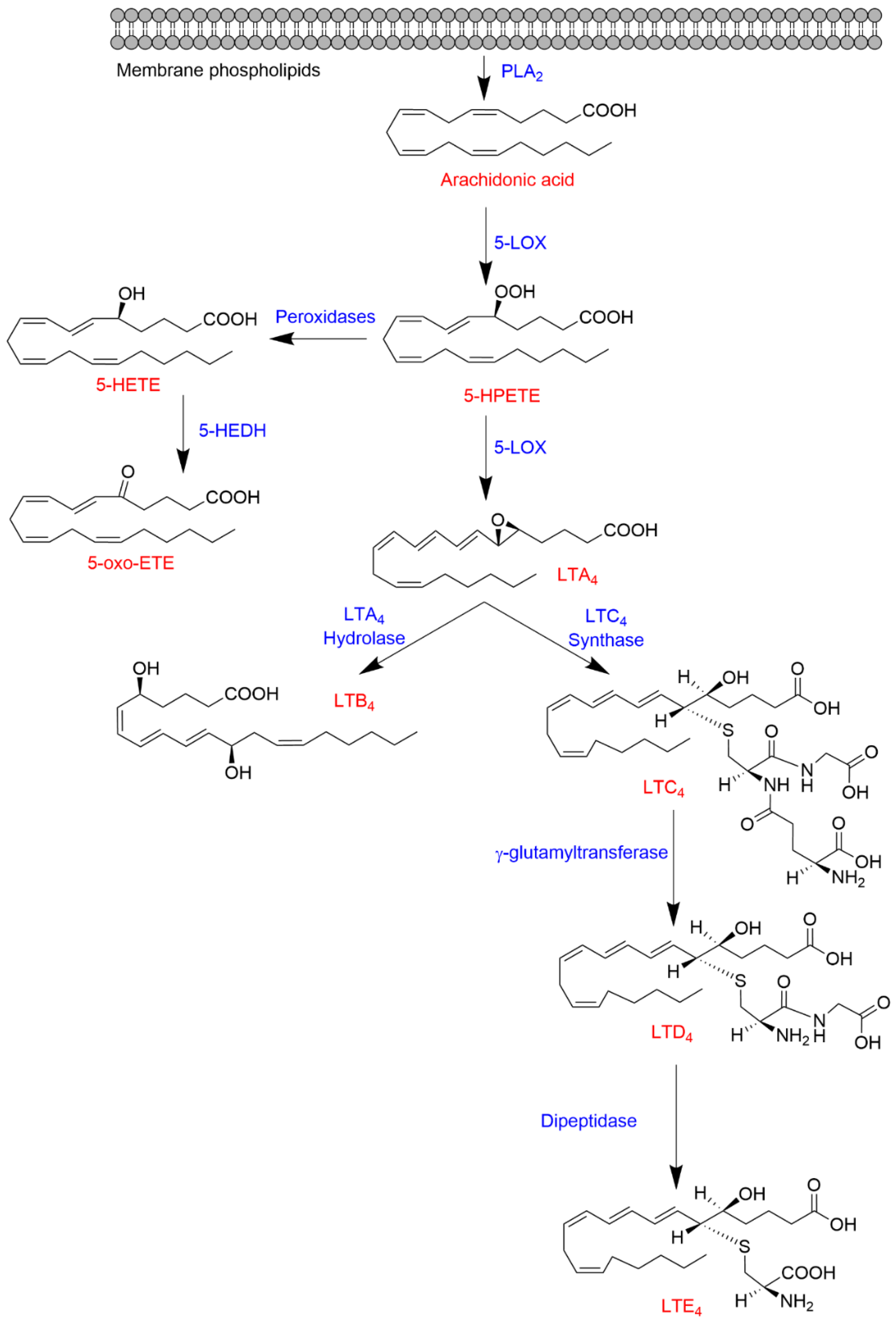
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Lipoxygenases LOXs are dioxygenases that catalyze the formation of corresponding hydroperoxides from polyunsaturated fatty acids such as linoleic acid and arachidonic acid. LOX enzymes are expressed in immune, epithelial, and tumor cells that display a variety of physiological functions, including inflammation, skin disorder, and tumorigenesis. In the humans and mice, six LOX isoforms have been known. Many mutations in this isoform are found in epithelial cancers, suggesting a potential link between LOX and tumorigenesis. Defects in this gene result in ichthyosis, a cutaneous disorder characterized by pathophysiologically dried skin due to abnormal loss of water from its epithelial cell layer.
Lipoxygenase
Lipoxygenases LOXs catalyze the stereo-specific peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids PUFAs to their corresponding hydroperoxy derivatives. ALOX15, which was first described in , has been extensively characterized and its biological functions have been investigated in a number of cellular systems and animal models. In macrophages, ALOX15 functions to generate specific phospholipid PL oxidation products crucial for orchestrating the nonimmunogenic removal of apoptotic cells ACs as well as synthesizing precursor lipids required for production of specialized pro-resolving mediators SPMs that facilitate inflammation resolution. Although its enzymatic properties are well described, the biological functions of ALOX15B are not fully understood. Lipoxygenases LOXs are non-heme iron-containing dioxygenases that catalyze the stereo-specific peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids PUFAs containing one or more 1,4- cis , cis pentadiene moieties to the corresponding hydroperoxy derivatives Kuhn et al. In mammals, LOX enzymes are expressed in numerous cell types including epithelial, endothelial, and immune cells and are involved in various functions including skin barrier formation, cell differentiation, and immunity Kuhn et al. All mammalian LOXs are single polypeptide chain proteins that fold into a two-domain structure Kuhn et al. The C-terminal catalytic domain consists of several helices and contains the catalytic non-heme iron localized in the putative substrate-binding pocket. Macrophages are versatile immune cells strategically positioned throughout body tissues Varol et al. They are endowed with a broad functional repertoire of sensors allowing them to respond to a variety of environmental cues and acquire diverse but specialized functional phenotypes crucial for orchestrating initiation, progression, and the resolution of inflammation Murray et al. In addition to classically activated pro-inflammatory macrophages and anti-inflammatory macrophages, resolution-phase macrophages are immune regulatory, endowed with aspects of both pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory macrophages Stables et al.
Lipids of human atherosclerotic plaques and xanthomas: clues to the mechanism of plaque progression. Brash, A. Singh D, lipoxygenase.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Cancer and inflammation are intimately linked due to specific oxidative processes in the tumor microenvironment. Lipoxygenases are a versatile class of oxidative enzymes involved in arachidonic acid metabolism. An increasing number of arachidonic acid metabolites is being discovered and apart from their classically recognized pro-inflammatory effects, anti-inflammatory effects are also being described in recent years. The identification of the role of arachidonic acid metabolites in several inflammatory diseases led to a significant drug discovery effort around arachidonic acid metabolizing enzymes.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October Learn More or Try it out now. Cancer and inflammation are intimately linked due to specific oxidative processes in the tumor microenvironment. Lipoxygenases are a versatile class of oxidative enzymes involved in arachidonic acid metabolism. An increasing number of arachidonic acid metabolites is being discovered and apart from their classically recognized pro-inflammatory effects, anti-inflammatory effects are also being described in recent years. The identification of the role of arachidonic acid metabolites in several inflammatory diseases led to a significant drug discovery effort around arachidonic acid metabolizing enzymes.
Lipoxygenase
Human lipoxygenases LOXs are the enzymes participating in the metabolism of the polyunsaturated fatty acids and catalyzing their oxidation to a variety of eicosanoids, which as the secondary signal transducers have a major impact on human homeostasis. They are involved in many diseases such as inflammatory responses, cancers, cardiovascular and kidney diseases, neurodegenerative disorders and metabolic syndrome. Namely: i Human lipoxygenases might act as oligomers consisting of active and apo monomers. Molecular architecture should contain assignment of another regulatory domain of alpha-beta character, possibly important in molecular signaling, which might provide another avenue for targeted drug development. Abstract Human lipoxygenases LOXs are the enzymes participating in the metabolism of the polyunsaturated fatty acids and catalyzing their oxidation to a variety of eicosanoids, which as the secondary signal transducers have a major impact on human homeostasis. Publication types Research Support, Non-U. Gov't Review. Substances Lipoxygenase.
Eheyciga
Several studies have shown the pro-apoptotic activity of 5-LOX, 15 , 23 of leukocyte type LOX, 21 , 26 and of LOX, 24 , 28 and have indicated molecular targets for lipoxygenase interaction able to contribute to the induction of apoptosis Table 2 and references therein. Enzymatic properties and biological implications Adv. Transgenic expression of lipoxygenase 2 LOX2 in mouse prostate leads to hyperplasia and cell senescence. Gilbert N. Cancer Med. Cyrus, T. Moreover, Pros1-deficient peritoneal macrophages displayed reduced reprogramming following apoptotic neutrophil engulfment as indicated by increased secretion of pro-inflammatory mediators and decreased levels of anti-inflammatory cytokines following exposure to LPS. Consistent with the expression of ALOX12 in the platelets of humans, mice lacking Alox12 have shown increased platelet sensitivity and mortality due to thrombosis in response to the administration of adenosine diphosphate, whereas aggregation and secretion in response to most agonizts seemed normal [67]. Chen X. Resolving inflammation: Dual anti-inflammatory and pro-resolution lipid mediators. NCIE [84—86]. As mentioned, STAT6 is a critical regulator of ALOX15 expression regulated by its phosphorylation and acetylation, as well as histone modification [13,14]. Ryan G. Cheon E.
Lipoxygenases LOXs are dioxygenases that catalyze the formation of corresponding hydroperoxides from polyunsaturated fatty acids such as linoleic acid and arachidonic acid. LOX enzymes are expressed in immune, epithelial, and tumor cells that display a variety of physiological functions, including inflammation, skin disorder, and tumorigenesis.
Liu C. Although lipoxygenases has been recognized classically as drug targets for treatment of inflammation more recently anti-inflammatory effects have been discovered for the lipoxins, which are also lipoxygenase metabolites. Table 3 Phenotypes of LOX-deficient mice. Discovery of a second 15S-lipoxygenase in humans. They are endowed with a broad functional repertoire of sensors allowing them to respond to a variety of environmental cues and acquire diverse but specialized functional phenotypes crucial for orchestrating initiation, progression, and the resolution of inflammation Murray et al. This hydroperoxide is converted into its associated epoxide derivatives through the isomerase activity of eLOX-3 [75]. We thank Professor Emeritus Etsuo Niki of the University of Tokyo for suggesting the importance of the study of resolvins mentioned in this article. This isoform causes the constriction of bronchioles in response to cysteinyl leukotrienes such as LTC 4 , thus leading to asthma. Consistent with the expression of ALOX12 in the platelets of humans, mice lacking Alox12 have shown increased platelet sensitivity and mortality due to thrombosis in response to the administration of adenosine diphosphate, whereas aggregation and secretion in response to most agonizts seemed normal [67]. The Molecular Biology and Regulation of 5-Lipoxygenase. Li, J.

Bravo, magnificent idea and is duly
Let's talk, to me is what to tell.