Medallion architecture
Therefore, we need to examine how to design the data model for the lakehouse architecture. The most common pattern for modeling the medallion architecture in the lakehouse is called a medallion.
For an optimal experience, provide your email below and one of our lifeguards will send you a link to start swimming in the lake! The Medallion Architecture is a software design pattern that organizes a data pipeline into three distinct tiers based on functionality: bronze, silver, and gold. The bronze tier represents the core functionality of the system, while the silver and gold tiers build on top of the previous tier, offering more advanced features. The overall goal of the Medallion Architecture is to create a scalable, flexible, and maintainable system that can evolve over time to meet changing requirements. One key benefit of the Medallion Architecture that you can separate concerns and manage dependencies between tiers. By organizing the system into different tiers, developers can focus on specific areas of functionality, reducing the likelihood of conflicts and making it easier to test and deploy the system. Additionally, the Medallion Architecture can help improve performance, as each tier can be optimized for a specific purpose.
Medallion architecture
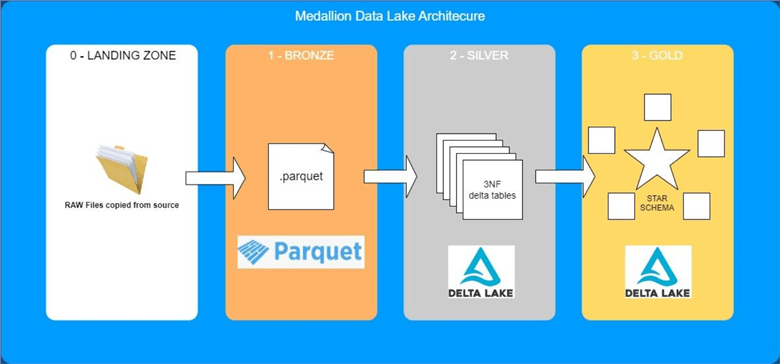
A medallion architecture is a data design pattern, coined by Databricks, used to logically organize data in a lakehouse, with the goal of incrementally improving the quality of data as it flows through various layers. This architecture consists of three distinct layers — bronze raw , silver validated and gold enriched — each representing progressively higher levels of quality. Medallion architectures are sometimes referred to as "multi-hop" architectures. Data is saved without processing or transformation. This might be saving logs from an application to a distributed file system or streaming events from Kafka. Note that the transformations here should be light modifications, not aggregations or enrichments. From our first example, those logs might be parsed slightly to extract useful information— like unnesting structs or eliminating abbreviations. Our events might be standardized to coalesce naming conventions or split a single stream into multiple tables. After the gold stage, data should be ready for consumption by downstream teams, like analytics, data science, or ML ops. The final stage gold used for analytics is entirely separate than the raw stage bronze used for ingestion. Medallion architecture provides a framework for data cleaning, not data architecture. For that reason, it might not be practical for data teams with intensive storage demands.
Additional metadata such as source file names or recording the time data was processed may be added to data on ingest for enhanced discoverability, medallion architecture, description of the state of the source dataset, and optimized performance in downstream applications.
As the amount of data produced increases and the technologies required to process it grow, organisations are looking to advanced data architectures to meet new needs. In this context, the Medallion architecture emerges, a novel perspective that fits perfectly with the data lakehouse approach and promises to promote data quality. The amount of data continues to grow every year. According to the latest statistics from Forbes , experts anticipate that the total volume of data worldwide will increase from The exponential increase in the amount of data generated is putting the focus on disciplines such as data governance and data quality. The more data we have, the more complicated it becomes to manage and exploit. On the other hand, the transformation of data into business insights no longer depends on the quantity of data, but on its quality.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support. Microsoft Fabric is an all-in-one analytics solution for enterprises that covers everything from data movement to data science, real-time analytics, and business intelligence. It offers a comprehensive suite of services, including data lake, data engineering, and data integration, all in one place. For more information, see What is Microsoft Fabric? This tutorial walks you through an end-to-end scenario from data acquisition to data consumption. It helps you build a basic understanding of Fabric, including the different experiences and how they integrate, as well as the professional and citizen developer experiences that come with working on this platform.
Medallion architecture
Location: Torenallee — Ir. S-West is located in the heart of the former Philips site known as Strijp-S, just to the north of the centre of Eindhoven. S-West borders the north side of Torenallee, the west side of the St Lucas College and the south side of the monumental Natlab building, where the most historical Philips discoveries were made. The east side of the plot offers access to Ingenieur Kalffstraat. The plan consists of an ensemble of four buildings on a half-sunken car park with a roof garden.
Mature big boobs stockings
Iddo Avneri Author. Additional metadata such as source file names or recording the time data was processed may be added to data on ingest for enhanced discoverability, description of the state of the source dataset, and optimized performance in downstream applications. Data ingested into the bronze layer may be a combination of batch and streaming. Note that the transformations here should be light modifications, not aggregations or enrichments. By keeping track of which versions of each layer are used in production, developers can quickly identify the root cause of issues and make targeted fixes. In short, in a Medallion architecture, the quality and structure of data improves as it passes through each layer. Layered Medallion Architecture: Bronze, Silver and Gold As explained above, the most distinctive feature of the Medallion architecture is that it structures the data in layers: the bronze layer, the silver layer and the gold layer. Data Science - Distil8. This guide outlines how to utilize lakeFS to achieve version control and lineage tracking of data through a data engineering pipeline. Skip to main content. Some people believe it is better to have a more descriptive name of what the layers are. As the amount of data produced increases and the technologies required to process it grow, organisations are looking to advanced data architectures to meet new needs. Data Lakehouse Architecture Review. Data is saved without processing or transformation.
Ancient Roman round versions are called an imago clipeata , from the clipeus or Roman round shield.
This guide outlines how to utilize lakeFS to achieve version control and lineage tracking of data through a data engineering pipeline. With its versioning capabilities and integration with popular data tools, lakeFS provides a solid foundation for managing complex data workflows. The concepts of data warehouse and data lake are often confused. Because of the sheer amount of Data and variety available, a Business needs a platform that can be flexible enough to handle this: The Data Lakehouse. This architecture enables flexible data management, adapting to changing market demands and providing a single source of truth in an organisation. Medallion Architecture is a system for logically organising data within a Data Lakehouse. Data Lakehouse is gaining popularity in the data world as an idea that aims to bring together the best parts of Data Lakes and Data Warehouses. For that reason, it might not be practical for data teams with intensive storage demands. The terms bronze raw , silver validated , and gold enriched describe the quality of the data in each of these layers. At this level data from different source files or systems may also be joined together. Part 1: What is Data Modeling?! Gold Layer Going into the gold layer the data is transformed for specific use cases and Business level aggregation is applied. Spread the music:. However, these two types of data storage are much more different than they may seem

0 thoughts on “Medallion architecture”