Met office northern lights map
Plenty of people have seen great photos of the auroras, but how do you take a great photo of them? Auroras — best known in the northern hemisphere as the aurora borealis — are amongst the most dramatic and engaging sights of the natural world.
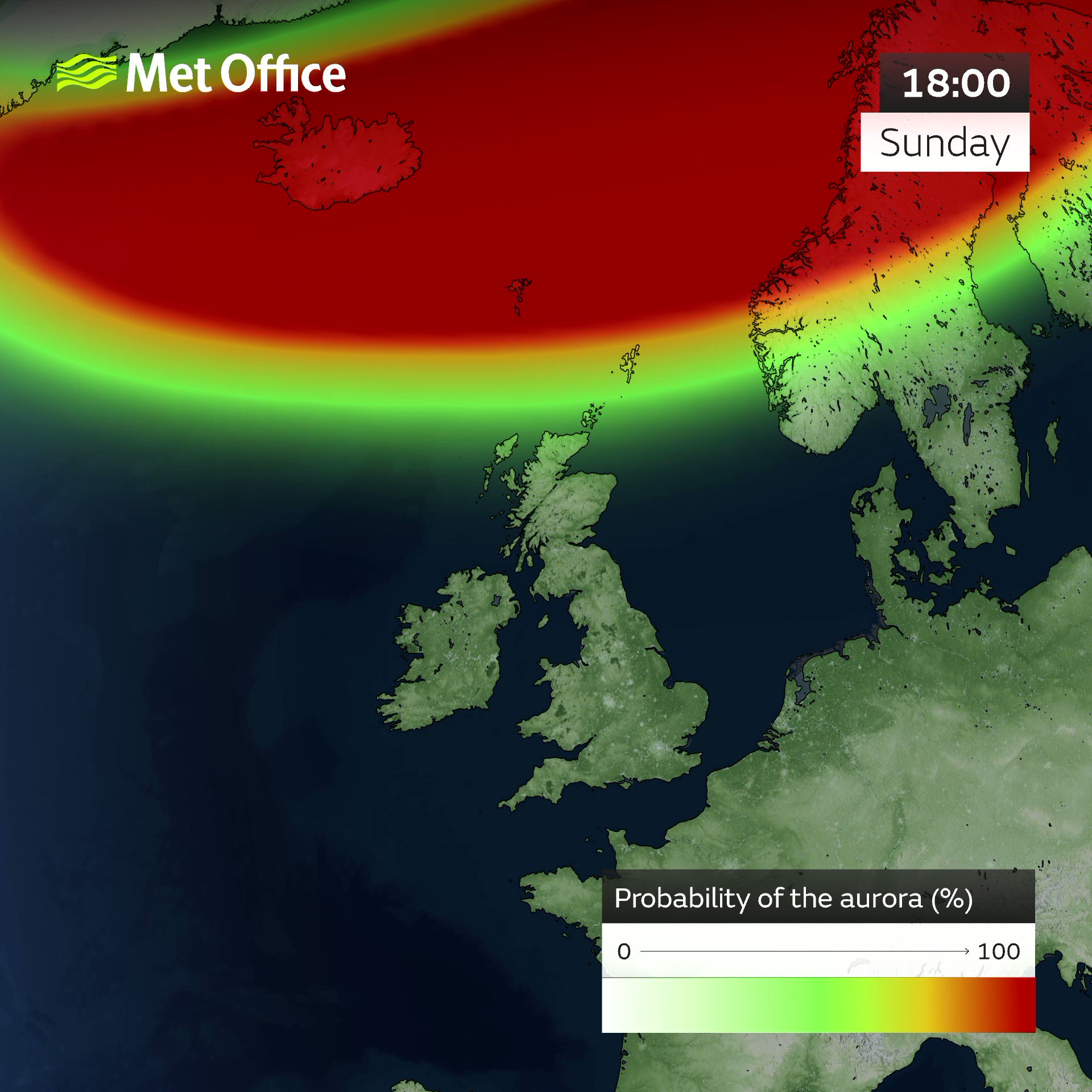
This is a short-term forecast of the location and intensity of the aurora. The forecast lead time is the time it takes for the solar wind to travel from the L1 observation point to Earth. The two maps show the North and South poles of Earth respectively. The green ovals turn red when the aurora is forecasted to be more intense. The sunlit side of Earth is indicated by the lighter blue of the ocean and the lighter color of the continents. Aurora can often be observed somewhere on Earth from just after sunset or just before sunrise.
Met office northern lights map
Space weather describes changing environmental conditions in near-Earth space. Learn more about Space Weather. The auroral oval may be enhanced into Sunday 25 Feb. This gives a slight chance of seeing the aurora in the far north of Scotland and similar geomagnetic latitudes under favorable viewing conditions. Otherwise no significant enhancements are forecast, with visible aurora unlikely to be seen away from high latitudes. The auroral oval may be enhanced into Sunday 25 Feb, but visible aurora is unlikely to be seen away from high latitudes. Space Weather Forecast Headline: High solar activity. Current strongest flare of the solar cycle recorded with a chance of further strong flares. This continues to be by far the largest and most complex of the seven sunspot regions on the visible disc, despite some apparent reduction in complexity in the past 12 hours or so. The remaining regions are much smaller and appear simpler, however, the three regions close to the eastern limb may reveal more complexity as they rotate into clear view on the disc. Geomagnetic activity was Quiet Kp Solar Activity: Activity is forecast to remain Moderate to High, with occasional Moderate flares expected and a chance of further isolated Strong flares, particularly in the near term, from the large region in the northeast. No other CMEs currently feature in the forecast. Current solar winds are near background values but faster solar winds are expected to connect with Earth perhaps as early as day 2 24 Feb but more likely by day 3 25 Feb , and persist through the remainder of the period. Geomagnetic activity is forecast to remain Quiet initially.
Hot active regions, solar flares, and coronal mass ejections will appear bright here.
Information about the auroras - what are they and when are you likely to be able to see them This is a very rare occurrence. During more moderate to strong geomagnetic storms Kp , the Aurora borealis often moves southwards across southern Iceland or towards the Faeroes. These auroras can be faintly visible from the UK because they occur at high altitudes. The Sun goes through an 11 year solar cycle, from solar minimum, through solar maximum and back to solar minimum. Solar maximum occurred in early so we are now in the declining phase of the solar cycle. During this phase the position of coronal holes on the Sun's equator give rise to high speed solar wind streams that buffet the Earth, disturbing the Earth's magnetic field and increasing the likelihood of auroras.
And while more space weather than our usual earthly phenomena, you do need the right weather conditions to see them namely clear skies! Back in the early 17th century, the Italian scientist Galileo Galilei christened these lights the aurora borealis. Aurora was the Roman goddess of dawn and Boreas was the Greek name for north wind. Their equivalent in the southern hemisphere are the aurora australis southern lights. Usually, our magnetic field deflects the stream of charged particles expelled from the outer layer of the Sun. But around the poles the field is weaker, so particles can get into the upper atmosphere and bump into gas molecules. When this happens, the gas molecule gains and then loses energy by releasing tiny flashes of light. Each gas emits a particular colour of light, depending on where they are in the atmosphere, somewhere between 50 and miles up.
Met office northern lights map
Finland is one of the best inhabited regions in the world for viewing northern lights, i. Finland is on the southern rim of the auroral oval. The probability for seeing auroras is best in the northernmost part of the country, i. During geomagnetic storms the auroral oval expands southward and then auroras are seen also in Central and Southern Finland. The statistical probability for seeing auroras during a dark and cloudless night is approximately:. Helsinki, Turku : once in a month on average. The typical time for auroral displays is at midnight, and a couple of hours before and after. However, auroras may occur randomly anytime when the sky is dark enough for seeing them. Auroras occur quite evenly throughout the year, although the rate is slightly higher during spring and autumn than during winter and summer. However, in summer the nights are generally too light for seeing the auroras.
Wonyoung icons
Check the internet to look for strong geomagnetic storm activity. This is a short-term forecast of the location and intensity of the aurora. You may be happy with the images you have captured which is great. This gives a slight chance of seeing the aurora in the far north of Scotland and similar geomagnetic latitudes under favorable viewing conditions. The latest 24 hours of image frames comprising the Northern and Southern hemisphere loops with time-tagged file names are available: Northern , Southern The most recent Northern and Southern Hemisphere images with static file names are available: Northern , Southern Auroral data in a grided format for the entire Earth is available in compressed JSON format: The latest JSON file is available as well. We often talk about it beginning to feel like autumn when the nights start to draw in and temperatures start feeling cooler. The larger the Kp index is, the stronger the storm and the further south the northern lights will be visible. A circumzenithal arc is an optical effect which looks like an upside-down rainbow. Find out about how and why the northern lights form, and where to see them in the UK. The southern oval covers the Antarctic regions. Solar maximum occurred in early so we are now in the declining phase of the solar cycle. Nitrogen causes the sky to glow blue yet when higher in the atmosphere the glow has a purple hue. This incredible occurrence can be occasionally seen in the night sky over Britain.
The northern lights could illuminate skies across the UK on Saturday evening into Sunday morning, according to the Met Office. The forecaster predicts the natural phenomenon could be as strong as the lights that were spotted last weekend by webcams from Shetland and from onlookers in central and eastern parts of England.
The bright areas show places where the plasma has a high density. More information on the map and the different layers available here. The southern oval covers the Antarctic regions. This is simply the result of how the photos are taken. Check the Met Office Space Weather forecast that will tell you where and when you are likely to observe an aurora. SDO AIA This channel is especially good at showing areas where cooler dense plumes of plasma filaments and prominences are located above the visible surface of the Sun. These links provide a discussion of the aurora phenomena and tips for the best opportunities to view aurora at various locations around the world. Video playback not supported. The good timing is important as the northern lights are a result of a geomagnetic storm. Usually, when we talk about the first day of summer, we are referring to the astronomical summer which is defined by the Earth's axis and orbit around the Sun. Hot active regions, solar flares, and coronal mass ejections will appear bright here. In other parts of the solar cycle these disturbances are largely the result of coronal mass ejections , which can give larger magnitude disturbances than these high speed streams. Ideally, the lights will be best viewed away from any light pollution, in remote areas, facing the northern horizon - north facing coasts produce some of the best viewing locations.

It is remarkable, it is the valuable answer
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are not right. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.
Perhaps, I shall agree with your opinion