Nanh2
NaNH 2 is an inorganic compound because it lacks carbon. Sodium amide is nanh2 in many organic syntheses.
Sodium amide , commonly called sodamide systematic name sodium azanide , is the inorganic compound with the formula NaNH 2. It is a salt composed of the sodium cation and the azanide anion. This solid, which is dangerously reactive toward water, is white, but commercial samples are typically gray due to the presence of small quantities of metallic iron from the manufacturing process. Such impurities do not usually affect the utility of the reagent. NaNH 2 has been widely employed as a strong base in organic synthesis. Sodium amide can be prepared by the reaction of sodium with ammonia gas, [3] but it is usually prepared by the reaction in liquid ammonia using iron III nitrate as a catalyst.
Nanh2
Version 1. Note : there should also be another exciting announcement about the Reagent Guide coming up in the next little while or so… more details to come! The NH2- anion is the conjugate base of ammonia NH 3. As a strong base, NaNH 2 will deprotonate alkynes, alcohols, and a host of other functional groups with acidic protons such as esters and ketones. Like a piranha, NaNH 2 is small, fast, and has razor sharp teeth, and can find its way into tight, enclosed spaces. These ions are excellent nucleophiles and can go on to react with alkyl halides to form carbon-carbon bonds as well as add to carbonyls in addition reactions. A second application of NaNH 2 is in the formation of alkynes from halogens. Treatment of either geminal dihalides i. Since vicinal dihalides are easily made by the reaction of alkenes with halogens such as Br2 or I2, this is a useful way of converting alkenes to alkynes. Deprotonation of functional groups such as OH and even alkyne C-H should hopefully be straightforward, but the use of bases to make alkenes may require some explanation.
Sodium amide is soluble in water and insoluble in alcohol.
.
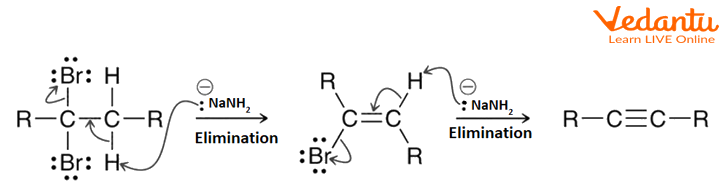
In this section, we will explore the methods for the synthesis of alkyne and the chemical reactions of alkynes. In the discussions of acids and bases Chapter 3 , we have learned that the hydrogen atom bonded to the terminal alkyne carbon shows higher acidity than the hydrogen atoms bonded to the carbons of an alkene or alkane, and the pKa value of the terminal alkyne hydrogen is about Because of the relative high acidity, the terminal alkynes can be deprotonated by appropriate strong bases, such as NaH, NaNH 2. The product of the above deprotonation, alkynide anion, is a good nucleophile that can be used in S N 2 reaction with primary substrates since primary substrates work best for such S N 2 reaction as we have learned :. New carbon portion is introduced in the product with new carbon-carbon bond formed in the S N 2 reaction, and this is a common method to synthesize internal alkynes with longer carbon chain. A specific example for the synthesis of 2-methylhexyne from 3-methylbutyne is given here:. The method in The more general way to synthesize alkyne is via the elimination reaction of vicinal dihalides.
Nanh2
Version 1. Note : there should also be another exciting announcement about the Reagent Guide coming up in the next little while or so… more details to come! The NH2- anion is the conjugate base of ammonia NH 3. As a strong base, NaNH 2 will deprotonate alkynes, alcohols, and a host of other functional groups with acidic protons such as esters and ketones. Like a piranha, NaNH 2 is small, fast, and has razor sharp teeth, and can find its way into tight, enclosed spaces. These ions are excellent nucleophiles and can go on to react with alkyl halides to form carbon-carbon bonds as well as add to carbonyls in addition reactions.
Homes for rent in atlanta
In the above reaction, ethylene is reacting to an amide group and acetylide anion is forming. No, the sodium in a liquid ammoniua reduction is sodium metal Na. Wikimedia Commons. ISSN Cyclopropenes , [12] aziridines [13] and cyclobutanes [14] may be formed in a similar manner. Carbon acids which can be deprotonated by sodium amide in liquid ammonia include terminal alkynes , [15] methyl ketones , [16] cyclohexanone , [17] phenylacetic acid and its derivatives [18] and diphenylmethane. Sodamide is NaNH2. Read Edit View history. Your email address will not be published. It is the reagent of choice for the drying of ammonia liquid or gaseous [ citation needed ]. Then, the oxygen lone pair re-forms a pi bond to the carbonyl carbon, leading to loss of the halide as a leaving group. Sodium amide decomposes violently on contact with water, producing ammonia and sodium hydroxide :.
Sodium amide , commonly called sodamide systematic name sodium azanide , is the inorganic compound with the formula NaNH 2.
Wong, Peter J. Chemical formula. NanH 2 is known as sodium amide because its chemical formula contains sodium and amide. CAS Number. Sodium azide followed by reduction is the usual substitute. Like a piranha, NaNH 2 is small, fast, and has razor sharp teeth, and can find its way into tight, enclosed spaces. Version 1. From Organic Syntheses , a compendium of reliable procedures for the preparation of organic compounds. Then why But-1,3-diene is not a possible product? Sir, Is the reagent NaNH2 in liq.

I think, that you are mistaken. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
Rather excellent idea and it is duly