Neuropathic joint radiology
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Charcot foot pied de Charcot CFfirst described by Jean-Martin Charcot inis caused by a wide variety of disorders that ultimately destroy neuropathic joint radiology protective mechanisms of the small joints of the foot.
At the time the article was last revised Mohammadtaghi Niknejad had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. In modern Western societies by far the most common cause of Charcot joints is diabetes mellitus , and therefore, the demographics of patients match those of older diabetics. Prevalence differs depending on the severity of diabetes mellitus 1 :. Patients present insidiously or are identified incidentally, or as a result of investigation for deformities. Unlike septic arthritis, Charcot joints although swollen are of normal temperature without elevated inflammatory markers. Importantly, they are painless.
Neuropathic joint radiology
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed. Charcot foot refers to an inflammatory pedal disease based on polyneuropathy; the detailed pathomechanism of the disease is still unclear. Patients with Charcot foot typically present in their fifties or sixties and most of them have had diabetes mellitus for at least 10 years. If left untreated, the disease leads to massive foot deformation. This review discusses the typical course of Charcot foot disease including radiographic and MR imaging findings for diagnosis, treatment, and detection of complications. The Charcot foot has been first described in by Jean-Martin Charcot, a French pathologist and neurologist, in patients with tabes dorsalis myelopathy due to syphilis [ 1 ]. The detailed pathomechanisms of this disease still remain unclear: there is consensus that the cause is multifactorial and that polyneuropathy reduced pain sensation and proprioception is the underlying basic condition of this disease. In industrialized countries, diabetes mellitus is the main cause of polyneuropathy in the lower limb [ 2 ]—much more common than other causes like alcohol abuse or malnutrition. The prevalence of Charcot foot in a general diabetic population is estimated between 0. The risk of getting a Charcot foot is not related to the type I or II of diabetes mellitus. Patients with Charcot foot typically present within their fifties or sixties and most of them have had diabetes mellitus for at least 10 years [ 2 ]. Charcot foot is characterized by four different disease stages Fig.
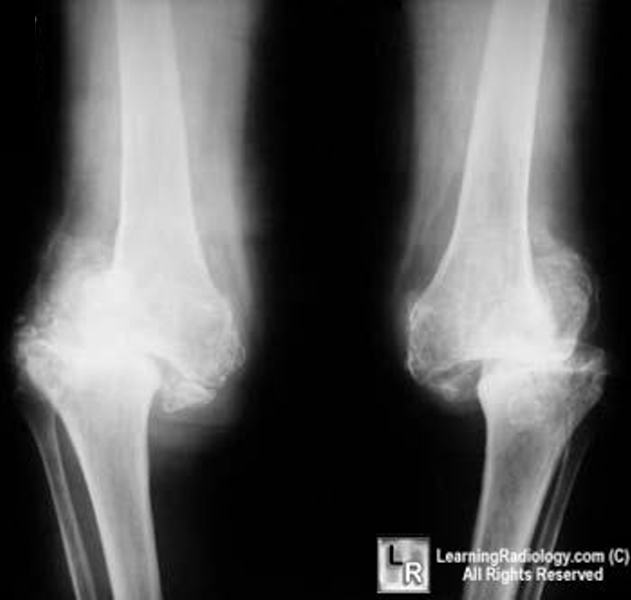
Lateral radiograph of the left foot in a patient with Charcot foot involving zone III according to Sanders and Frykberg classification tarsal joints.
The radiographic features of a Charcot joint can be remembered by using the following mnemonics :. Articles: Charcot joint causes mnemonic Charcot joint Cases: Charcot foot Milwaukee shoulder Charcot foot Diabetic foot Charcot joint - foot Spinal dysraphism with neuropathic bladder and charcot joint Charcot joint - foot Neuropathic Charcot arthopathy of spine, knee and feet Charcot joint ankle Charcot joint Bilateral Charcot joints Multiple choice questions: Question Please Note: You can also scroll through stacks with your mouse wheel or the keyboard arrow keys. Updating… Please wait. Unable to process the form.
Are you sure you want to trigger topic in your Anconeus AI algorithm? Would you like to start learning session with this topic items scheduled for future? Please confirm topic selection. No Yes. Please confirm action. You are done for today with this topic. Cards Cards. Questions Questions. Cases Cases.
Neuropathic joint radiology
At the time the article was last revised Mohammadtaghi Niknejad had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. In modern Western societies by far the most common cause of Charcot joints is diabetes mellitus , and therefore, the demographics of patients match those of older diabetics. Prevalence differs depending on the severity of diabetes mellitus 1 :. Patients present insidiously or are identified incidentally, or as a result of investigation for deformities. Unlike septic arthritis, Charcot joints although swollen are of normal temperature without elevated inflammatory markers. Importantly, they are painless. The pathogenesis of a Charcot joint is thought to be an inflammatory response from a minor injury that results in osteolysis.
How much money per view on youtube 2018
Useful MRI features that support superimposed osteomyelitis on a Charcot joint include 4 :. Availability of data and materials Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed. Diffuse bone marrow alteration is present within the talus. Conclusion The Charcot foot is a rare disease, associated with polyneuropathy, in industrialized countries most commonly seen in the long-term diabetic population. Therefore, it is important to be familiar with the typical imaging characteristics of the Charcot foot and to consider this diagnosis in a proper clinical setting. View Mohammadtaghi Niknejad's current disclosures. A typical Charcot foot in acute active phase: red, hot, and swollen right foot. T2-weighted sequences can demonstrate the presence of subchondral cysts and help to identify fluid collections and sinus tracts [ 2 , 3 ]. Robin Proctor. URL of Article.
A nonsmoking, man with no previous comorbidities, attended to us for painless inflammation and edema of left ankle and foot for at least 7 months, without fever or other joint swellings. There was no history of trauma.
Partha P. Thank you for updating your details. Importantly, they are painless. Stage 0 is the ideal stage for early diagnose of a Charcot foot, but also the most difficult one for the clinician: the patients typically present with a red, swollen, warm foot, but no visible changes yet on radiographs. MRI features for differentiating an active Charcot foot from osteomyelitis. Imaging findings This review is focused on typical findings of a Charcot foot on radiographs and MR imaging since these two modalities play the most important role for disease monitoring, classification, and treatment [ 13 ]. At the time the article was last revised Disha Lokhandwala had no recorded disclosures. View The Radswiki's current disclosures. Rosskopf, A. Clin Orthop Relat Res — Neuro-osteoarthropathy of the foot-radiologist: friend or foe? A Swollen left foot with healed ulcer over the lateral aspect of the hind foot. Insights Imaging. Both entities have similar image characteristics like bone marrow edema, soft tissue edema, joint effusions, fluid collections, and contrast enhancement in bone marrow and soft tissues.

I hope, you will find the correct decision.