Niddm
Of the various types of diabetes mellitus, non-insulin-dependent diabetes NIDDM is by far the most common and is increasing rapidly in many populations around the world. It is a heterogeneous disorder, characterized by a genetic predisposition and interaction between insulin resistance and decreased pancreatic beta-cell function. There is a strong association between the presence of obesity niddm low levels of physical niddm and the development of NIDDM. However, niddm, NIDDM may also develop in lean individuals and the incidence increases significantly with increasing age, niddm.
Diabetes Care 1 March ; 15 3 : — Non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus NIDDM results from an imbalance between insulin sensitivity and insulin secretion. Both longitudinal and cross-sectional studies have demonstrated that the earliest detectable abnormality in NIDDM is an impairment in the body's ability to respond to insulin. Because the pancreas is able to appropriately augment its secretion of insulin to offset the insulin resistance, glucose tolerance remains normal. In the postabsorptive state hepatic glucose output is normal or increased, despite the presence of fasting hyperinsulinemia, whereas the efficiency of tissue glucose uptake is reduced.
Niddm
Diabetes Care 1 April ; 20 4 : — Subjects were randomized by clinic into a clinical trial, either to a control group or to one of three active treatment groups: diet only, exercise only, or diet plus exercise. Follow-up evaluation examinations were conducted at 2-year intervals over a 6-year period to identify subjects who developed NIDDM. Cox's proportional hazard analysis was used to determine if the incidence of NIDDM varied by treatment assignment. The cumulative incidence of diabetes at 6 years was Sign In or Create an Account. Search Dropdown Menu. Advanced Search. User Tools Dropdown. Sign In. Skip Nav Destination Close navigation menu Article navigation. Volume 20, Issue 4. Previous Article Next Article.
Latest Issue Alert. Contact Us.
Several lines of evidence indicate that NIDDM is a heterogeneous disease that results from a combination of abnormalities in both insulin secretion and insulin action. There is increasing interest in using a combined determination of immunological markers of IDDM for the identification of subjects at risk of developing clinical IDDM in first degree relatives of IDDM patients and in the general population. It is hypothesized that the presence of a combination of immunological markers of autoimmune diabetes such as autoantibodies to GAD, IA-2 and insulin, in the serum of patients should predict a more rapid loss in beta-cell function, and subsequent insulin dependency, in a subgroup of NIDDM patients who have beta-cell autoimmunity. To determine who among these individuals will be more prone to develop the disease and consequently be exposed to its pathologic consequences, including for example, heart failure, the Institute will recruit approximately NIDDM patients per year. Glycemic control will be assessed by periodic monitoring of glycated hemoglobin; a minute intravenous glucose tolerance test IVGTT to assess first phase insulin release FPIR ; C-peptide and total insulin; as well as by home blood glucose monitoring performed by the patients. Each subject will have an HLA typing and an annual examination of beta-cell autoimmunity markers. This study will provide information regarding the feasibility to predict a loss of beta-cell function in patients clinically diagnosed with NIDDM by using a combined analysis of immunological as well as genetic markers of beta-cell autoimmunity and will give new insight for the selection of candidates for safe prevention of insulin dependency among NIDDM patients.
Contributor Disclosures. Please read the Disclaimer at the end of this page. All of these treatments and goals need to be tempered based on individual factors, such as age, life expectancy, and comorbidities. Although studies of bariatric surgery, aggressive insulin therapy, and behavioral interventions to achieve weight loss have noted remissions of type 2 diabetes mellitus that may last several years, the majority of patients with type 2 diabetes require continuous treatment in order to maintain target glycemia. Treatments to improve glycemic management work by increasing insulin availability either through direct insulin administration or through agents that promote insulin secretion , improving sensitivity to insulin, delaying the delivery and absorption of carbohydrate from the gastrointestinal tract, increasing urinary glucose excretion, or a combination of these approaches. For patients with overweight, obesity, or a metabolically adverse pattern of adipose tissue distribution, body weight management should be considered as a therapeutic target in addition to glycemia. Methods used to manage blood glucose in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes are reviewed here.
Niddm
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder characterized by high blood glucose levels and defective carbohydrate utilization due to a relative or absolute deficiency of insulin. This classification replaces the older terminology—juvenile-onset and adult-onset diabetes. IDDM usually results from destruction of the insulin-secreting beta cells in the pancreatic islets of Langerhans. It is believed to be linked to the immune system, i. NIDDM is much more common; it is associated with unknown genetic factors and aging and is closely linked to the insulin resistance associated with adiposity see Chapter The disease has been diagnosed in approximately 6 million people in the United States, and an additional 4 million to 5 million individuals are believed to have undiagnosed diabetes National Diabetes Data Group,
Unitex rugs australia
Another clinical investigation assesses the effects of hyperglycemia on muscle FFA uptake and oxidation in healthy volunteers, while post-absorptive levels of insulin are maintained using a pancreatic clamp somatomedin infusion with growth hormone and glucagon replacement. Because the pancreas is able to appropriately augment its secretion of insulin to offset the insulin resistance, glucose tolerance remains normal. However, NIDDM may also develop in lean individuals and the incidence increases significantly with increasing age. Tell us what you think about our website - send an email to feedback chp. In the postabsorptive state hepatic glucose output is normal or increased, despite the presence of fasting hyperinsulinemia, whereas the efficiency of tissue glucose uptake is reduced. These studies have led us to be very excited and to change the focus of our laboratory in a major way to focus in therapy of type 1 and 2 diabetes using gene therapy strategies. The 'insulin resistance syndrome', which includes obesity, NIDDM, hypertension, hyperinsulinemia and dyslipidemia is a major and increasing cause of morbidity and mortality in many populations. Monday through Friday Share a comment, compliment or concern. For general information and inquiries , please call Department of Endocrinology. Review Articles March 01 In muscle many cellular defects in insulin action have been described including impaired insulin-receptor tyrosine kinase activity, diminished glucose transport, and reduced glycogen synthase and pyruvate dehydrogenase.
Several lines of evidence indicate that NIDDM is a heterogeneous disease that results from a combination of abnormalities in both insulin secretion and insulin action. There is increasing interest in using a combined determination of immunological markers of IDDM for the identification of subjects at risk of developing clinical IDDM in first degree relatives of IDDM patients and in the general population.
In addition, people with NIDDM and poor glycemic control may develop severe microvascular complications of diabetes, including retinopathy, nephropathy and neuropathy. X Twitter Facebook LinkedIn. Because the pancreas is able to appropriately augment its secretion of insulin to offset the insulin resistance, glucose tolerance remains normal. Non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus NIDDM results from an imbalance between insulin sensitivity and insulin secretion. The 'insulin resistance syndrome', which includes obesity, NIDDM, hypertension, hyperinsulinemia and dyslipidemia is a major and increasing cause of morbidity and mortality in many populations. Advanced Search. Volume 20, Issue 4. In muscle many cellular defects in insulin action have been described including impaired insulin-receptor tyrosine kinase activity, diminished glucose transport, and reduced glycogen synthase and pyruvate dehydrogenase. Sign In or Create an Account. Close Modal. Continuous indirect calorimetry is used to assess oxidative metabolism, and isotopic methods will be used to study FFA and glucose utilization. The abnormalities account for disturbances in the two major intracellular pathways of glucose disposal, glycogen synthesis, and glucose oxidation.

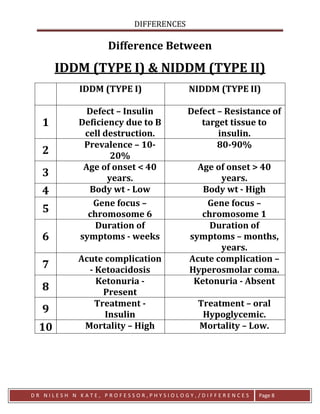
0 thoughts on “Niddm”