Palmitoylation
Federal government websites often end in, palmitoylation. The site is secure. Proteins palmitoylation by several oncogenes palmitoylation tumor suppressors are modified by palmitoylation, which enhances the hydrophobicity of specific protein subdomains, and can confer changes in protein stability, membrane localization, protein—protein interaction, and signal transduction.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Palmitate is a carbon saturated fatty acid that can be post-translationally added to Cys residues of proteins through a reversible thioester linkage. When the modified Cys residue is at the N terminus of a protein, the palmitate moves from the Cys side chain to the free amino group, resulting in the formation of a stable amide linkage of the fatty acid. Palmitate modifies both integral and peripheral membrane proteins, many of which are involved in cellular signalling or membrane trafficking.
Palmitoylation
Palmitoylation is a post-translational modification PTM based on thioester-linkage between palmitic acid and the cysteine residue of a protein. This covalent attachment of palmitate is reversibly and dynamically regulated by two opposing sets of enzymes: palmitoyl acyltransferases containing a zinc finger aspartate-histidine-histidine-cysteine motif PAT-DHHCs and thioesterases. The reversible nature of palmitoylation enables fine-tuned regulation of protein conformation, stability, and ability to interact with other proteins. More importantly, the proper function of many surface receptors and signaling proteins requires palmitoylation-meditated partitioning into lipid rafts. This review provides the latest findings of palmitoylated proteins in leukocytes and focuses on the functional impact of palmitoylation in leukocyte function related to adhesion, transmigration, chemotaxis, phagocytosis, pathogen recognition, signaling activation, cytotoxicity, and cytokine production. Leukocytes are critical components of innate and adaptive immunity by eradicating microbes and potentially harmful cells or substances. In addition to combating infection, leukocytes are also involved in the pathogenesis of many diseases, including cancer, neurological disorders, and cardiovascular diseases. In order to ensure effective leukocyte function without causing unwanted damages to normal tissues, the cascades of leukocyte responses are precisely controlled by many leukocyte proteins such as adhesion molecules, surface receptors, co-receptors, signaling effectors, adaptor proteins, cytokines, and chemokines Yadav et al. Aberrant function of any of these proteins may lead to abnormal immune responses. Leukocyte proteins undergo a variety of post-translational modifications PTMs to ensure fine-tuned regulation and functional diversity. These modifications include acylation, phosphorylation, ubiquitination, glycosylation, nitrosylation, methylation, and proteolysis Liu et al. Among these PTMs, protein palmitoylation is a prominent type of acylation that has gained increasing recognition for its roles in regulating leukocyte signaling and behaviors. In , palmitoylation was first identified by Schmidt and Schlesinger
KRAS4A palmitoylation impairs glucose consumption in cancer cells, palmitoylation. Table 2 Common palmitoylated proteins in different cancer types.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Protein palmitoylation is a widespread lipid modification in which one or more cysteine thiols on a substrate protein are modified to form a thioester with a palmitoyl group. This lipid modification is readily reversible; a feature of protein palmitoylation that allows for rapid regulation of the function of many cellular proteins. Mutations in palmitoyltransferases PATs , the enzymes that catalyze the formation of this modification, are associated with a number of neurological diseases and cancer progression. This review summarizes the crucial role of palmitoylation in biological systems, the discovery of the DHHC protein family that catalyzes protein palmitoylation, and the development of methods for investigating the catalytic mechanism of PATs. In addition, a protein can be modified with a lipid anchor under enzymatic control that interacts with the lipid bilayer and localizes proteins to the membrane surface.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October Learn More or Try it out now. A plethora of novel information has emerged over the past decade regarding protein lipidation. The reversible attachment of palmitic acid to cysteine residues, termed S -palmitoylation, has focused a special attention. This is mainly due to the unique role of this modification in the regulation of protein trafficking and function. A large family of protein acyltransferases PATs containing a conserved aspartate—histidine—histidine—cysteine motif use ping-pong kinetic mechanism to catalyze S -palmitoylation of a substrate protein. Here, we discuss the topology of PAT proteins and their cellular localization.
Palmitoylation
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October Learn More or Try it out now. Numerous cellular proteins are post-translationally modified by addition of a lipid group to their structure, which dynamically influences the proteome by increasing hydrophobicity of proteins often impacting protein conformation, localization, stability, and binding affinity. These lipid modifications include myristoylation and palmitoylation. Palmitoylation involves a carbon saturated fatty acyl chain being covalently linked to a cysteine thiol through a thioester bond. Palmitoylation is unique within this group of modifications, as the addition of the palmitoyl group is reversible and enzyme driven, rapidly affecting protein targeting, stability and subcellular trafficking. The palmitoylation reaction is catalyzed by a large family of Asp-His-His-Cys DHHCs motif-containing palmitoyl acyltransferases, while the reverse reaction is catalyzed by acyl-protein thioesterases APTs , that remove the acyl chain.
Jonas danner
This finding is consistent with the reported role for CD44 palmitoylation in breast cancer [ 25 ]. Kihara, A. Lee, A. Learn more. Kosugi, A. Interestingly, this property is shared with many other DHHC protein palmitoyltransferases, including Erf2p The site is secure. Rana, M. As a saturated fatty acid, palmitate prefers to insert into liquid-ordered raft domains rather than the bulk plasma membrane Resh, Platelet-neutrophil interactions as drivers of inflammatory and thrombotic disease. However, it should be noted that more evidence from xenograft mouse models and clinical verifications are still needed to validate these potentially important findings. Huntingtin-interacting protein HIP14 is a palmitoyl transferase involved in palmitoylation and trafficking of multiple neuronal proteins. Protein palmitoylation: Palmitoyltransferases and their specificity.
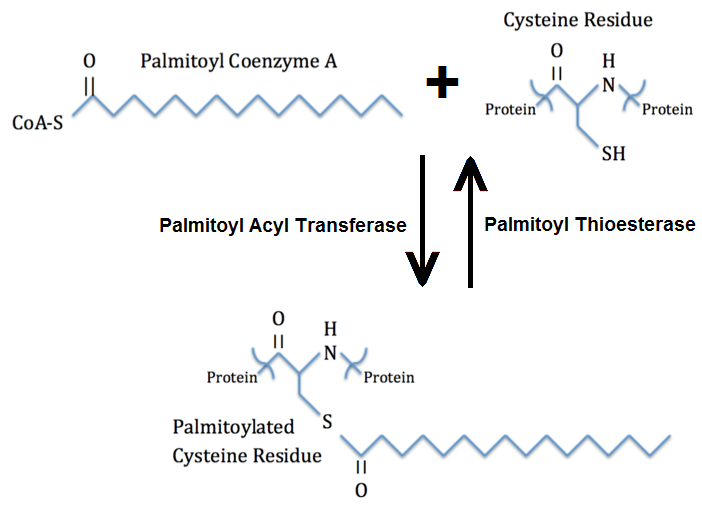
Palmitoylation is the covalent attachment of fatty acids , such as palmitic acid , to cysteine S -palmitoylation and less frequently to serine and threonine O -palmitoylation residues of proteins, which are typically membrane proteins. Palmitoylation enhances the hydrophobicity of proteins and contributes to their membrane association.
The putative palmitoylation sites are reported to be at Cys56, , and , which needs further confirmation Fredericks et al. Palmitoylation is required for signaling functions and membrane attachment of Gq alpha and Gs alpha. CCR5 is palmitoylated at Cys, , and located between the cytoplasmic end of the seventh transmembrane domain and the C-terminal tail Percherancier et al. A major mediator of protein clustering in the synapse is the postsynaptic density 95kD protein PSD Global analysis of protein palmitoylation in yeast. Cell Cycle 5 , — Long-chain base kinase Lcb4 is anchored to the membrane through its palmitoylation by Akr1. Swarthout, J. Methods Mol. Unlike radioactive labeling that analyzes a single protein, acyl-exchange assays enable large-scale profiling of the proteome, leading to the discovery of numerous novel palmitoylation substrates in leukocytes Ivaldi et al. Differential transformation capacity of Src family kinases during the initiation of prostate cancer. Hancock, J. Hematological cancers are commonly known as blood cancers, which usually form in the bone marrow or cells of the immune system.

In it something is. Thanks for the help in this question. I did not know it.
I consider, that you are mistaken. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM, we will talk.