Peptidase
Federal government websites peptidase end in, peptidase. The site is secure. Peptidases are enzymes capable of cleaving, and thereby often inactivating, small peptides.
A protease also called a peptidase , proteinase , or proteolytic enzyme [1] is an enzyme that catalyzes proteolysis , breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids , and spurring the formation of new protein products. Proteases are involved in numerous biological pathways, including digestion of ingested proteins, protein catabolism breakdown of old proteins , [3] [4] and cell signaling. In the absence of functional accelerants, proteolysis would be very slow, taking hundreds of years. They have independently evolved multiple times , and different classes of protease can perform the same reaction by completely different catalytic mechanisms. Proteases can be classified into seven broad groups: [6].
Peptidase
Protease and peptidase are two types of enzymes with a few significant differences between them. Papain-like peptidases: structure, function, and evolution. Navigation Menu. AAT Bioquest. Cart 0. Sign In. What are the differences between protease and peptidase? Posted May 19, Cellular Processes. Protease Protease is a type of hydrolytic enzyme that breaks down proteins by cleaving the peptide bond in protein molecules. They have an affinity for intact proteins. Proteases can be either endopeptidases or exopeptidases.
Crystal structure of inhibitor-bound bacterial oligopeptidase B in the closed state: Similarity and difference between peptidase andbBacterial enzymes, peptidase. Cell Stem Cell 6—
The MEROPS database is an information resource for peptidases also termed proteases, proteinases and proteolytic enzymes and the proteins that inhibit them. The Summary describes the classification and nomenclature of the peptidase and offers links to supplementary pages showing sequence identifiers, the structure if known, literature references and more. In this, each peptidase is assigned to a Family on the basis of statistically significant similarities in amino acid sequence, and families that are thought to be homologous are grouped together in a Clan. There is a Summary page for each family and clan, and these again have indexes. Each of the Summary pages offers links to supplementary pages. Please use the Menu in the side-bar to navigate through the database, and consult the About pages to discover more. Many authors find it useful to include data from MEROPS in their publications, and that is very much what we are here for, but please cite the appropriate publication as well as the URL when you do so.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Peptidases are enzymes capable of cleaving, and thereby often inactivating, small peptides. They are widely distributed on the surface of many different cell types, with the catalytic site exposed only at the external surface. In addition, some peptidases may have functions that are not based on their enzymatic activity. Peptidases are classified according to the location of the cleavage site in the putative substrate Table 1.
Peptidase
Enjoy free shipping today! Peptidase is an enzyme that makes sure we absorb the most nutrients from the food we consume. Learn all the digestive benefits of peptidase here, and more.
Used toyota corolla for sale by private owner
Structure of SARS coronavirus spike receptor-binding domain complexed with receptor. In addition, sialic acid may act as a receptor for some coronaviruses Figure 1. This will give insight in the contribution of tachykinins to the chronic inflammatory process in the airways of asthmatic patients. ACE, also known as peptidyl peptidase A or kinase II, is a type II integral membrane endopeptidase belonging to the superfamily of metallopeptidases reviewed in [ 24 ]. NEP is a glycoprotein of amino acids, with a single 24 amino acid hydrophobic segment that functions as both a transmembrane region and a signal peptide [ 1 ]. Immunology ; 91 Lancet ; Organization of the gene encoding common acute lymphoblastic leukaemia antigen neutral endopeptidase Proteases were first grouped into 84 families according to their evolutionary relationship in , and classified under four catalytic types: serine , cysteine , aspartic , and metallo proteases. The homeostasis of the coagulation—fibrinolysis system is based on a delicate balance between proteases and their activators and inhibitors.
Federal government websites often end in.
Bacterial peptidases represent a large group of enzymes with a high potential in biotechnology, food industry, and crop protection. Lipophilic ligands, attached to lipocalin proteins, have been found to possess tumor protease inhibiting properties. The Biochemical Journal. Neuropeptides and peptidases: important in asthma? Exposure to ozone also results in increased responsiveness for SP, and this effect could not be enhanced by inhibition of NEP [ 41 ]. DPP IV may also function as an auxiliary adhesion factor. Basic carboxypeptidases: regulators of peptide hormone activity. Bibcode : Natur. Eur J Clin Invest ; 26 7. For example, trypsin is specific for the sequences NEP is a glycoprotein of amino acids, with a single 24 amino acid hydrophobic segment that functions as both a transmembrane region and a signal peptide [ 1 ]. PMID

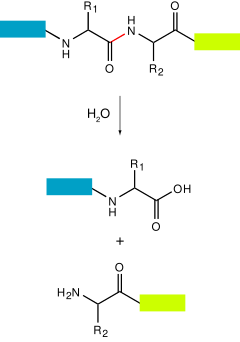
It is interesting. Tell to me, please - where I can find more information on this question?
It is interesting. Prompt, where I can read about it?