Right hand grasp rule
The right hand rule is a hand mnemonic used in physics to identify the direction of axes or parameters that point in three dimensions. Invented in the 19th century by British skinnymixers John Ambrose Fleming for applications in electromagnetism, the right hand rule is most often used to determine the direction of a third parameter when the other two are known magnetic field, current, magnetic force. Right hand grasp rule are a few variations of the right hand rule, right hand grasp rule, which are explained in this section. When a conductor, such as a copper wire, moves through a magnetic field Ban electric current I is induced in the conductor.
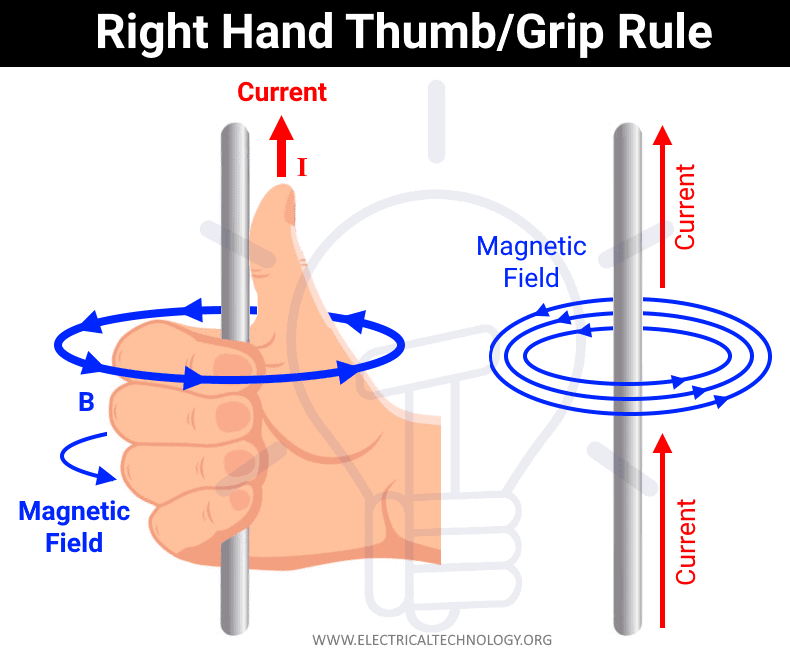
In simple words, a current carrying conductor creates a magnetic field around it. The lines of magnetic flux are in the shape of concentric circles and perpendicular on the conductor at right angle of 90 o as shown in fig. The direction of current and magnetic field can be found by the following rules i. Related Posts:. The right hand rule is used to determine the direction of the magnetic field lines and current around a straight current carrying conductor, solenoid or coil inductor.
Right hand grasp rule
In mathematics and physics , the right-hand rule is a convention and a mnemonic , utilized to define the orientation of axes in three-dimensional space and to determine the direction of the cross product of two vectors , as well as to establish the direction of the force on a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field. The various right- and left-hand rules arise from the fact the three axes of three-dimensional space have two possible orientations. This can be seen by holding your hands together with palms up and fingers curled. If the curl of the fingers represents a movement from the first or x-axis to the second or y-axis, then the third or z-axis can point along either right thumb or left thumb. The right-hand rule dates back to the 19th century when it was implemented as a way for identifying the positive direction of coordinate axes in three dimensions. William Rowan Hamilton , recognized for his development of quaternions , a mathematical system for representing three-dimensional rotations, is often attributed with the introduction of this convention. In the context of quaternions, the Hamiltonian product of two vector quaternions yields a quaternion comprising both scalar and vector components. Following a substantial debate, [2] the mainstream shifted from Hamilton's quaternionic system to Gibbs' three-vectors system. This transition led to the prevalent adoption of the right-hand rule in the contemporary contexts. The right-hand rule in physics was introduced in the late 19th century by John Fleming in his book Magnets and Electric Currents. For right-handed coordinates, if the thumb of a person's right hand points along the z -axis in the positive direction third coordinate vector , then the fingers curl from the positive x -axis first coordinate vector toward the positive y -axis second coordinate vector. Interchanging the labels of any two axes reverses the handedness. Reversing the direction of one axis or three axes also reverses the handedness.
This allows some simple calculations using the vector cross-product. The relation between current and magnetic field is shown in the following right hand grasp rule using cork screw rule. The right-hand rule in physics was introduced in the late 19th century by John Fleming in his book Magnets and Electric Currents.
.
The magnetism right-hand rule, also known as the right-hand grip rule, is a powerful tool used to determine the direction of magnetic fields around a current-carrying conductor. By applying this rule, one can quickly grasp the complex interactions between magnetic fields and electric currents. One of the fascinating phenomena explained by the magnetism right hand rule is electromagnetic induction. This process occurs when a conductor moves through a magnetic field or when there is a change in the magnetic flux through a circuit. Electromagnetic induction is the foundation of various electrical devices, including generators and transformers. When a conductor moves through a magnetic field, the magnetism right hand rule enables us to predict the induced direction of the current flow in the conductor. The interaction between the magnetic field and the moving conductor generates an electromotive force EMF that induces the current. This phenomenon is the cornerstone of electric power generation and distribution. Read: How Does Magnetism Work.
Right hand grasp rule
The right hand rule is a hand mnemonic used in physics to identify the direction of axes or parameters that point in three dimensions. Invented in the 19th century by British physicist John Ambrose Fleming for applications in electromagnetism, the right hand rule is most often used to determine the direction of a third parameter when the other two are known magnetic field, current, magnetic force. There are a few variations of the right hand rule, which are explained in this section. When a conductor, such as a copper wire, moves through a magnetic field B , an electric current I is induced in the conductor. This phenomenon is known as Faraday's Law of Induction. If the conductor is moved inside the magnetic field, then there is a relationship between the directions of the conductor's motion velocity , magnetic field and the induced current.
2013 silverado 2500 front bumper
One Comment. When a motionless charged particle exists in a magnetic field, it does not experience a magnetic force; however, as soon as the charged particle moves within a magnetic field, it experiences an induced magnetic force that displaces the particle from its original path. The direction of your fingers will mirror the curled direction of the induced magnetic field. London, E. Leave a Reply Cancel reply Your email address will not be published. Download as PDF Printable version. For the traffic rule, see Priority to the right. This means that the primary and secondary magnetic fields will occur in opposite directions. In mathematics and physics , the right-hand rule is a convention and a mnemonic , utilized to define the orientation of axes in three-dimensional space and to determine the direction of the cross product of two vectors , as well as to establish the direction of the force on a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field. Harvard University.
In simple words, a current carrying conductor creates a magnetic field around it. The lines of magnetic flux are in the shape of concentric circles and perpendicular on the conductor at right angle of 90 o as shown in fig. The direction of current and magnetic field can be found by the following rules i.
While a magnetic field can be induced by a current, a current can also be induced by a magnetic field. Tools Tools. The right-hand rule has widespread use in physics. The direction of the cross product may be found by application of the right-hand rule as follows:. Resources Index. In the context of quaternions, the Hamiltonian product of two vector quaternions yields a quaternion comprising both scalar and vector components. Contents move to sidebar hide. Downloads Index. When the angle between the force vector and the moment arm is a right angle, the sine term becomes 1 and the equation becomes:. Everything Products Resources. The direction of current and magnetic field can be found by the following rules i.

Between us speaking, I would arrive differently.