Rime medical abbreviation
The RIME framework provides terminology for describing the professional growth of medical students.
Medical -- and more Community » Educational. Miscellaneous » Unclassified. Miscellaneous » Unclassified -- and more Community » Music -- and more
Rime medical abbreviation
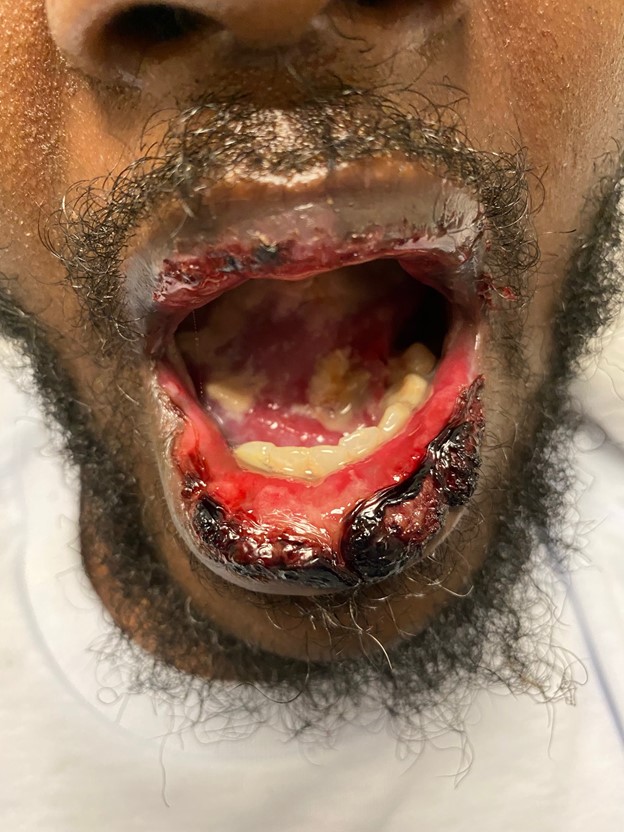
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Reactive infectious mucocutaneous eruption RIME is a recently proposed term used to describe cases of postinfectious rash and mucositis. This entity was previously termed mycoplasma-induced rash and mucositis MIRM ; however, numerous cases have been described with non M ycoplasma pneumoniae -associated causes. These patients are typically adolescents and have a prodromal cough followed by severe mucositis of 2 or more mucous membranes, with or without a cutaneous rash. He was initially treated at home with ibuprofen. Seven days later, he was presented to the emergency department with pharyngitis and painful oropharyngeal lesions. He was treated symptomatically with mouthwash containing lidocaine and oral nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications and discharged. During the next 2 days, he experienced worsening pharyngeal exudate, odynophagia, muffled voice, cervical edema, and fever and presented again to the emergency department. Physical examination revealed mucosal sloughing on the labial surfaces of the lips, tonsillar pillars, and hard and soft palate Fig 1 , A.
See " Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in children" and "Pneumonia caused by Chlamydia pneumoniae in children".
This is a new term defined by Dr. Second, skin lesions might be absent entirely or there may be sparse vesicular bullous or targetoid skin lesions. Third, patients have evidence of an infectious trigger. Fourth, the patient has not taken a medicine that could have caused the eruption. Terms that dermatologists are familiar with, including erythema multiforme EM major, Stevens-Johnson syndrome SJS , and toxic epidermal necrolysis TEN , can be problematic because they have been used in the literature to describe a spectrum of often overlapping conditions with different causes and outcomes, according to Dr.
This topic will discuss the pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and treatment of RIME. Why UpToDate? Learn how UpToDate can help you. Select the option that best describes you. View Topic. Font Size Small Normal Large. Reactive infectious mucocutaneous eruption RIME.
Rime medical abbreviation
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Reactive infectious mucocutaneous eruption RIME is a recently proposed term used to describe cases of postinfectious rash and mucositis. This entity was previously termed mycoplasma-induced rash and mucositis MIRM ; however, numerous cases have been described with non M ycoplasma pneumoniae -associated causes.
Funeral flower messages
In clinical medicine case counting, risk factor identification, and intervention testing often happen simultaneously, in a necessarily flawed yet estimable effort to help our patients. A cross-sectional study at a field Hospital. Rare complications include restrictive lung disease or chronic obliterative bronchitis, persistent cutaneous lesions, and B cell lymphopenia. Barve MD Gregory J. Underlying each step is the concept of a case definition, a set of standard criteria used to identify a particular condition. Since MIRM predominantly affects the pediatric population the differential diagnosis summarized in Table 2 lists possibilities more prevalent in this demographic. Paraneoplastic pemphigus in children and adolescents. These observations and refining of the case definition paved the way for Raimen et al to propose the term RIME and clarify that the clinical findings in MIRM can be caused by additional organisms. RIME is characterized by prominent mucositis, usually with sparse or even absent cutaneous involvement. Abstract Reactive infectious mucocutaneous eruption RIME was recently proposed to replace the term Mycoplasma pneumoniae MP -induced rash and mucositis to account for the fact that non-MP pathogens may also cause rash and mucositis. The latency times between symptoms of COVID infection and mucosal eruptions range from 4 days to 12 weeks, with oral lesions appearing 4 to 7 days after systemic symptoms and resolving in 5 to 21 days. Bernal, MD. Approximately one-quarter of patients with RIME require nutritional support, and 4 percent require intensive care [ 4,15 ].
The RIME framework provides terminology for describing the professional growth of medical students. It is used in many clerkships across the country.
Mucocutaneous disease and related clinical characteristics in hospitalized children and adolescents with COVID and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children. Intraoral erosions can be managed with the so-called "magic mouthwash" a variable combination of topical anesthetics, topical corticosteroids, antibiotics, and antacids several times a day, as long as the patient is old enough to know how to swish and spit [ 61 ]. Patients that fall in the mild and moderate categories were treated medically with a combination of drops and those that were severe or extremely severe required surgical amniotic membrane transplant AMT in addition to medical therapy. Popularity rank for the rime initials by frequency of use: rime 1 Don't keep it to yourself! Pediatr Dermatol ; In contrast with RIME, aphthous lesions are well demarcated and are typically limited to the nonkeratinized, mucosal surfaces picture 14 , without involvement of the vermillion lips. See " Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in children" and "Pneumonia caused by Chlamydia pneumoniae in children". Crissey MD Harold E. Most patients experience a prodrome of cough, malaise, and fever for approximately one week prior to the onset of their mucocutaneous eruption [ 4 ]. However, mucocutaneous eruptions indistinguishable from those described with M. See "Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: Pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, and diagnosis". Access archive Advertisement. Ramien notes that aside from Mycoplasma pneumoniae, other probable triggers include Chlamydophilia Chlamydia pneumoniae, influenza B, enterovirus, rhinovirus, human metapneumovirus, and human parainfluenzavirus 2.

Useful question
In my opinion you are mistaken. I suggest it to discuss. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.
And what here to speak that?