San francisco fault map
From space, the San Andreas Fault and its attending landforms are beautifully revealed. By using the buttons at the upper left to zoom and pan, and those in the upper right to switch between photographs and the base map or both san francisco fault map clicking 'Hybrid'the fault's intimate role in California becomes apparent.
Select your county from the dropdown menu above, or click on your county on the California map to the left to learn more about California earthquake risk and faults near you. How to Strengthen Your House. See the USGS interactive fault map to learn more about faults in this area. What is the Earthquake Risk in San Diego? What is the Earthquake Risk in San Francisco. Already a CEA policyholder? Manage your policy.
San francisco fault map
When we think of the next big earthquake, we think of the San Andreas fault. The San Andreas fault line formed about 30 million years ago as the North American plate engulfed nearly all of the Farallon plate. Since then, the North American plate has ground against the Pacific plate at a boundary called a strike-slip fault. This fault is one of the largest faults in the world, running more than miles from the Salton Sea to Cape Mendocino. It carves the state in two. The two plates crisscross with dozens of active and passive earthquake faults. See Your Local Earthquake Risk. It can cause powerful earthquakes—as big as magnitude 8—that would affect high population communities in SoCal. A San Andreas earthquake would be classified as occurring on a strike-slip fault. Strike-slip faults are found along boundaries of tectonic plates sliding past each other. The walls of rock move to the left relative to one another, or to the right relative to one another. These faults are formed by horizontal compression. USGS scenarios project more than 1, deaths, and 50, injuries due to a major Southern San Andreas fault earthquake. CoreLogic, a business analysis service, estimated a Southern San Andreas fault rupture will cause 3.
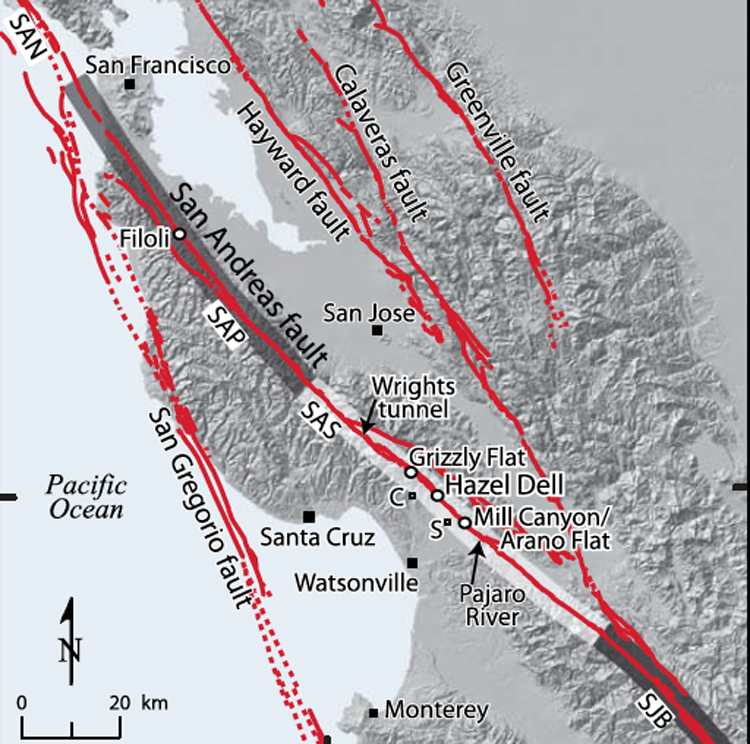
The mountains and the valley have been shaped by repeated earthquakes on faults in the region.
The San Andreas Fault is a continental right-lateral strike-slip transform fault that extends roughly 1, kilometers mi through California. Traditionally, for scientific purposes, the fault has been classified into three main segments northern, central, and southern , each with different characteristics and a different degree of earthquake risk. The average slip rate along the entire fault ranges from 20 to 35 mm 0. In the north, the fault terminates offshore near Eureka, California at the Mendocino Triple Junction , where three tectonic plates meet. It has been hypothesized that a major earthquake along the Cascadia Subduction Zone could trigger a rupture along the San Andreas Fault. Here, the plate motion is being reorganized from right-lateral to divergent. In this region known as the Salton Trough , the plate boundary has been rifting and pulling apart, creating a new mid-ocean ridge that is an extension of the Gulf of California.
Official websites use. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites. Real-Time Earthquakes. Earthquakes in Catalog. View past earthquakes in Google Earth. Tectonic Plate Boundaries. Explore multiple Google Earth layers related to the geology and geologic hazards of the greater Bay Area.
San francisco fault map
The Hazard Viewer is a one-of-its-kind interactive map of regional hazards, featuring the best available mapping resources and data for each hazard. The Hazard Viewer is a one-of-its-kind interactive map of regional hazards, curated from the most relevant, current maps for the nine-county Bay Area. It brings together the best set of mapping resources that exist in the region for each hazard. An easy-to-use tool for contextualizing local risk at the household-, neighborhood-, jurisdiction- and county-level, the Hazard Viewer includes layers for viewing:. The information provided in the Hazard Viewer is intended for planning use only and is not intended to be site-specific. Rather, it depicts general risks within the neighborhoods and the relative risks from community to community. Hazard levels are less likely to be accurate if your neighborhood is on or near the border between zones. The information in this map application is not a substitute for a site-specific investigation by a licensed professional. You are here.
15x6x6 tire and wheel
In Palmdale , a portion of the fault is easily examined at a roadcut for the Antelope Valley Freeway. Scientists believe quakes on the Cascadia subduction zone may have triggered most of the major quakes on the northern San Andreas within the past 3, years. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. In this region around the San Francisco Bay Area several significant "sister faults" run more-or-less parallel, and each of these can create significantly destructive earthquakes. A study found a link between the water level in Lake Cahuilla now the Salton Sea and seismic activity along the southern San Andreas Fault. These and numerous other faults are capable of damaging earthquakes , similar to the San Francisco and Loma Prieta earthquakes. The southern segment also known as the Mojave segment begins near Bombay Beach, California. It could be tomorrow or it could be 10 years or more from now. Strike-slip faults are found along boundaries of tectonic plates sliding past each other. The positions were measured from professional geological maps, primarily those of the United States Geological Survey, California Geological Survey, Dibblee maps and geological literature.
.
Inland Southern California Counties: Imperial, Riverside, San Bernardino Inland Southern California has scenic mountains, valleys, and deserts — all shaped by the tremendous geologic forces within the San Andreas fault system. Decrease your risk of San Andreas earthquake damage and injury from an earthquake by identifying possible home hazards: Tall, heavy furniture that could topple, such as bookcases, china cabinets, or modular wall units. The Pacific Plate , to the west of the fault, is moving in a northwest direction while the North American Plate to the east is moving toward the southwest, but relatively southeast under the influence of plate tectonics. Bibcode : ArJG Bibcode : Natur. California , Baja California , Sonora. Alamo River mouth. National Aeronautics and Space Administration. Strike-slip faults are found along boundaries of tectonic plates sliding past each other. Make sure to have water and snacks available in each room of your home. Nevertheless, in the 17 years since that publication there has not been a substantial quake in the Los Angeles area, and two major reports issued by the U. The location of the San Andreas Fault is shown on this map. Large-scale hundreds of miles lateral movement along the fault was first proposed in a paper by geologists Mason Hill and Thomas Dibblee.

0 thoughts on “San francisco fault map”