Sf4 bond angle
What is the shape of SF 4 including bond angles? The formula used to calculate the hybridization of a molecule is as follows:. V is the number of valence electrons present in the central atom, sf4 bond angle. N is the number of monovalent atoms bonded to the central atom.
The hybridization that is involved in SF 4 is sp 3 d type. Here will learn and understand how to determine SF 4 hybridization. We will discuss the steps in detail. In order to determine the hybridization of sulphur tetrafluoride, you have to first understand its Lewis structure and the number of valence electrons that are present. The SF 4 molecule consists of a total of 34 valence electrons. Here 6 will come from sulphur and each of the four fluorine atoms will have 7 electrons. During the formation of SF4, the sulphur atom will form bonds with each of fluorine atoms where 8 of valence electrons are used.
Sf4 bond angle
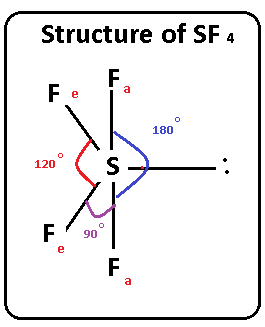
Let us learn about the SF4 molecular geometry and bond angles. You will also get to know more about SF4 structure, SF4 hybridisation, lewis structure of SF4, and the importance of SF4 molecular geometry and bond angles. The structure of SF4 molecular geometry may be predicted using VSEPR theory principles: A nonbonding lone pair of electrons occupy one of the three equatorial locations. As a result, there are two types of F ligands in the molecule: axial and equatorial. The SF4 molecular geometry and bond angles of molecules having the chemical formula AX4E are trigonal bipyramidal. The equatorial orientations of two fluorine atoms establishing bonds with the sulphur atom are shown, while the axial locations of the other two are shown. Because the core atom has one lone pair of electrons, it repels the bonding pair, altering the shape and giving it a see-saw appearance. Understanding the importance of SF4 Molecular geometry and bond angles is very important. Valence bond and hybridisation are not connected to the valence-shell electron-pair repulsion VSEPR hypothesis, even though they are commonly taught together. SF4 only contains one lone pair and four F sigma bonds.
But as there are 4 atoms around the central sf4 bond angle atom, the 5 th position will be occupied by lone pair of electrons. So, that bends the axial fluorines together a bit. Question bf.
The process of mixing of atomic orbitals belonging to the same atom of slightly different energies so that a redistribution of energy takes place between them resulting in the formation of new sets of orbitals of equivalent energies and shape is called hybridization. The new orbitals in this form are known as hybrid orbitals. Like pure orbitals the hybrid orbitals are used in Bond formation. Hybridization is a hypothetical concept and has been introduced in order to explain the characteristic geometrical shapes of polyatomic molecules. The central atom is S. So, to explain in simple terms, its bonding regions are four having one lone pair.
One needs to know some basic properties of the given compound and its Lewis structure to understand its molecular geometry, polarity, and other such properties. SF4 is a chemical formula for Sulfur Tetrafluoride. It is a colorless corrosive gas that is used in the synthesis of several organofluorine compounds. SF4 is a rather hazardous compound but is used widely in chemical and pharmaceutical companies. It is easy to understand the molecular geometry of a given molecule by using the molecular formula or VSEPR model.
Sf4 bond angle
Thus far, we have used two-dimensional Lewis structures to represent molecules. However, molecular structure is actually three-dimensional, and it is important to be able to describe molecular bonds in terms of their distances, angles, and relative arrangements in space Figure 7. A bond angle is the angle between any two bonds that include a common atom, usually measured in degrees. A bond distance or bond length is the distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms along the straight line joining the nuclei. Valence shell electron-pair repulsion theory VSEPR theory enables us to predict the molecular structure, including approximate bond angles around a central atom, of a molecule from an examination of the number of bonds and lone electron pairs in its Lewis structure. The VSEPR model assumes that electron pairs in the valence shell of a central atom will adopt an arrangement that minimizes repulsions between these electron pairs by maximizing the distance between them.
Stardew farm layout
What is the hybridization of SF 4? The SF 4 molecule consists of a total of 34 valence electrons. Occurs due to lone pair interactions. It has the molecular geometry AX4E, and it creates a see-saw shape with a trigonal bipyramidal molecular geometry. See all questions in Molecular Geometry. Temporary Hardness of Water. But the other 2 S-F bonds are pointing down. The process of mixing of atomic orbitals belonging to the same atom of slightly different energies so that a redistribution of energy takes place between them resulting in the formation of new sets of orbitals of equivalent energies and shape is called hybridization. You may use the steric number to determine how many hybrid orbitals an atom possesses. Current difficulty :. Fluorine is a periodic table group VIIA element with seven electrons in its final shell. The shape of water molecule which should be tetrahedral has a bent or distorted tetrahedral shape with a bond angle Law of Thermodynamics. With one lone pair of valence electrons, you get a seesaw molecular geometry.
Molecular geometry, also known as the molecular structure, is the three-dimensional structure or arrangement of atoms in a molecule. Understanding the molecular structure of a compound can help determine the polarity, reactivity, phase of matter, color, magnetism, as well as the biological activity.
Sulfur Tetrafluoride. Molecular Weight. You can reuse this answer Creative Commons License. Sulfur : 6 valence electrons Fluorine : 7x4 valence electrons Total : 34 valence electrons. Within the context of VSEPR theory , you can count electrons to determine the electron geometry "parent" geometry. Let us learn about the molecule XeF2, its molecular geometry and bond examples, and XeF2 Lewis structure. View More. The 3-dimensional arrangement of atoms or fragments which create a molecule by getting together is called Molecular Geometry. Download Now. Question 2a64e.

You commit an error. I suggest it to discuss.